User Plane is a crucial component in modern telecommunications, responsible for carrying user data such as voice, video, and internet traffic between devices and networks. It ensures efficient data transfer with low latency, supporting seamless communication and high-quality service delivery. Explore the rest of this article to understand how the User Plane impacts your network experience and its role in emerging technologies.
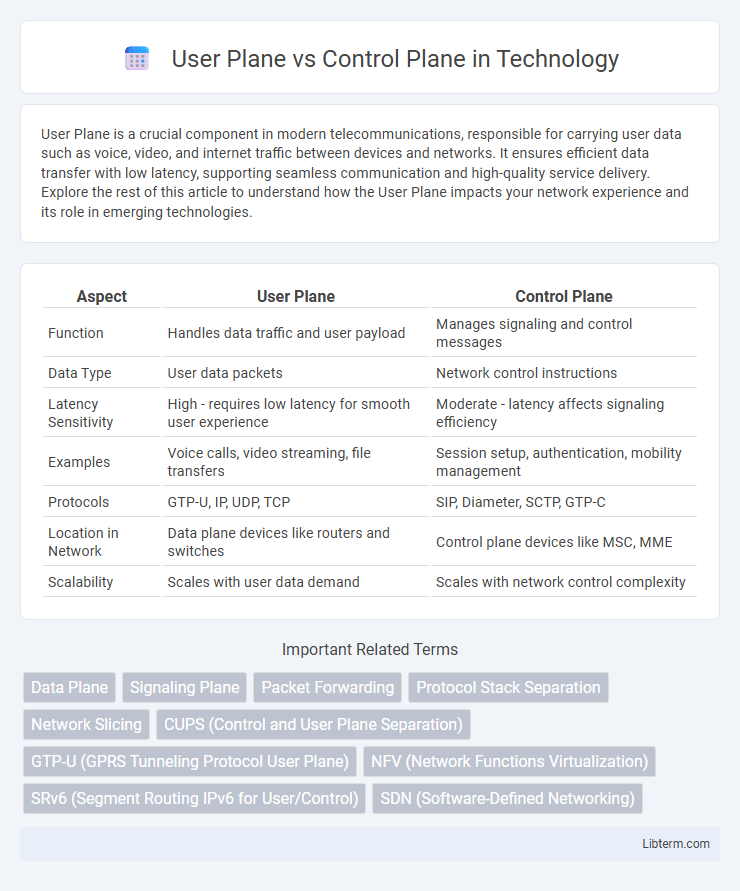
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | User Plane | Control Plane |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Handles data traffic and user payload | Manages signaling and control messages |
| Data Type | User data packets | Network control instructions |
| Latency Sensitivity | High - requires low latency for smooth user experience | Moderate - latency affects signaling efficiency |
| Examples | Voice calls, video streaming, file transfers | Session setup, authentication, mobility management |
| Protocols | GTP-U, IP, UDP, TCP | SIP, Diameter, SCTP, GTP-C |
| Location in Network | Data plane devices like routers and switches | Control plane devices like MSC, MME |
| Scalability | Scales with user data demand | Scales with network control complexity |
Introduction to User Plane and Control Plane
The User Plane (UP) manages the actual data transfer between devices, including internet traffic, voice calls, and multimedia streaming, ensuring efficient routing and forwarding of user data packets. The Control Plane (CP) handles signaling and control functions such as session management, mobility control, and authentication, orchestrating network resource allocation and communication setup. Both planes operate together to maintain network performance and service quality in telecommunication systems.
Definition of User Plane
The User Plane refers to the part of a network responsible for carrying the actual user data, such as voice, video, and internet traffic, between devices. It operates at the data plane level, managing data forwarding and transmission through packet switching. Unlike the Control Plane, which handles signaling and network control functions, the User Plane ensures the efficient delivery of end-user information across the communication network.
Definition of Control Plane
The Control Plane is responsible for managing signaling, network routing, and session establishment, enabling communication between devices by controlling data flow paths. It handles tasks such as authentication, call setup, and mobility management, ensuring the network operates efficiently and securely. Unlike the User Plane, which carries actual user data, the Control Plane directs traffic and maintains network infrastructure integrity.
Key Functions of the User Plane
The User Plane is responsible for the actual transmission of user data such as voice, video, and internet packets between devices and network endpoints. Key functions include data packet forwarding, routing, and encapsulation, ensuring efficient and secure delivery of user traffic. It handles real-time data processing while maintaining Quality of Service (QoS) parameters critical for performance in 4G and 5G networks.
Key Functions of the Control Plane
The control plane manages signaling and network control functions, including session management, mobility management, and authentication, ensuring efficient communication setup and resource allocation. It handles routing decisions, connection establishment, and maintenance between devices and network elements. Centralized control plane functions enable seamless handovers, quality of service enforcement, and security management across the network infrastructure.
Differences Between User Plane and Control Plane
User Plane carries user data and handles the actual transmission of voice, video, and internet traffic, ensuring low latency and high throughput. Control Plane manages signaling and control messages, orchestrating session setup, mobility management, and network resource allocation. The primary difference lies in their functions: User Plane deals with the payload traffic, whereas Control Plane manages the signaling required to establish and maintain communication paths.
Real-World Examples of User and Control Planes
In 5G networks, the User Plane carries actual user data such as video streaming and web browsing traffic between devices and servers, exemplified by high-definition video calls over mobile networks. The Control Plane manages signaling, session establishment, and mobility management, seen in handoff procedures when a smartphone switches cell towers during movement. This separation allows efficient network resource allocation and improved quality of service by isolating data transmission from network control tasks.
Impact on Network Performance
User Plane handles the actual data traffic between devices, directly influencing throughput, latency, and overall user experience. Control Plane manages signaling and network control functions, affecting the speed of session establishment and handover efficiency. Efficient separation and optimization of both planes enhance network performance by reducing congestion and improving response times.
User Plane and Control Plane in 5G Networks
User Plane in 5G networks handles the actual user data traffic, facilitating high-speed data transfer and low latency essential for applications like streaming and real-time communications. Control Plane manages signaling, network connectivity, and session management by coordinating handovers, authentication, and resource allocation between the user devices and the network core. The separation of User Plane and Control Plane in 5G architecture enhances network efficiency, scalability, and flexibility, enabling advanced features such as network slicing and edge computing.
Future Trends in User and Control Plane Technologies
Emerging trends in User Plane and Control Plane technologies emphasize the integration of AI-driven network slicing and edge computing to enhance real-time data processing and reduce latency. Future architectures prioritize programmable, software-defined interfaces that enable dynamic resource allocation and improved security through zero-trust models. Advancements in 5G and upcoming 6G networks will leverage decentralized control mechanisms and intelligent user plane functions to optimize network efficiency and enable massive IoT deployments.
User Plane Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com