Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances your online security by requiring two forms of verification before granting access to your accounts, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Common methods include a password combined with a code sent to your phone or generated by an authentication app. Discover how implementing 2FA can protect your digital life throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
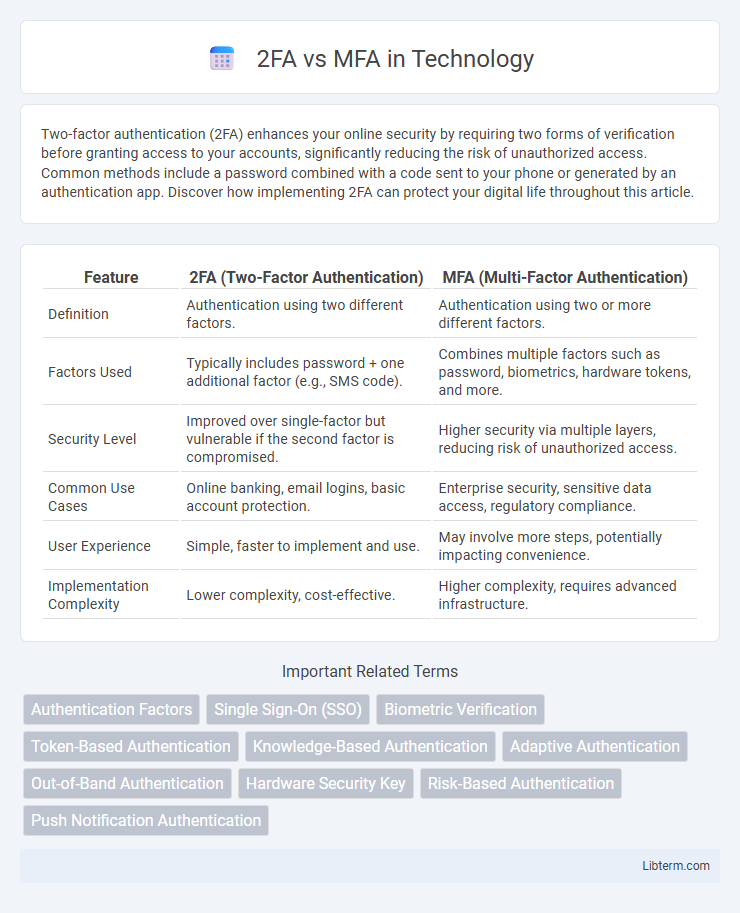
| Feature | 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) | MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authentication using two different factors. | Authentication using two or more different factors. |
| Factors Used | Typically includes password + one additional factor (e.g., SMS code). | Combines multiple factors such as password, biometrics, hardware tokens, and more. |
| Security Level | Improved over single-factor but vulnerable if the second factor is compromised. | Higher security via multiple layers, reducing risk of unauthorized access. |
| Common Use Cases | Online banking, email logins, basic account protection. | Enterprise security, sensitive data access, regulatory compliance. |
| User Experience | Simple, faster to implement and use. | May involve more steps, potentially impacting convenience. |
| Implementation Complexity | Lower complexity, cost-effective. | Higher complexity, requires advanced infrastructure. |
Introduction to 2FA and MFA
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) requires users to provide two distinct forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to a mobile device, to enhance security. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) expands on this by incorporating two or more verification methods, including biometric data, security tokens, or location-based authentication. Both 2FA and MFA significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access by combining multiple layers of user verification.
Understanding Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two distinct forms of identification, typically combining something they know (a password) with something they have (a smartphone or hardware token). Unlike Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), which may involve three or more verification factors including biometric data, 2FA strictly uses two separate methods to reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Implementing 2FA significantly lowers the chances of account breaches, making it a foundational security measure for online services.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource, such as an application or online account. Unlike Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), which specifically uses two types of authentication factors, MFA can involve multiple layers, including something you know (password), something you have (security token), and something you are (biometric verification). This layered approach in MFA significantly enhances security by making unauthorized access more difficult compared to single or two-factor methods.
Key Differences Between 2FA and MFA
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) requires exactly two forms of verification, typically combining something you know (password) with something you have (a phone or token). Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) extends beyond two factors, incorporating additional layers such as biometrics (fingerprints or facial recognition) or location-based verification to enhance security. The key difference lies in the number and variety of authentication methods, with MFA providing a more robust defense against unauthorized access compared to 2FA.
Security Benefits of 2FA
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two distinct types of credentials, typically something they know (password) and something they have (a mobile device or hardware token), effectively reducing the risk of unauthorized access. This layered approach significantly protects sensitive data and accounts from phishing attacks, password breaches, and keyloggers compared to single-factor authentication. 2FA is widely supported across platforms, making it an accessible and robust security measure that strengthens user authentication without the complexity often associated with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
Advantages of MFA Over 2FA
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to verify their identity through two or more independent credentials, such as something they know (password), something they have (security token), and something they are (biometric verification). Unlike two-factor authentication (2FA), which uses only two types of factors, MFA provides a more robust defense against unauthorized access and phishing attacks by layering multiple authentication methods. This increased complexity reduces the risk of credential compromise and offers stronger protection for sensitive data and online accounts.
Common Use Cases: 2FA vs MFA
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is commonly used for securing online banking, email accounts, and social media platforms by requiring two types of credentials, such as a password and a one-time code. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) extends security in enterprise environments, healthcare systems, and government networks by incorporating multiple verification methods including biometrics, smart cards, and physical tokens alongside passwords. Organizations prioritize MFA for high-risk access points to enhance protection against cyber threats and comply with regulatory standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementing 2FA and MFA often faces challenges such as user resistance, increased operational costs, and integration complexity with existing systems. Solutions include employing adaptive authentication methods that balance security and user convenience, leveraging cloud-based MFA services for easier deployment, and providing comprehensive user training to minimize friction. Organizations must also continuously monitor and update authentication protocols to address evolving security threats and compliance requirements.
Choosing Between 2FA and MFA for Your Business
Choosing between 2FA and MFA for your business depends on the level of security needed and user convenience. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) typically requires two distinct verification methods, such as a password and a one-time code, offering a strong but simpler layer of protection. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security further by incorporating three or more verification factors, like biometrics, security tokens, or location-based checks, making it ideal for high-risk environments and sensitive data protection.
Future Trends in Authentication Methods
Future trends in authentication methods are moving beyond traditional two-factor authentication (2FA) towards more robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems integrating biometric data, behavioral analytics, and AI-driven risk assessment. Passwordless authentication using biometrics such as fingerprint, facial recognition, and voice patterns is gaining traction for enhanced security and user convenience. The rise of decentralized identity frameworks and adaptive authentication techniques further supports personalized, context-aware access controls that anticipate and mitigate emerging cyber threats.
2FA Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com