WebSockets provide a full-duplex communication channel over a single, long-lived TCP connection, enabling real-time data transfer between clients and servers with minimal latency. This technology significantly enhances the responsiveness and interactivity of web applications by allowing instant updates without repeated HTTP requests. Discover how WebSockets can transform your web experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
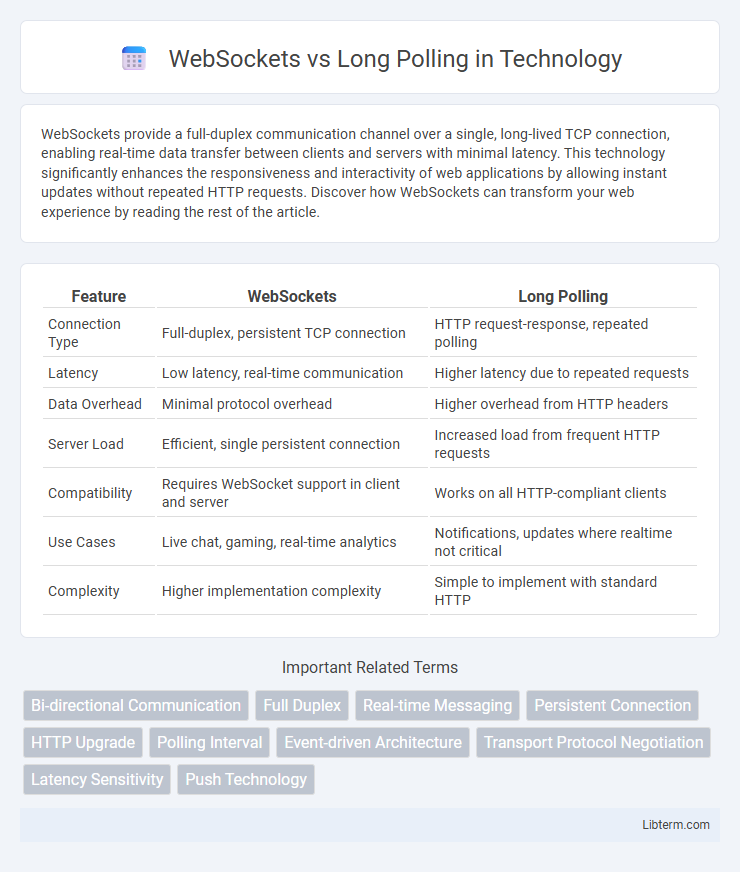
| Feature | WebSockets | Long Polling |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Full-duplex, persistent TCP connection | HTTP request-response, repeated polling |
| Latency | Low latency, real-time communication | Higher latency due to repeated requests |
| Data Overhead | Minimal protocol overhead | Higher overhead from HTTP headers |
| Server Load | Efficient, single persistent connection | Increased load from frequent HTTP requests |
| Compatibility | Requires WebSocket support in client and server | Works on all HTTP-compliant clients |
| Use Cases | Live chat, gaming, real-time analytics | Notifications, updates where realtime not critical |
| Complexity | Higher implementation complexity | Simple to implement with standard HTTP |
Introduction to Real-Time Web Communication
WebSockets provide a full-duplex communication channel over a single TCP connection, enabling low-latency, bidirectional data exchange essential for real-time web applications. Long polling simulates real-time updates by repeatedly sending HTTP requests to the server, causing increased overhead and higher latency compared to WebSockets. Real-time web communication requires efficient protocols like WebSockets to support instant data transfer essential for applications such as chat, gaming, and live notifications.
What Are WebSockets?
WebSockets are a communication protocol enabling full-duplex, persistent connections between a client and server over a single TCP connection, facilitating real-time data exchange. Unlike long polling, which repeatedly sends HTTP requests to check for updates, WebSockets maintain an open connection that allows instantaneous data transmission without the overhead of HTTP headers for each message. This results in lower latency, reduced network traffic, and improved efficiency for applications like chat, gaming, and live streaming.
Understanding Long Polling
Long Polling is a technique where the client sends a request to the server and waits for a response until new data is available or a timeout occurs, creating a near real-time communication channel. Unlike traditional polling, Long Polling reduces unnecessary server requests by holding the connection open until an update is ready, which improves efficiency compared to frequent repeated requests. While WebSockets provide a full-duplex communication channel, Long Polling remains a simpler fallback solution compatible with older browsers and networks lacking WebSocket support.
How WebSockets Work
WebSockets establish a persistent, full-duplex communication channel over a single TCP connection, enabling real-time data exchange between client and server. After the initial HTTP handshake, the protocol upgrades the connection to WebSocket, maintaining an open channel for low-latency, bidirectional messaging. This mechanism reduces overhead compared to HTTP-based long polling, which repeatedly sends requests to simulate real-time interaction.
How Long Polling Works
Long polling operates by the client sending a request to the server, which holds the connection open until new data is available or a timeout occurs. When the server sends a response with updated information, the client immediately initiates another request, maintaining a near-real-time communication loop. This method reduces latency compared to traditional polling but can create increased overhead due to frequent HTTP request cycle management.
Key Differences Between WebSockets and Long Polling
WebSockets establish a persistent, full-duplex communication channel between client and server, enabling real-time data exchange with minimal latency and overhead. Long Polling relies on repeated HTTP requests where the client polls the server, maintaining an open connection until new data is available, resulting in higher latency and increased server load. WebSockets provide more efficient and scalable solutions for applications requiring instant updates, such as chat apps or live feeds, whereas Long Polling serves as a fallback when WebSocket support is limited or unavailable.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
WebSockets offer superior performance by establishing a persistent, full-duplex connection that enables real-time data exchange with minimal latency, reducing overhead caused by repeated HTTP requests typical in long polling. Scalability is enhanced in WebSocket implementations due to reduced server resource consumption and lower network traffic, which supports a larger number of concurrent clients more efficiently than long polling's continual HTTP connection reestablishments. High-throughput applications, such as live chat and online gaming, benefit significantly from WebSockets' efficient use of CPU and memory compared to the comparatively heavier load long polling imposes on server infrastructure.
Use Cases: When to Use WebSockets or Long Polling
WebSockets are ideal for real-time applications requiring low latency and bidirectional communication, such as online gaming, live chat, and stock trading platforms. Long Polling suits scenarios where server push is needed but WebSocket support is limited or unnecessary, like simple notifications or updates in legacy systems and environments with strict firewall rules. Choosing between them depends on factors like application complexity, scalability requirements, and client-server compatibility.
Security Considerations
WebSockets provide a full-duplex communication channel over a single TCP connection, enhancing security by supporting TLS encryption with the wss:// protocol, which safeguards data integrity and confidentiality. Long Polling relies on repeated HTTP requests, making it more susceptible to interception and replay attacks due to the stateless nature of HTTP and the lack of persistent encryption across multiple requests. Implementing proper authentication, secure tokens, and TLS in both methods is crucial, but WebSockets inherently reduce the attack surface by maintaining a continuous, encrypted connection, minimizing exposure to man-in-the-middle and session hijacking threats.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Real-Time Solution
WebSockets provide a true full-duplex communication channel ideal for low-latency real-time applications like gaming or live chat, offering better efficiency and lower overhead than long polling. Long polling remains a reliable fallback for environments where WebSockets are unsupported, benefiting simpler or legacy systems with moderate real-time needs. Selecting between WebSockets and long polling depends on factors such as application complexity, infrastructure capacity, and real-time performance requirements.
WebSockets Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com