Managed devices provide businesses with enhanced control, security, and efficiency by centralizing the administration of hardware and software across an organization. These devices allow IT teams to monitor performance, deploy updates, and enforce security policies seamlessly, reducing downtime and operational risks. Explore the benefits and best practices of managed devices in the rest of this article to optimize your organization's technology infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
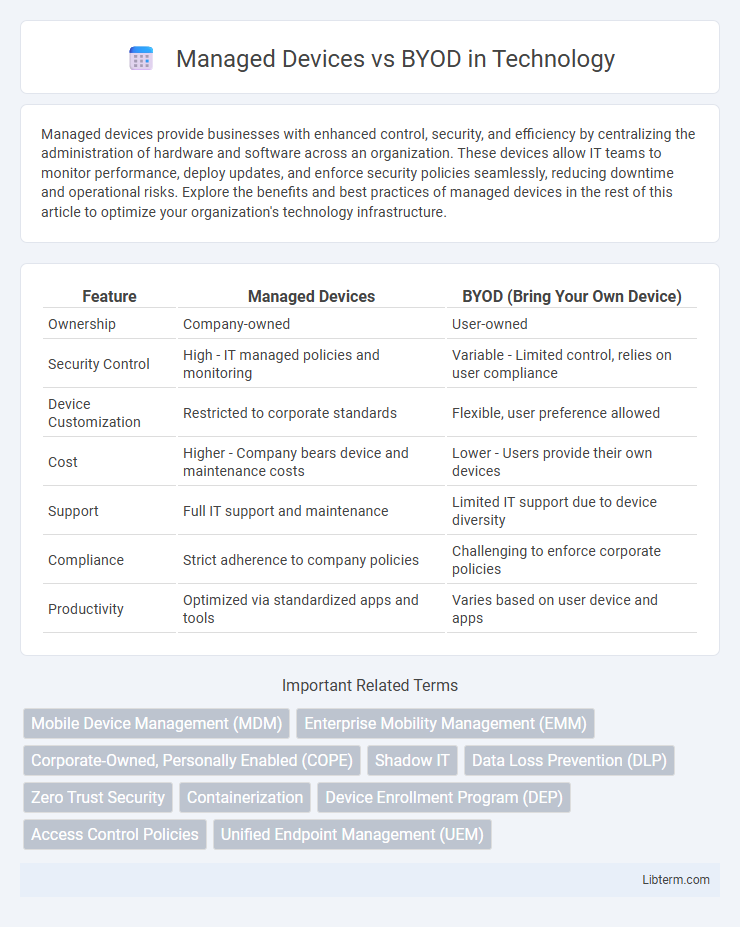
| Feature | Managed Devices | BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Company-owned | User-owned |
| Security Control | High - IT managed policies and monitoring | Variable - Limited control, relies on user compliance |
| Device Customization | Restricted to corporate standards | Flexible, user preference allowed |
| Cost | Higher - Company bears device and maintenance costs | Lower - Users provide their own devices |
| Support | Full IT support and maintenance | Limited IT support due to device diversity |
| Compliance | Strict adherence to company policies | Challenging to enforce corporate policies |
| Productivity | Optimized via standardized apps and tools | Varies based on user device and apps |
Introduction to Managed Devices and BYOD
Managed Devices refer to company-owned hardware configured, maintained, and monitored by IT departments to ensure security, compliance, and optimal performance. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies allow employees to use personal devices for work purposes, increasing flexibility but raising concerns about data security and access control. Both approaches require distinct management strategies to balance productivity, user convenience, and corporate security protocols.
Defining Managed Devices
Managed devices are company-owned hardware that IT departments configure, monitor, and secure through centralized management tools such as Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) systems. These devices maintain strict compliance with corporate security policies and enable controlled access to organizational resources, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized use. Enterprises prefer managed devices for their ability to enforce software updates, restrict applications, and provide detailed usage analytics, ensuring both productivity and data integrity.
Understanding BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) allows employees to access corporate networks using personal smartphones, laptops, and tablets, enhancing flexibility and productivity. However, it introduces security risks such as data breaches and malware infections due to inconsistent device management and varied security standards. Effective BYOD policies require robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions and strict access controls to safeguard sensitive company information.
Security Implications: Managed Devices vs BYOD
Managed devices offer enhanced security through centralized control, enabling IT teams to deploy consistent updates, enforce encryption, and monitor for threats in real-time. BYOD introduces significant security risks such as data leakage, unauthorized access, and inconsistent patch management due to varied personal device configurations. Implementing robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions and strict usage policies is essential to mitigate vulnerabilities inherent in BYOD environments.
Cost Considerations: Company-Owned vs Employee-Owned Devices
Company-owned managed devices typically incur higher upfront costs including hardware purchase, software licensing, and ongoing IT support, but offer greater control over security and compliance. Employee-owned BYOD reduces initial expenses for the company but may lead to increased costs in securing diverse devices, managing compatibility issues, and potential data breaches. Total cost of ownership analysis often favors managed devices for enterprises prioritizing long-term security investment, while BYOD can optimize short-term budget flexibility.
Employee Productivity and User Experience
Managed devices offer enhanced employee productivity by providing pre-configured, secure access to corporate resources, minimizing downtime caused by technical issues or security breaches. BYOD policies can improve user experience by allowing employees to work on familiar devices, but often require robust security measures to prevent productivity disruptions from malware or incompatible software. Balancing device management and user flexibility ensures optimized performance while maintaining a seamless workflow and consistent access to necessary applications.
IT Management and Support Challenges
Managed devices offer IT teams centralized control, streamlined updates, and enhanced security protocols, reducing the complexity of support and risk of breaches. BYOD policies create significant challenges in IT management due to diverse device types, varying security standards, and limited control over software and data access. Supporting a wide range of personal devices increases the workload for IT staff, complicates troubleshooting, and elevates the risk of data leaks and compliance issues.
Data Privacy and Compliance Risks
Managed devices provide enhanced data privacy and compliance control through centralized security protocols, enabling IT teams to enforce encryption, access controls, and regular updates. BYOD policies introduce higher risks as personal devices often lack uniform security measures, increasing vulnerabilities to data breaches and non-compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. Organizations must implement stringent monitoring and endpoint protection solutions to mitigate privacy risks and ensure regulatory compliance in mixed device environments.
Scalability and Flexibility for Growing Businesses
Managed devices provide scalable IT infrastructure by enabling centralized control, seamless updates, and consistent security policies, essential for growing businesses with expanding device fleets. BYOD offers unmatched flexibility by allowing employees to use personal devices, reducing hardware costs and supporting remote work environments, but may introduce challenges in maintaining uniform security and compliance. Balancing managed devices and BYOD strategies optimizes scalability and adaptability, ensuring robust growth while addressing evolving workforce needs.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Managed Devices or BYOD?
Choosing the right strategy between managed devices and BYOD depends on factors such as security requirements, employee flexibility, and cost efficiency. Managed devices offer enhanced control, uniform security policies, and streamlined IT support, ideal for organizations with strict compliance needs. BYOD increases employee satisfaction and reduces hardware expenses but requires robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions to mitigate security risks and protect sensitive data.
Managed Devices Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com