Block storage delivers high-performance data storage by dividing data into fixed-size blocks, ideal for databases and virtual machines. This method ensures fast, efficient access and flexible scalability to meet evolving business needs. Explore the rest of the article to discover how block storage can enhance your storage strategy.
Table of Comparison
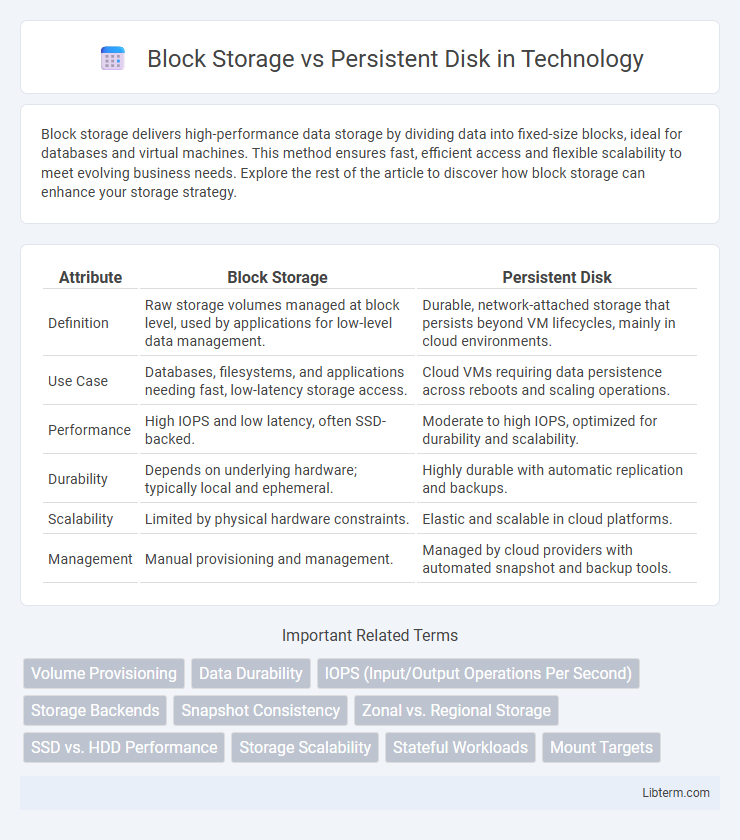
| Attribute | Block Storage | Persistent Disk |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw storage volumes managed at block level, used by applications for low-level data management. | Durable, network-attached storage that persists beyond VM lifecycles, mainly in cloud environments. |
| Use Case | Databases, filesystems, and applications needing fast, low-latency storage access. | Cloud VMs requiring data persistence across reboots and scaling operations. |
| Performance | High IOPS and low latency, often SSD-backed. | Moderate to high IOPS, optimized for durability and scalability. |
| Durability | Depends on underlying hardware; typically local and ephemeral. | Highly durable with automatic replication and backups. |
| Scalability | Limited by physical hardware constraints. | Elastic and scalable in cloud platforms. |
| Management | Manual provisioning and management. | Managed by cloud providers with automated snapshot and backup tools. |
Introduction to Block Storage and Persistent Disks
Block storage organizes data into fixed-size blocks, enabling efficient and high-performance access ideal for databases and virtual machines. Persistent disks provide durable, scalable block storage that retains data independently of instance lifecycles in cloud environments, ensuring data integrity and availability. Both technologies support random read/write operations, but persistent disks offer built-in redundancy and snapshot capabilities tailored for cloud reliability.
Core Concepts: What is Block Storage?
Block storage is a data storage method that divides data into fixed-size blocks, each with a unique identifier, allowing efficient data management and rapid access. It operates at the lowest storage level, enabling high performance for databases and virtual machines by optimizing read/write speeds and scalability. Commonly used in SANs (Storage Area Networks) and cloud environments, block storage provides raw storage volumes suitable for complex applications requiring direct disk access.
Core Concepts: What is a Persistent Disk?
A Persistent Disk is a durable block storage device designed for cloud environments, providing data persistence beyond virtual machine lifecycles. It stores data in fixed-size blocks, enabling efficient read/write operations and seamless integration with cloud-based compute instances. Unlike ephemeral block storage, Persistent Disks retain data even after instance termination, ensuring data reliability and availability.
Key Differences Between Block Storage and Persistent Disk
Block storage provides raw storage volumes at the hardware level, allowing the operating system or applications to format and manage the file system directly. Persistent disk, commonly used in cloud environments like Google Cloud Platform, offers managed block storage with integrated data redundancy, snapshots, and seamless scalability. Key differences include persistence--persistent disks maintain data beyond instance lifecycles--while traditional block storage may require manual management of durability and redundancy features.
Performance Comparison: Block Storage vs Persistent Disk
Block Storage typically offers lower latency and higher IOPS, making it ideal for transactional applications requiring rapid data access. Persistent Disk, especially in cloud environments like Google Cloud, provides consistent throughput and durability with seamless scalability, though it may have slightly higher latency compared to local block storage. Performance differences largely depend on workload type, with block storage excelling in random I/O and persistent disks optimizing for data persistence and fault tolerance.
Scalability and Flexibility Features
Block Storage offers high scalability by allowing independent scaling of storage capacity and performance, making it suitable for applications requiring rapid data access and low latency. Persistent Disk provides flexible storage options with automatic resizing and seamless integration within cloud environments, optimizing resource allocation without service interruption. Both solutions support dynamic provisioning, but Block Storage excels in fine-grained IOPS customization while Persistent Disk emphasizes ease of management and data durability across distributed systems.
Use Cases for Block Storage
Block storage is ideal for performance-sensitive applications like databases, virtual machines, and enterprise applications requiring low latency and high IOPS. It excels in use cases involving frequent read/write operations, such as transactional systems, big data processing, and content management systems. Unlike persistent disks, block storage offers greater flexibility in formatting and mounting, making it suitable for customized storage architectures and scalable cloud environments.
Use Cases for Persistent Disks
Persistent disks are ideal for scenarios requiring reliable, high-performance storage that retains data beyond instance lifecycles, such as databases, content management systems, and virtual machine boot disks. They support scalable workloads with consistent input/output operations per second (IOPS), making them suitable for applications demanding low latency and high throughput. Persistent disks also facilitate seamless snapshots and backups, enabling efficient disaster recovery and data replication.
Security and Reliability Considerations
Block storage provides granular data encryption at rest and supports robust access control mechanisms, enhancing security for sensitive workloads. Persistent disks offer automatic data replication and built-in fault tolerance, ensuring high availability and reliability in cloud environments. Both storage types implement versioning and snapshot capabilities to minimize data loss risks and facilitate quick recovery.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution for Your Needs
Choosing the right storage solution depends on your workload requirements, with block storage offering high performance and low latency for databases and transactional systems, while persistent disk provides durable, managed storage ideal for cloud-based virtual machines and containerized applications. Block storage excels in scenarios needing fast random access and scalability, whereas persistent disks ensure data persistence and easy snapshots for backup and recovery. Evaluate factors like IOPS, throughput, cost, and integration with your infrastructure to optimize storage performance and reliability.
Block Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com