Virtual LAN (VLAN) technology segments a physical network into multiple, isolated logical networks, enhancing security and reducing broadcast traffic. By assigning devices to specific VLANs, your network can improve performance and simplify management through traffic separation. Explore the rest of the article to learn how VLANs can optimize your network infrastructure effectively.
Table of Comparison
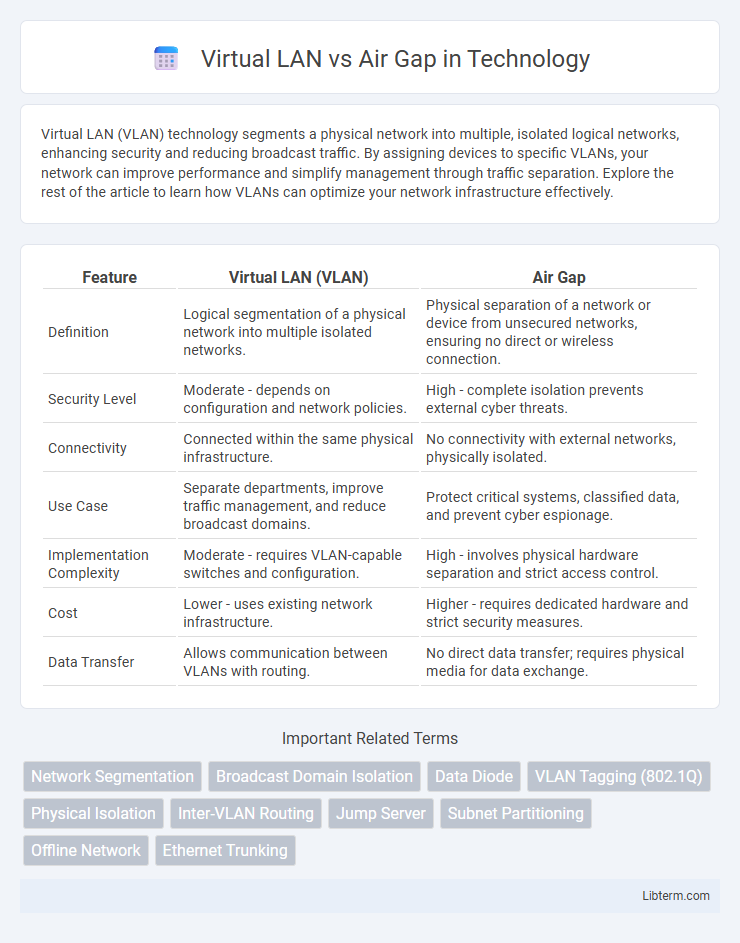
| Feature | Virtual LAN (VLAN) | Air Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Logical segmentation of a physical network into multiple isolated networks. | Physical separation of a network or device from unsecured networks, ensuring no direct or wireless connection. |
| Security Level | Moderate - depends on configuration and network policies. | High - complete isolation prevents external cyber threats. |
| Connectivity | Connected within the same physical infrastructure. | No connectivity with external networks, physically isolated. |
| Use Case | Separate departments, improve traffic management, and reduce broadcast domains. | Protect critical systems, classified data, and prevent cyber espionage. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate - requires VLAN-capable switches and configuration. | High - involves physical hardware separation and strict access control. |
| Cost | Lower - uses existing network infrastructure. | Higher - requires dedicated hardware and strict security measures. |
| Data Transfer | Allows communication between VLANs with routing. | No direct data transfer; requires physical media for data exchange. |
Introduction to Virtual LAN (VLAN) and Air Gap
Virtual LAN (VLAN) segments a physical network into multiple logical networks, enhancing security and traffic management by isolating network devices within the same infrastructure. An air gap represents a physical isolation technique that completely separates a secure network from unsecured networks or the internet, preventing any digital communication between them. VLANs facilitate controlled internal access using software-defined boundaries, while air gaps ensure absolute network isolation for highly sensitive environments.
