Marshalling is the process of organizing, arranging, and coordinating resources or data efficiently to optimize workflow and system performance. This technique is widely used in programming, logistics, and data management to ensure seamless communication between different components or stages. Explore the rest of the article to understand how marshalling can enhance Your operational efficiency and technical processes.
Table of Comparison
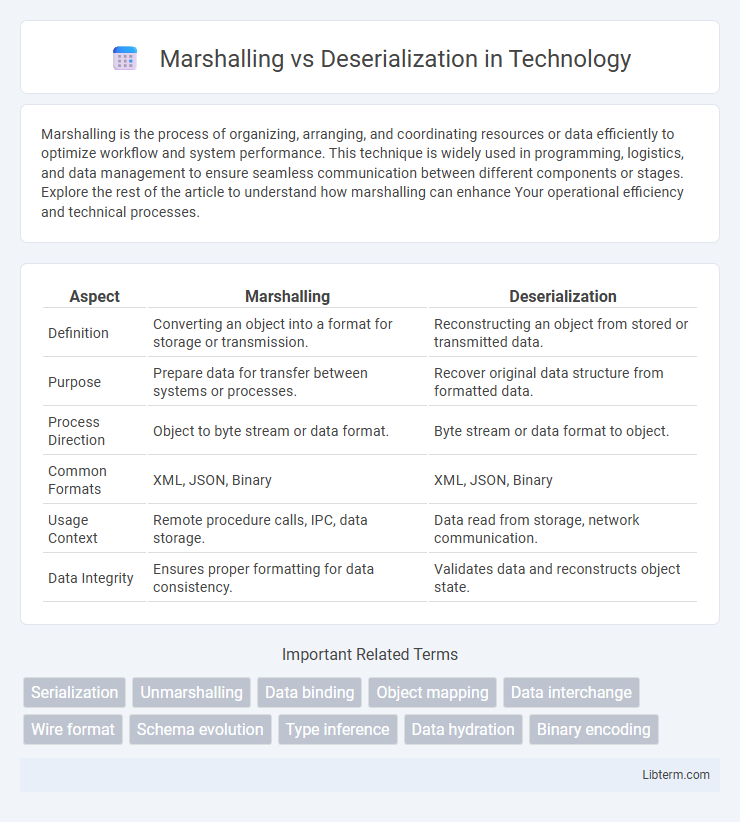
| Aspect | Marshalling | Deserialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting an object into a format for storage or transmission. | Reconstructing an object from stored or transmitted data. |
| Purpose | Prepare data for transfer between systems or processes. | Recover original data structure from formatted data. |
| Process Direction | Object to byte stream or data format. | Byte stream or data format to object. |
| Common Formats | XML, JSON, Binary | XML, JSON, Binary |
| Usage Context | Remote procedure calls, IPC, data storage. | Data read from storage, network communication. |
| Data Integrity | Ensures proper formatting for data consistency. | Validates data and reconstructs object state. |
Introduction to Marshalling and Deserialization
Marshalling converts complex data structures or objects into a standardized byte stream for storage or transmission, ensuring interoperability between different systems or components. Deserialization reverses this process by reconstructing the original data structure or object from the byte stream, enabling applications to restore data into usable formats. Both processes are fundamental in distributed computing, remote procedure calls (RPC), and data persistence mechanisms.
Defining Marshalling: Concepts and Use Cases
Marshalling is the process of transforming an object's memory representation into a data format suitable for storage or transmission, enabling interoperability between different systems or components. It is commonly used in distributed computing, such as remote procedure calls (RPC) and web services, where data needs to be serialized for network communication. Unlike general deserialization, marshalling includes handling metadata and object references to preserve the object's state and structure accurately across diverse environments.
Understanding Deserialization: Key Principles
Deserialization is the process of converting data from a byte stream or format like JSON or XML back into an object or data structure usable by a program. It involves reconstructing the object's state, including properties and nested objects, while ensuring data integrity and compatibility with the target environment. Understanding deserialization requires recognizing security risks such as injection attacks and implementing validation and sanitization protocols to protect applications during this conversion.
Core Differences Between Marshalling and Deserialization
Marshalling converts objects or data structures into a format suitable for storage or transmission, enabling remote procedure calls or data persistence, whereas deserialization reconstructs objects from serialized data back into usable program objects. Marshalling often involves packing data with metadata to preserve type and structure, while deserialization focuses on accurately interpreting this packed data to restore the original object's state. The core difference lies in marshalling preparing data for transfer or storage, while deserialization reverses this process to restore the data for application use.
Serialization Explained: The Link Between Marshalling and Deserialization
Serialization is the process of converting complex data objects into a format that can be easily stored or transmitted. Marshalling involves preparing and packaging these objects for serialization to ensure accurate data structure preservation across different systems. Deserialization reverses this process by reconstructing the original objects from the serialized data, enabling seamless data exchange and interoperability.
Common Scenarios for Marshalling in Programming
Marshalling is commonly used when transmitting data between different parts of a distributed system, such as remote procedure calls (RPC) or web services, where objects need to be converted into a transferable format. It plays a critical role in inter-process communication (IPC) by encoding complex data structures into byte streams for network or file storage. Unlike deserialization, which focuses on reconstructing objects from serialized data, marshalling emphasizes preparing data for transport or storage with preservation of state and type fidelity.
Practical Applications of Deserialization
Deserialization transforms data formats like JSON or XML into usable objects within programming environments, enabling seamless data exchange between systems. It plays a critical role in APIs, microservices, and data persistence by reconstructing data structures for application logic processes. Practical applications include loading configuration files, restoring game states, and processing user input in web applications.
Security Implications: Marshalling vs Deserialization
Marshalling and deserialization both involve converting data between formats but differ in security implications; marshalling typically involves structured, controlled data exchange, reducing risks of code injection or tampering, while deserialization often handles data from untrusted sources, increasing vulnerability to attacks such as remote code execution and object injection. Secure deserialization requires strict validation, use of updated libraries, and limiting classes that can be instantiated to prevent exploitation. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for implementing robust security measures in distributed systems and applications.
Performance Considerations in Data Transformation
Marshalling converts objects into a format suitable for storage or transmission, often requiring less processing overhead compared to deserialization, which reconstructs objects from serialized data. Performance in marshalling hinges on efficient serialization algorithms and minimizing data size, while deserialization performance depends on the complexity of object graphs and validation processes. Optimal performance in data transformation demands selecting formats and libraries that balance speed, memory usage, and compatibility with application requirements.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between marshalling and deserialization depends on factors such as data format compatibility, performance requirements, and security considerations. Marshalling is ideal for converting complex objects into a platform-independent format for transmission, while deserialization is focused on reconstructing objects from data, often requiring strict validation to prevent vulnerabilities. Evaluate system architecture, data complexity, and intended use cases to determine the approach that ensures efficiency and safety in data processing workflows.
Marshalling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com