Steganography conceals information within digital files, making messages invisible to unauthorized viewers while preserving the original content's appearance. It enhances privacy and security by embedding data in images, audio, or video without altering their perceptible quality. Explore the article to understand how steganography can protect Your sensitive communication effectively.
Table of Comparison
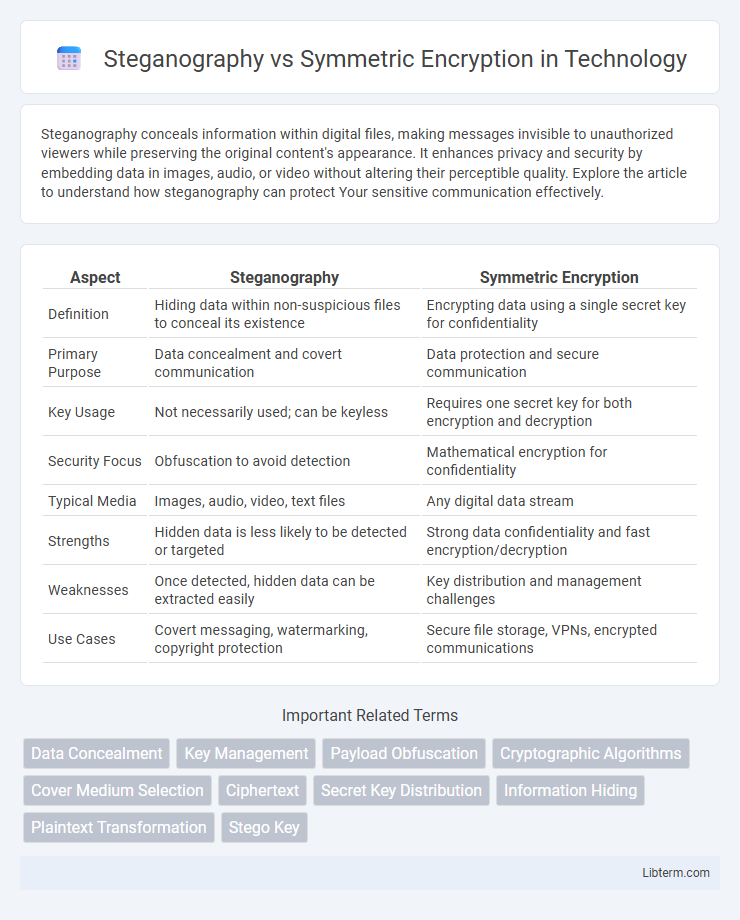
| Aspect | Steganography | Symmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiding data within non-suspicious files to conceal its existence | Encrypting data using a single secret key for confidentiality |
| Primary Purpose | Data concealment and covert communication | Data protection and secure communication |
| Key Usage | Not necessarily used; can be keyless | Requires one secret key for both encryption and decryption |
| Security Focus | Obfuscation to avoid detection | Mathematical encryption for confidentiality |
| Typical Media | Images, audio, video, text files | Any digital data stream |
| Strengths | Hidden data is less likely to be detected or targeted | Strong data confidentiality and fast encryption/decryption |
| Weaknesses | Once detected, hidden data can be extracted easily | Key distribution and management challenges |
| Use Cases | Covert messaging, watermarking, copyright protection | Secure file storage, VPNs, encrypted communications |
Introduction to Steganography and Symmetric Encryption
Steganography conceals the existence of a message by embedding it within ordinary digital files such as images, audio, or video, making the communication invisible to unauthorized parties. Symmetric encryption transforms the original plaintext into ciphertext using a single secret key, ensuring data confidentiality during transmission or storage. Both techniques enhance security, with steganography focusing on hiding the message and symmetric encryption emphasizing secure encryption and decryption processes using shared keys.
Defining Steganography: Concealing Information
Steganography involves concealing information within non-suspicious carriers such as images, audio, or video files, making the message invisible to unintended recipients. Unlike symmetric encryption, which transforms data into an unreadable format using shared keys, steganography hides the very existence of the message. This technique enhances confidentiality by masking communication rather than merely scrambling its content.
Understanding Symmetric Encryption: Protecting Data with Keys
Symmetric encryption protects data by using a single secret key for both encryption and decryption, ensuring confidentiality through shared key management. Common algorithms such as AES, DES, and Blowfish provide strong security by transforming plaintext into ciphertext, making data inaccessible without the correct key. Key distribution and management remain critical challenges in symmetric encryption, as unauthorized access to the key compromises the entire system's security.
Key Differences Between Steganography and Symmetric Encryption
Steganography conceals the existence of a message by embedding it within another medium, such as an image or audio file, while symmetric encryption scrambles the message content using a shared secret key. In steganography, the key focus is on hiding communication, making the presence of information undetectable, whereas symmetric encryption protects data confidentiality by transforming it into unreadable ciphertext. Steganography requires cover media and is vulnerable if detected, whereas symmetric encryption relies on secure key management and mathematical algorithms like AES for robust data protection.
Use Cases: When to Use Steganography vs Symmetric Encryption
Steganography is ideal for covert communication where the presence of hidden data must remain undetected, such as watermarking digital media or secret messaging within images. Symmetric encryption suits scenarios requiring fast and secure data protection during transmission or storage, like securing databases or encrypting communication channels within closed networks. Use steganography for stealth purposes and symmetric encryption for robust data confidentiality and integrity.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Steganography
Steganography excels in concealing the existence of a secret message by embedding it within innocuous carriers such as images, audio, or video files, making detection difficult. Its primary weakness lies in its vulnerability to compression, noise, or format conversion that can distort or destroy the hidden data without error-correction mechanisms. Unlike symmetric encryption, which secures data by transforming it into unreadable ciphertext, steganography relies on secrecy through obscurity, leaving it susceptible to steganalysis techniques that can reveal hidden content.
Advantages and Limitations of Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption offers the advantage of high-speed data encryption and decryption due to the use of a single secret key, making it efficient for processing large volumes of data. Its primary limitation lies in key distribution challenges, as securely sharing and managing the secret key between communicating parties can be difficult and vulnerable to interception. Despite strong confidentiality when the key is protected, symmetric encryption is less effective against key compromise, which directly jeopardizes all encrypted data security.
Combined Approaches: Steganography with Symmetric Encryption
Combining steganography with symmetric encryption enhances data security by first encrypting the message using algorithms like AES and then embedding the ciphertext within a cover medium such as images or audio files. This dual-layer approach conceals both the content and the existence of the message, making unauthorized detection and decryption significantly more difficult. Applications in secure communications, digital watermarking, and covert data transmission demonstrate increased robustness against cryptanalysis and steganalysis attacks.
Security Threats and Attack Vectors
Steganography conceals the existence of a message within innocuous media, making detection difficult but vulnerable to steganalysis attacks that exploit statistical anomalies and media artifacts. Symmetric encryption secures data by transforming plaintext into unreadable ciphertext using a shared secret key, facing threats such as brute-force key searches, key compromise, and chosen-plaintext attacks. Both methods require robust key management and threat modeling to mitigate risks like interception, tampering, and unauthorized extraction of hidden or encrypted information.
Choosing the Right Method for Data Protection
Steganography hides the existence of data within another medium, making it ideal for covert communication when secrecy is paramount. Symmetric encryption transforms data into an unreadable format using a shared secret key, offering strong protection against unauthorized access and efficient processing for large datasets. Choosing between these methods depends on whether the priority is concealing the presence of data or securing data content against interception.
Steganography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com