A/B testing is a powerful method for comparing two versions of a webpage or app to determine which one performs better in achieving specific goals like increasing conversions or engagement. By analyzing user behavior and response data, you can make informed decisions that optimize your digital strategies effectively. Discover how implementing A/B testing can transform your results by exploring the insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
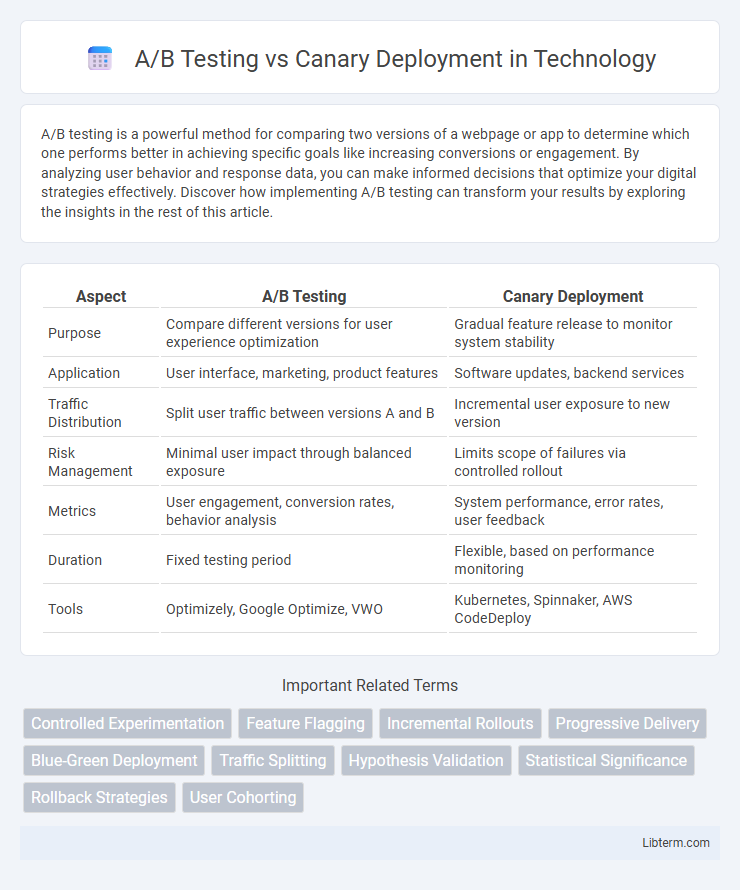
| Aspect | A/B Testing | Canary Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Compare different versions for user experience optimization | Gradual feature release to monitor system stability |
| Application | User interface, marketing, product features | Software updates, backend services |
| Traffic Distribution | Split user traffic between versions A and B | Incremental user exposure to new version |
| Risk Management | Minimal user impact through balanced exposure | Limits scope of failures via controlled rollout |
| Metrics | User engagement, conversion rates, behavior analysis | System performance, error rates, user feedback |
| Duration | Fixed testing period | Flexible, based on performance monitoring |
| Tools | Optimizely, Google Optimize, VWO | Kubernetes, Spinnaker, AWS CodeDeploy |
Introduction to A/B Testing and Canary Deployment
A/B Testing involves comparing two versions of a webpage or app to determine which performs better based on key metrics such as conversion rates and user engagement. Canary Deployment gradually releases new software updates to a small subset of users to monitor system performance and detect potential issues before full rollout. Both strategies optimize user experience and minimize risks but serve distinct purposes in feature validation and deployment safety.
Core Concepts: A/B Testing Explained
A/B testing involves comparing two versions of a webpage or app feature by directing users randomly to variant A or B to measure performance differences based on user behavior metrics such as click-through rates or conversions. This controlled experimentation method isolates variable changes to identify the most effective design or content for improving user engagement. Data-driven insights from A/B testing enable product teams to make informed decisions by analyzing statistically significant results in real time.
Core Concepts: Understanding Canary Deployment
Canary deployment is a software release strategy that gradually rolls out a new version to a small subset of users before full-scale deployment, minimizing risk by monitoring performance and errors in real-time. This method enables quick rollback if issues arise, ensuring system stability while introducing updates. It contrasts with A/B testing by focusing on controlled release and system reliability rather than experimental user behavior analysis.
Key Differences Between A/B Testing and Canary Deployment
A/B testing primarily measures user response by comparing two or more versions of a feature to determine which performs better based on predefined metrics, focusing on user experience and data-driven decisions. Canary deployment gradually releases a new software version to a small subset of users to monitor system stability and detect potential issues before a full rollout, prioritizing risk mitigation and system reliability. The key difference lies in A/B testing optimizing features through user feedback, whereas canary deployment ensures safe, controlled software updates.
Use Cases: When to Choose A/B Testing
A/B testing is ideal for comparing user experience variations to determine which design, feature, or content drives better engagement and conversion rates. It works best when experimenting with distinct user interface elements or marketing messages to gather statistically significant data from controlled user groups. This method is preferred when precise measurement of user preferences and behavior impact is crucial before a full-scale rollout.
Use Cases: When to Opt for Canary Deployment
Canary deployment is ideal for rolling out new features gradually to a subset of users, minimizing risk and enabling real-time monitoring for issues before full-scale release. It is particularly useful in complex systems requiring continuous delivery where immediate rollback capabilities are essential to maintain system stability. Organizations often choose canary deployment when testing critical updates in production without affecting the entire user base, ensuring better control over performance and error rates.
Pros and Cons of A/B Testing
A/B testing enables precise comparison between two variants by splitting user traffic, providing clear insights into user preferences and behavior, which optimizes decision-making for feature releases and design changes. This method may introduce risks such as user experience inconsistency and potential bias from sample segmentation, affecting the validity of results. A/B testing's scalability issues and increased resource requirements for statistically significant data collection further complicate its implementation in complex or rapidly changing environments.
Pros and Cons of Canary Deployment
Canary deployment enables gradual software release to a subset of users, minimizing the risk of widespread failures by isolating potential issues before full rollout. It enhances system reliability and user experience through real-time monitoring and quick rollback capabilities, but requires sophisticated infrastructure and careful traffic management to avoid complexity and inconsistent user experiences. Unlike A/B testing, which focuses on comparing variants for optimization, canary deployment prioritizes controlled release and risk mitigation in production environments.
Best Practices for Implementation
A/B testing and canary deployment each require meticulous planning to optimize user experience and minimize risk during software rollout. Implementing A/B testing involves random user segmentation and consistent metric tracking to evaluate feature effectiveness, while canary deployment demands gradual traffic shifting with automated monitoring for error rates and performance anomalies. Best practices emphasize robust data collection, clear rollback strategies, and continuous integration with CI/CD pipelines to ensure seamless transitions and informed decision-making.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Strategy
Choosing between A/B testing and canary deployment depends on the primary goal: A/B testing optimizes user experience and conversion rates by comparing variations, while canary deployment focuses on minimizing risk during software releases by gradually rolling out changes. Companies aiming for data-driven product improvements benefit from A/B testing, whereas those prioritizing system reliability and early detection of issues should opt for canary deployment. Understanding the specific objectives and organizational priorities ensures the selection of the most effective strategy for software development and deployment.
A/B Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com