Core Principles of VLAN Technology
Virtual LAN (VLAN) technology segments a physical network into multiple logical networks, enhancing security and traffic management by isolating broadcast domains within the same infrastructure. VLANs operate using tags defined in the IEEE 802.1Q standard, enabling devices to communicate as if they were on separate networks despite sharing the same hardware. This segmentation improves network efficiency, reduces congestion, and limits unauthorized access without requiring physical separation like an air gap.
Core Principles of Air Gap Security
Air Gap Security relies on physical isolation by ensuring critical systems are completely disconnected from unsecured networks, preventing any external access or data transfer. This method secures sensitive information through strict segmentation, eliminating potential cyber attack vectors common in Virtual LAN (VLAN) configurations that still allow network connectivity. The core principle is absolute network separation, reducing risks by eliminating pathways for unauthorized communication or malware infiltration.
Key Differences Between VLAN and Air Gap
Virtual LAN (VLAN) segments a physical network into multiple logical networks to improve security and traffic management within the same infrastructure, using tagging protocols like IEEE 802.1Q. An air gap physically isolates a network or system from unsecured networks, preventing any data exchange to enhance security against cyber threats. VLAN allows controlled interconnectivity and resource sharing, while air gaps enforce complete disconnection for maximum protection.
Use Cases for VLAN Implementation
Virtual LAN (VLAN) implementation is essential for segmenting network traffic within organizations, improving security by isolating sensitive departments such as finance or HR, and enhancing performance through traffic management. VLANs are widely used in enterprise networks to create multiple distinct broadcast domains over a single physical infrastructure, facilitating efficient resource sharing and access control. Unlike air gap security that physically isolates networks to prevent cyber threats, VLANs support dynamic network design suitable for data centers, campus environments, and multi-tenant office buildings requiring flexible and scalable connectivity.
Use Cases for Air Gap Deployment
Air Gap deployment is ideal for securing highly sensitive environments such as military networks, critical infrastructure systems, and classified government databases where preventing any external network access is paramount. Unlike Virtual LANs (VLANs) that segment networks logically within the same infrastructure, Air Gaps provide physical isolation, eliminating risks from remote cyber threats and insider attacks through network interfaces. Organizations handling top-secret data or mission-critical operations deploy Air Gaps to ensure total isolation, safeguarding against ransomware, advanced persistent threats, and data exfiltration attempts.
Security Advantages of VLANs
Virtual LANs (VLANs) enhance network security by segmenting traffic within the same physical infrastructure, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and limiting broadcast domains. VLANs enable strict access controls and policy enforcement through network switches, isolating sensitive data and minimizing attack surfaces. Compared to air gaps, VLANs offer dynamic scalability and easier access management without sacrificing the integrity of network segmentation.
Security Advantages of Air Gap Solutions
Air gap solutions provide superior security by physically isolating sensitive networks from external connections, eliminating risks associated with remote cyberattacks and unauthorized access. Unlike Virtual LANs (VLANs), which rely on logical segmentation over shared infrastructure, air gaps prevent data leakage by ensuring no digital pathways exist between secured and non-secured networks. This physical separation is critical for safeguarding high-value assets in government, military, and critical infrastructure environments where maximum threat mitigation is essential.
Limitations and Challenges: VLAN vs Air Gap
Virtual LANs (VLANs) face limitations such as potential VLAN hopping attacks and the need for complex configurations to maintain network segmentation, which can increase administrative overhead. Air gaps provide stronger security by physically isolating systems, but this approach challenges scalability and remote access, making data transfers cumbersome and prone to human error. Both methods require meticulous management to mitigate vulnerabilities: VLANs depend on proper configuration and monitoring, while air gaps rely on strict procedural controls and physical security.
Choosing the Best Network Isolation Method
Choosing between Virtual LAN (VLAN) and air gap for network isolation depends on security requirements and operational needs; VLANs provide segmented network traffic within a shared infrastructure using logical separation, ideal for flexible and cost-effective management. Air gaps offer physical isolation, completely disconnecting systems from unsecured networks, thus providing the highest security level against cyber threats but with increased complexity and limited accessibility. Evaluating factors such as threat models, data sensitivity, and maintenance resources ensures selecting the optimal network isolation strategy.
Virtual LAN Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com