A checksum is a unique value calculated from a data set to verify its integrity during transmission or storage. It helps detect errors by comparing the calculated checksum against the original to ensure data has not been altered. Explore this article to understand how checksums protect your digital information.
Table of Comparison
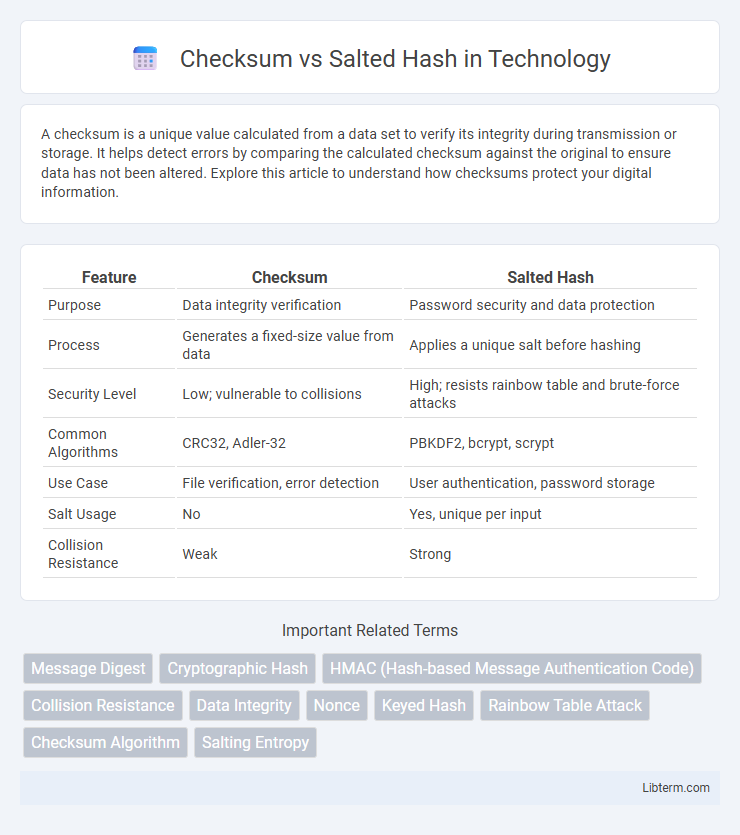
| Feature | Checksum | Salted Hash |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Data integrity verification | Password security and data protection |
| Process | Generates a fixed-size value from data | Applies a unique salt before hashing |
| Security Level | Low; vulnerable to collisions | High; resists rainbow table and brute-force attacks |
| Common Algorithms | CRC32, Adler-32 | PBKDF2, bcrypt, scrypt |
| Use Case | File verification, error detection | User authentication, password storage |
| Salt Usage | No | Yes, unique per input |
| Collision Resistance | Weak | Strong |
Introduction to Checksum and Salted Hash
A checksum is a numeric value derived from a data set using hash functions like CRC or MD5 to verify data integrity during transmission or storage. Salted hash enhances security by combining a unique random value, called a salt, with the original data before hashing, preventing attacks such as rainbow table exploits. While checksums primarily detect accidental data corruption, salted hashes protect against intentional data manipulation and unauthorized access in password storage.
What is a Checksum?
A checksum is a calculated value used to verify the integrity of data by detecting errors in files or transmissions. It works by applying a hash function or algorithm, such as CRC32 or MD5, to generate a unique fixed-size string representing the original data. Unlike salted hashes, checksums do not include a random value (salt) and are primarily designed for error-checking rather than secure password storage.
What is a Salted Hash?
A salted hash is a cryptographic technique that combines a unique, random value called a salt with the original data before hashing, significantly enhancing security by preventing attacks like rainbow table lookups. Unlike a simple checksum, which is a straightforward hash used mainly for error-checking, a salted hash ensures that identical inputs produce distinct hash outputs due to the unique salt. This method is particularly crucial in password storage, where it safeguards against precomputed hash attacks and increases the difficulty of reverse-engineering the original input.
Key Differences Between Checksum and Salted Hash
A checksum is a fixed-size string derived from data to detect errors, primarily used for data integrity verification. In contrast, a salted hash combines input data with a unique random value, or salt, before hashing to enhance security and prevent attacks like rainbow table lookups. Key differences lie in their purpose: checksums verify data accuracy, while salted hashes protect sensitive information by adding randomness to the hashing process.
Common Use Cases for Checksums
Checksums are commonly used for error detection in data transmission and file integrity verification, ensuring that data remains unaltered during transfer or storage. They provide a simple way to detect accidental corruption by generating a fixed-size hash value from the original data. Unlike salted hashes, which aim to securely store passwords by adding random data to thwart attacks, checksums prioritize speed and efficiency for verifying data consistency in everyday applications like downloads and backups.
Applications of Salted Hashing
Salted hashing is extensively applied in securing user passwords for authentication systems, where unique salts prevent rainbow table attacks and enhance protection against brute-force attempts. It is crucial in database security to ensure stored credentials cannot be easily reverse-engineered even if the database is compromised. Furthermore, salted hashes are integral to cryptographic protocols and digital signatures, providing enhanced data integrity and verification by introducing randomness into the hashing process.
Security Implications: Checksum vs Salted Hash
A checksum provides basic data integrity verification but is vulnerable to collisions and intentional tampering, making it unsuitable for robust security applications. Salted hashes incorporate a unique random value (salt) with the input before hashing, significantly enhancing resistance against rainbow table attacks and improving password security. Implementing salted hashes is essential for protecting sensitive data, whereas checksums are primarily designed for error detection rather than cryptographic security.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Checksums offer faster computation and lower resource consumption compared to salted hashes, making them suitable for quick data integrity checks. Salted hashes provide enhanced security by incorporating unique salts into the hashing process, but this added complexity results in increased processing time and memory usage. In performance-critical environments where security is less of a concern, checksums outperform salted hashes, whereas salted hashes are preferred for secure password storage despite their higher computational cost.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing between checksum and salted hash depends on the primary goal: data integrity or secure verification. Checksums efficiently detect accidental data corruption through simple algorithms like CRC, making them ideal for error-checking in file transfers. Salted hashes utilize cryptographic functions combined with random salts, enhancing password security by preventing rainbow table attacks, thus preferred for authentication and sensitive data protection.
Conclusion: Checksum or Salted Hash?
Salted hashes provide significantly stronger security compared to simple checksums by adding random data (salt) to the original input before hashing, effectively mitigating risks like rainbow table attacks. Checksums primarily serve data integrity verification, detecting accidental errors but lack robust protection against intentional tampering or credential theft. For enhancing security in password storage and sensitive data handling, salted hashes are the recommended approach.
Checksum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com