Developing new skills and strategies can significantly enhance your personal and professional growth. Embracing continuous learning allows you to adapt to changing environments and stay ahead in competitive fields. Discover how to effectively cultivate development in various areas by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
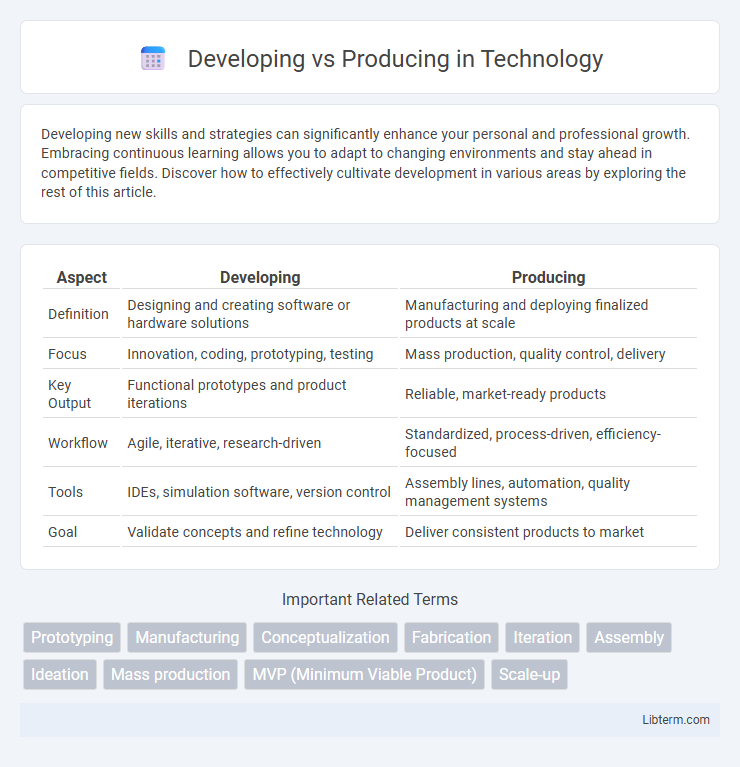
| Aspect | Developing | Producing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Designing and creating software or hardware solutions | Manufacturing and deploying finalized products at scale |
| Focus | Innovation, coding, prototyping, testing | Mass production, quality control, delivery |
| Key Output | Functional prototypes and product iterations | Reliable, market-ready products |
| Workflow | Agile, iterative, research-driven | Standardized, process-driven, efficiency-focused |
| Tools | IDEs, simulation software, version control | Assembly lines, automation, quality management systems |
| Goal | Validate concepts and refine technology | Deliver consistent products to market |
Understanding the Difference: Developing vs Producing
Developing involves the initial stages of creating a product, focusing on research, design, prototyping, and refining concepts to ensure functionality and feasibility. Producing refers to the actual manufacturing or execution phase, where the finalized design is transformed into a tangible product or delivered service at scale. Understanding the difference between developing and producing is crucial for efficient project management, resource allocation, and meeting market demands effectively.
Key Stages in Development and Production
Developing involves conceptualizing, planning, scriptwriting, and securing financing, which are critical stages that shape the project's creative direction and feasibility. Production focuses on the execution phase, including casting, shooting, set design, and post-production editing, which transforms the script into the final visual product. Efficient coordination between development and production stages ensures project timelines, budget adherence, and quality control are maintained.
Roles and Responsibilities in Each Phase
Developing involves strategic planning, design, research, and prototyping, with key roles including product managers, designers, and developers who focus on concept validation and technical feasibility. Producing emphasizes execution, manufacturing, quality assurance, and distribution, where production managers, engineers, and logistics coordinators ensure the product meets specifications and reaches the market efficiently. Clear delineation of responsibilities in development and production phases enhances workflow, reduces errors, and drives timely project completion.
Strategic Planning: When to Develop, When to Produce
Strategic planning in product lifecycle management involves assessing market demand, resource availability, and competitive positioning to decide when to transition from development to production. Development focuses on innovation, prototyping, and testing to ensure product-market fit, while production emphasizes scaling, quality control, and cost efficiency to meet customer demand. Effective decision-making hinges on metrics such as time-to-market, development costs, and predicted sales volumes to optimize resource allocation and maximize ROI.
Challenges Faced in Development vs Production
Developing a product involves challenges like uncertainty in design specifications, iterative testing, and resource allocation for prototyping, which require flexibility and innovation. Producing, however, faces operational challenges including maintaining quality control, managing supply chain logistics, and ensuring consistent output at scale under tight deadlines. Both stages demand distinct problem-solving approaches, with development focusing on creativity and experimentation, while production emphasizes efficiency and reliability.
Measuring Success: Development Metrics vs Production Metrics
Measuring success in software projects requires distinct metrics for development and production phases to optimize outcomes. Development metrics focus on code quality, velocity, bug detection rates, and feature completion timelines, providing insights into team efficiency and product robustness. Production metrics emphasize system uptime, response times, error rates, user engagement, and customer satisfaction to gauge real-world performance and user experience.
Resource Allocation: Budgeting for Development and Production
Efficient resource allocation requires distinct budgeting strategies for development and production phases, with development focusing on research, prototyping, and testing costs, while production emphasizes materials, labor, and manufacturing expenses. Development budgets often fluctuate due to iterative design changes, necessitating flexible financial planning, whereas production budgets benefit from standardized cost estimations driven by volume and process optimization. Accurate forecasting in both areas is crucial to balance investment, minimize waste, and ensure project profitability throughout the product lifecycle.
Risk Management in Development and Production
Risk management in development centers on identifying potential design flaws, technology uncertainties, and feasibility challenges early to mitigate costly rework and project delays. In production, risk management shifts to ensuring process stability, quality control, and supply chain reliability to prevent defects, downtime, and compliance issues. Effective collaboration between development and production teams facilitates seamless transition and adaptive strategies to minimize financial losses and operational disruption.
Case Studies: Successful Development and Production Processes
Case studies of successful development and production processes reveal critical factors such as iterative prototyping, cross-functional team collaboration, and rigorous quality control. For example, Apple's product launch strategy emphasizes continuous development cycles followed by streamlined mass production, ensuring product innovation coincides with scalable manufacturing. Toyota's lean production system highlights just-in-time inventory and kaizen practices that optimize production efficiency while maintaining development agility.
Evolving Trends in Development and Production
Evolving trends in software development emphasize agile methodologies and continuous integration, enabling faster iteration and adaptive product improvements. Production now leverages containerization and cloud-native infrastructures to ensure scalable, reliable deployments in real-time environments. Enhanced automation and AI-driven tools bridge development and production, optimizing workflows and reducing time-to-market.
Developing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com