Disaggregated infrastructure separates computing components such as CPU, memory, and storage into individual modules, allowing more flexible and efficient resource allocation. This approach reduces hardware costs, simplifies upgrades, and enhances scalability to meet evolving business demands. Discover how adopting disaggregated infrastructure can optimize your IT environment in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
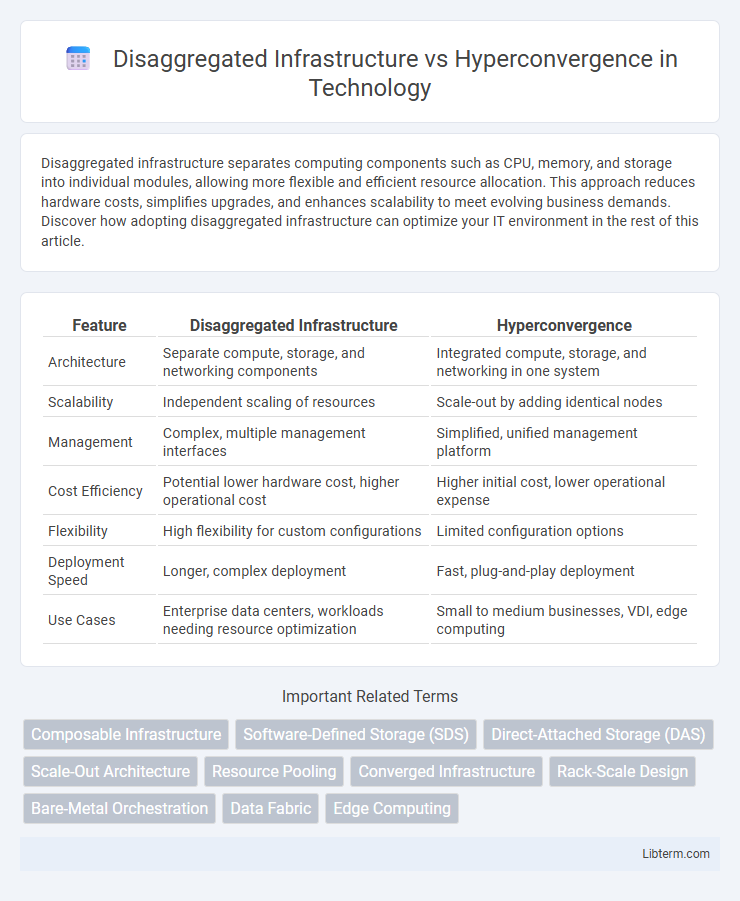
| Feature | Disaggregated Infrastructure | Hyperconvergence |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Separate compute, storage, and networking components | Integrated compute, storage, and networking in one system |
| Scalability | Independent scaling of resources | Scale-out by adding identical nodes |
| Management | Complex, multiple management interfaces | Simplified, unified management platform |
| Cost Efficiency | Potential lower hardware cost, higher operational cost | Higher initial cost, lower operational expense |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for custom configurations | Limited configuration options |
| Deployment Speed | Longer, complex deployment | Fast, plug-and-play deployment |
| Use Cases | Enterprise data centers, workloads needing resource optimization | Small to medium businesses, VDI, edge computing |
Introduction to Modern IT Infrastructure Trends
Disaggregated infrastructure separates compute, storage, and networking resources into independent modules, enabling flexible scaling and optimized resource utilization, while hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) integrates these components into a unified system managed through a single software platform. Modern IT infrastructure trends emphasize agility, cost-efficiency, and simplified management, with disaggregated models supporting heterogeneous environments and hyperconvergence catering to streamlined deployment and centralized control. Enterprises increasingly adopt hybrid cloud strategies where disaggregated infrastructure offers granular resource allocation, and HCI accelerates application delivery with built-in automation and virtualization.
What is Disaggregated Infrastructure?
