Virtualization enables multiple virtual environments to run on a single physical hardware system, optimizing resource use and reducing costs. It enhances scalability, flexibility, and disaster recovery capabilities for businesses of all sizes. Discover how virtualization can transform Your IT infrastructure by exploring the benefits and applications detailed in this article.
Table of Comparison
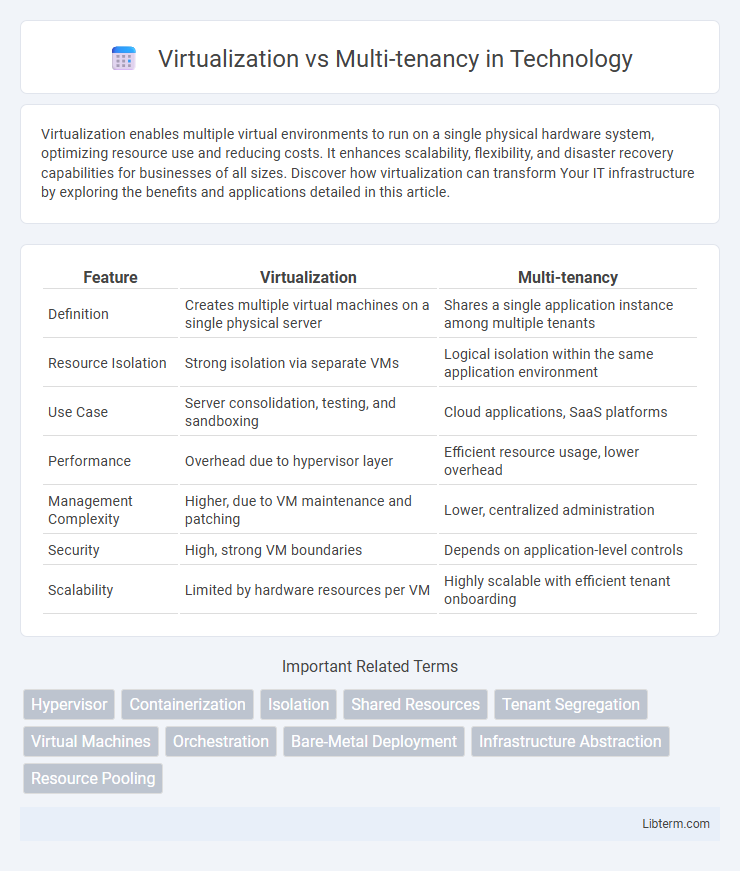
| Feature | Virtualization | Multi-tenancy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creates multiple virtual machines on a single physical server | Shares a single application instance among multiple tenants |
| Resource Isolation | Strong isolation via separate VMs | Logical isolation within the same application environment |
| Use Case | Server consolidation, testing, and sandboxing | Cloud applications, SaaS platforms |
| Performance | Overhead due to hypervisor layer | Efficient resource usage, lower overhead |
| Management Complexity | Higher, due to VM maintenance and patching | Lower, centralized administration |
| Security | High, strong VM boundaries | Depends on application-level controls |
| Scalability | Limited by hardware resources per VM | Highly scalable with efficient tenant onboarding |
Introduction to Virtualization and Multi-tenancy
Virtualization is a technology that enables multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, enhancing resource utilization and isolation by abstracting hardware. Multi-tenancy refers to a software architecture where a single instance of an application serves multiple tenants, allowing data segregation and customized user experiences within shared infrastructure. Both concepts optimize IT resources but differ in scope: virtualization isolates operating environments, while multi-tenancy manages software-level resource sharing among users.
Core Concepts: Virtualization Defined
Virtualization refers to the creation of virtual versions of physical resources, such as servers, storage devices, or networks, enabling multiple operating systems and applications to run independently on a single physical machine. It abstracts hardware through a hypervisor, allowing efficient resource allocation and isolation. This foundational technology contrasts with multi-tenancy by emphasizing resource partitioning at the hardware or OS level rather than application-level resource sharing.
Core Concepts: Multi-tenancy Explained
Multi-tenancy enables a single instance of software to serve multiple customers (tenants), isolating data and configurations while sharing underlying resources efficiently. Unlike virtualization, which partitions physical hardware into separate virtual machines, multi-tenancy leverages shared infrastructure at the application level for cost-effective scalability. This core concept supports software-as-a-service (SaaS) models by maximizing resource utilization and simplifying maintenance across diverse user groups.
Architecture Comparison: Virtualization vs Multi-tenancy
Virtualization architecture isolates multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server using a hypervisor, enabling independent operating systems and applications to run concurrently. Multi-tenancy architecture, on the other hand, consolidates multiple tenants within a shared application instance, where tenant data and configurations remain logically separated but utilize common resources and code. While virtualization emphasizes hardware abstraction and isolation, multi-tenancy optimizes resource sharing and operational efficiency at the software layer.
Resource Management in Virtualization and Multi-tenancy
Resource management in virtualization involves allocating hardware resources like CPU, memory, and storage to multiple virtual machines, each running isolated operating systems to ensure performance and security. Multi-tenancy manages resources by enabling multiple tenants to share a single application instance while maintaining data isolation and customized user environments. Virtualization provides strong resource isolation through hypervisor-based controls, whereas multi-tenancy optimizes resource utilization within a single software platform by dynamically distributing resources among users.
Security Considerations: Isolation and Access Control
Virtualization provides strong isolation by creating separate virtual machines (VMs) with dedicated resources, reducing the risk of cross-tenant attacks through hypervisor-level enforcement. Multi-tenancy relies on software-level isolation within a shared environment, making access control crucial to prevent unauthorized data access and lateral movement between tenants. Security strategies in virtualization often include hypervisor hardening and VM-level firewalls, whereas multi-tenancy emphasizes robust authentication, role-based access control, and strict data segregation policies.
Cost Efficiency: Savings and Overheads
Virtualization reduces costs by allowing multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, optimizing hardware utilization and lowering capital expenditure. Multi-tenancy enhances cost efficiency by sharing resources and infrastructure among multiple users, minimizing operational overhead and streamlining maintenance expenses. While virtualization incurs overhead from hypervisor management, multi-tenancy's shared environment leads to greater economies of scale and cost savings in cloud service delivery.
Scalability and Performance Differences
Virtualization provides isolated environments by running multiple virtual machines on a single physical server, enhancing scalability through resource allocation but potentially introducing overhead that impacts performance. Multi-tenancy delivers a single software instance serving multiple tenants with shared resources, optimizing performance by reducing redundancy but requiring sophisticated data partitioning to maintain tenant isolation. Scalability in virtualization benefits from flexible hardware resource distribution, whereas multi-tenancy excels in application-level efficiency and cost-effective scaling.
Use Cases: When to Use Virtualization or Multi-tenancy
Virtualization is best suited for isolated workloads requiring dedicated resources, such as running multiple operating systems on the same physical hardware or for legacy application compatibility in data centers. Multi-tenancy is ideal for SaaS applications where many users or organizations share a single instance of software, optimizing resource use and simplifying maintenance. Use virtualization when security and performance isolation are critical, and prefer multi-tenancy for scalable, cost-efficient cloud services with shared infrastructure.
Future Trends in Virtualization and Multi-tenancy
Future trends in virtualization emphasize the rise of lightweight containerization technologies and edge computing to enhance resource efficiency and scalability. Multi-tenancy is evolving with advanced isolation techniques and AI-driven management to improve security and tenant-specific customization in cloud environments. Integration of both approaches is expected to optimize infrastructure utilization while supporting diverse workload requirements and compliance mandates.
Virtualization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com