Centralized management streamlines decision-making processes by consolidating authority within a single organizational unit, enhancing consistency and control. It allows for efficient resource allocation and rapid implementation of company-wide policies, reducing operational redundancies. Discover how centralized management can transform your organizational efficiency by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
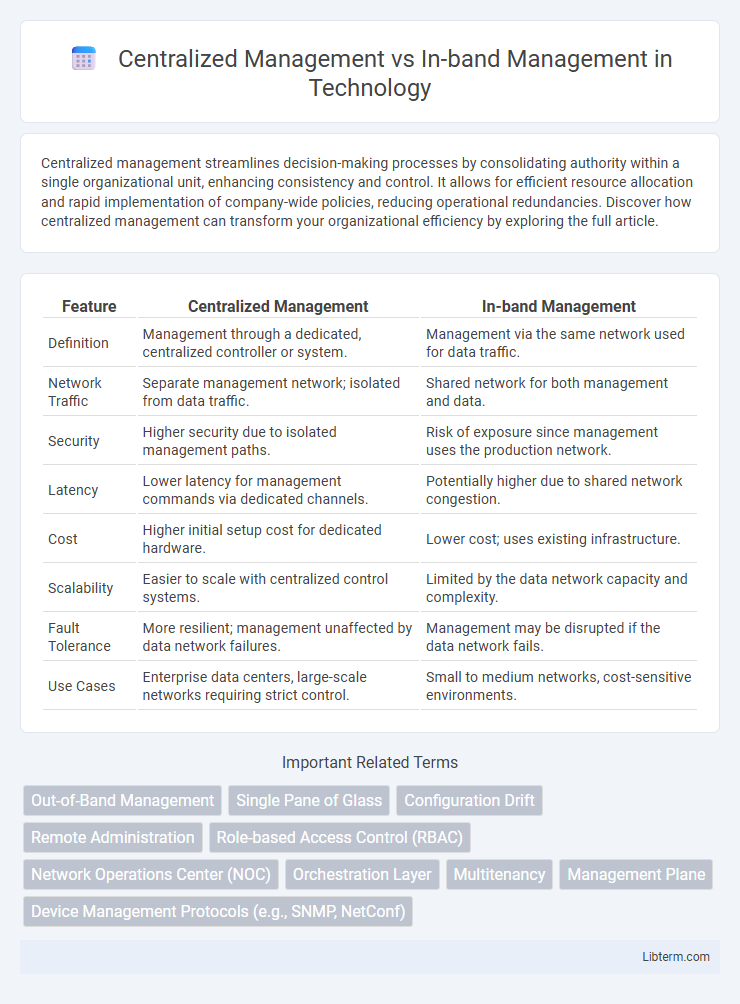
| Feature | Centralized Management | In-band Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management through a dedicated, centralized controller or system. | Management via the same network used for data traffic. |
| Network Traffic | Separate management network; isolated from data traffic. | Shared network for both management and data. |
| Security | Higher security due to isolated management paths. | Risk of exposure since management uses the production network. |
| Latency | Lower latency for management commands via dedicated channels. | Potentially higher due to shared network congestion. |
| Cost | Higher initial setup cost for dedicated hardware. | Lower cost; uses existing infrastructure. |
| Scalability | Easier to scale with centralized control systems. | Limited by the data network capacity and complexity. |
| Fault Tolerance | More resilient; management unaffected by data network failures. | Management may be disrupted if the data network fails. |
| Use Cases | Enterprise data centers, large-scale networks requiring strict control. | Small to medium networks, cost-sensitive environments. |
Introduction to Network Management Approaches
Centralized management consolidates network control into a single platform, enabling streamlined monitoring, configuration, and troubleshooting across all devices. In-band management utilizes the same network pathways for both data traffic and management commands, simplifying infrastructure but potentially risking network performance during issues. Selecting between centralized and in-band management affects scalability, security, and fault tolerance in enterprise network architectures.
Defining Centralized Management
Centralized Management refers to a network administration approach where all control and configuration tasks are handled from a single, unified platform, improving efficiency and consistency across devices. This method contrasts with In-band Management, which relies on managing devices through their own data paths, often causing challenges in scalability and security. Centralized Management provides enhanced visibility, streamlined updates, and stronger policy enforcement across complex network infrastructures.
Understanding In-band Management
In-band management refers to managing network devices through the same channel used for regular data traffic, leveraging protocols like SSH, Telnet, or SNMP. This method allows administrators to configure and monitor devices remotely but can be vulnerable to network outages and security breaches since it shares the operational data path. In contrast to centralized management, which often uses dedicated out-of-band paths or centralized consoles, in-band management prioritizes direct access and real-time control over devices within the existing network infrastructure.
Key Differences Between Centralized and In-band Management
Centralized management consolidates control of network devices through a single platform, enhancing visibility and simplifying configuration across distributed systems. In-band management relies on the same network used for data traffic, which can expose control channels to congestion or security vulnerabilities. Key differences include centralized management's use of dedicated out-of-band networks improving reliability and security, while in-band management shares resources with operational traffic, potentially impacting performance during high network load or failures.
Advantages of Centralized Management
Centralized management offers streamlined control over network devices from a single interface, significantly reducing operational complexity and improving efficiency. It enables consistent policy enforcement and faster troubleshooting by providing unified visibility and real-time monitoring across multiple systems. This approach also enhances security by centralizing access controls and audit trails, minimizing the risk of configuration errors and unauthorized access.
Pros and Cons of In-band Management
In-band management leverages the same network used for regular data traffic, simplifying implementation and reducing the need for additional hardware, but it can expose devices to security risks if the network is compromised. It offers cost-effective remote management and troubleshooting but may suffer from decreased reliability during network outages or congestions. Limited isolation between management and user traffic in in-band management can lead to potential performance degradation and increased vulnerability to attacks.
Security Implications: Centralized vs. In-band Management
Centralized management enhances security by consolidating control and monitoring in a single platform, reducing the attack surface and simplifying incident response. In-band management transmits management traffic over the same network used for regular data, increasing vulnerability to interception and attacks if the network is compromised. Effective security policies must prioritize encrypted communication channels and strict access controls to mitigate risks inherent in both centralized and in-band management models.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
Centralized management systems enhance scalability by allowing administrators to control multiple devices through a unified interface, reducing complexity and improving performance efficiency in large network environments. In-band management, while simpler to implement, can lead to network congestion as management traffic shares the same data channels, potentially degrading performance during high demand. Enterprises with expansive and dynamic networks typically prefer centralized management to ensure consistent performance and scalability across all network components.
Use Cases and Best Practices
Centralized management excels in large-scale IT environments requiring unified control and streamlined policy enforcement across multiple devices and locations, enhancing security and reducing operational complexity. In-band management is best suited for scenarios with limited infrastructure, providing direct device access via regular network connections, ideal for routine configuration and troubleshooting when out-of-band resources are unavailable. Best practices recommend deploying centralized management for enterprise-wide oversight while reserving in-band management for immediate, granular device intervention and failover contingencies.
Choosing the Right Management Approach for Your Network
Choosing the right management approach for your network depends on scalability, security, and operational efficiency. Centralized management offers unified control and streamlined updates across multiple devices but may pose risks if the central system fails. In-band management enables direct access through the network itself, providing real-time troubleshooting and quick adjustments, yet it can be vulnerable to network disruptions and attacks.
Centralized Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com