Disaggregated infrastructure is a data center architecture that separates compute, storage, and networking resources into independent modules, allowing each to be scaled and managed individually. This approach enhances flexibility and resource utilization by avoiding the fixed configurations typical in traditional or hyperconverged systems. Disaggregated infrastructure supports dynamic allocation of hardware components, enabling tailored performance optimization and cost efficiency in large-scale IT environments.
Understanding Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI)
Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) integrates compute, storage, and networking into a single system, simplifying management and scalability compared to traditional disaggregated infrastructure. HCI leverages software-defined technology to virtualize all hardware components, enabling streamlined deployment and maintenance. This unified approach reduces complexity and operational costs while improving resource utilization and agility in modern data centers.
Core Differences: Disaggregated vs Hyperconverged
Disaggregated infrastructure separates compute, storage, and networking resources into independent modules, enabling customized scaling and optimized resource allocation, whereas hyperconverged infrastructure integrates these elements into a single, software-defined system for simplified management and deployment. The core difference lies in the architectural approach: disaggregated systems offer granular control and flexibility with independent scaling, while hyperconverged systems provide streamlined operations through tightly integrated hardware and software stacks. This fundamental distinction impacts performance, scalability, and use case suitability across enterprise data centers.
Performance and Scalability Comparisons
Disaggregated infrastructure separates compute, storage, and networking components, allowing independent scaling of each resource to optimize workload performance, especially in large-scale data centers. Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) tightly integrates these components into a single appliance, simplifying management but potentially limiting scalability due to resource interdependence. Performance in disaggregated systems generally outpaces HCI under heavy or varied workloads because it avoids resource bottlenecks, while HCI offers ease of deployment and consistent performance for moderate scale environments.
Flexibility and Resource Utilization
Disaggregated infrastructure offers superior flexibility by allowing independent scaling of compute, storage, and networking resources, optimizing resource utilization based on specific workload demands. Hyperconverged systems integrate these resources into a single appliance, simplifying management but often limiting the ability to tailor resource allocation granularly. Enterprises seeking dynamic resource optimization and customized scaling benefit more from the modularity of disaggregated infrastructure compared to the fixed configurations typical of hyperconvergence.
Cost Implications and Investment Considerations
Disaggregated infrastructure offers cost flexibility by allowing organizations to scale compute, storage, and networking resources independently according to specific needs, potentially reducing capital expenditure on unused components. Hyperconverged systems consolidate resources into a single appliance, often resulting in higher upfront costs but simplified management and operational efficiency that can lower total cost of ownership over time. Investment considerations must weigh initial procurement expenses against long-term scalability, maintenance costs, and the agility requirements of the IT environment.
Use Cases: When to Choose Each Architecture
Disaggregated infrastructure excels in environments requiring flexible resource allocation, such as large-scale data centers with variable workloads and high-performance computing needs, enabling independent scaling of compute, storage, and networking components. Hyperconverged infrastructure is ideal for small to medium enterprises seeking simplified management, rapid deployment, and cost efficiency by integrating compute, storage, and networking into a single appliance. Choosing disaggregated infrastructure supports customization for complex use cases, whereas hyperconvergence suits remote offices, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), and edge computing scenarios with predictable workloads.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Disaggregated infrastructure faces challenges in managing complex networking and interoperability between loosely coupled components, leading to increased operational overhead and potential latency issues. Hyperconverged infrastructure often encounters limitations in scalability due to tightly integrated resources and can struggle with performance bottlenecks when handling resource-intensive workloads. Both approaches require careful consideration of workload requirements and IT management capabilities to mitigate potential inefficiencies and ensure optimized system performance.
Future Trends in Data Center Infrastructure
Disaggregated infrastructure enables flexible scaling by separating compute, storage, and networking components, while hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) integrates these resources into a single software-driven platform. Future trends emphasize increased adoption of disaggregated models powered by AI-driven management, enabling efficient resource allocation and cost optimization in large-scale data centers. Emerging technologies such as NVMe-over-Fabrics and edge computing further drive the evolution toward modular, high-performance infrastructure that supports dynamic workloads and hybrid cloud environments.
Disaggregated Infrastructure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com