Corporate-owned businesses often benefit from centralized management and consistent brand standards, ensuring a uniform customer experience across all locations. These entities can leverage greater financial resources and strategic planning to drive growth and innovation. Explore the full article to understand how corporate ownership impacts your industry and what it means for your investments.
Table of Comparison
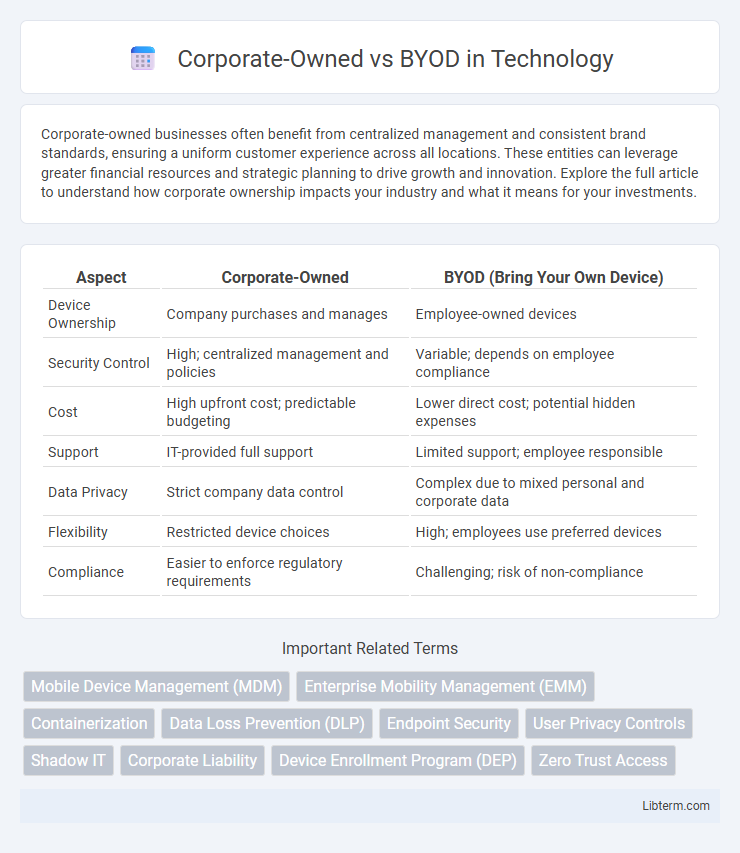
| Aspect | Corporate-Owned | BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) |
|---|---|---|
| Device Ownership | Company purchases and manages | Employee-owned devices |
| Security Control | High; centralized management and policies | Variable; depends on employee compliance |
| Cost | High upfront cost; predictable budgeting | Lower direct cost; potential hidden expenses |
| Support | IT-provided full support | Limited support; employee responsible |
| Data Privacy | Strict company data control | Complex due to mixed personal and corporate data |
| Flexibility | Restricted device choices | High; employees use preferred devices |
| Compliance | Easier to enforce regulatory requirements | Challenging; risk of non-compliance |
Introduction to Corporate-Owned and BYOD Models
Corporate-Owned and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) models represent two distinct approaches to device management in the workplace. Corporate-Owned models involve the company providing and maintaining devices for employees, ensuring standardized security and software compliance. BYOD allows employees to use personal devices for work purposes, offering flexibility but requiring robust security measures to protect corporate data.
Definitions: What Is Corporate-Owned vs BYOD?
Corporate-Owned devices are company-provided hardware such as laptops, smartphones, or tablets fully managed and controlled by the organization's IT department. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies allow employees to use their personal devices for work purposes, blending personal and professional usage under varying levels of corporate oversight. The choice between Corporate-Owned and BYOD influences security protocols, device management strategies, and employee flexibility in corporate environments.
Key Differences Between Corporate-Owned and BYOD
Corporate-owned devices are managed and secured by the company, ensuring consistent control over hardware, software, and data compliance, while BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies allow employees to use personal devices, presenting challenges in security and data privacy management. Corporate-owned models often include centralized IT support, standardized configurations, and stricter access controls, whereas BYOD requires robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions to mitigate risks associated with diverse device types and user behaviors. Cost differences also emerge as corporate-owned devices incur higher upfront expenses but enable tighter security, whereas BYOD shifts costs to employees but demands increased investment in monitoring and safeguarding data across multiple personal devices.
Security Considerations in Both Approaches
Corporate-owned devices offer centralized control over security policies, enabling organizations to enforce encryption, regular updates, and strong access controls, reducing risks of data breaches. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) introduces challenges such as inconsistent security standards, increased vulnerability to malware, and difficulties in monitoring personal devices, requiring robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions and employee training. Effective security in both approaches hinges on implementing multi-factor authentication, data loss prevention (DLP) tools, and clear usage policies to safeguard sensitive corporate information.
Cost Implications: Corporate-Owned vs BYOD
Corporate-owned devices involve higher upfront costs due to bulk purchasing, management, and maintenance expenses, while BYOD significantly reduces capital expenditure by leveraging employee-owned technology. Ongoing costs for corporate-owned assets include IT support, security enforcement, and device replacement, which can escalate operational budgets. BYOD shifts some security and support expenses to employees, potentially increasing risks and indirect costs related to data breaches or compatibility issues.
Employee Productivity and User Experience
Corporate-owned devices generally enhance employee productivity by providing standardized hardware and software, ensuring reliable performance and seamless access to enterprise applications. BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies boost user experience by allowing employees to use familiar personal devices, increasing comfort and flexibility, but may introduce security challenges and inconsistent performance. Balancing corporate control with personal device convenience is essential for optimizing productivity while maintaining a positive user experience.
IT Management and Support Challenges
Corporate-owned devices provide centralized IT management, enabling consistent security policies, streamlined software updates, and easier troubleshooting. BYOD introduces complexity with diverse operating systems and varied device capabilities, increasing support workload and complicating data protection measures. IT teams face challenges in balancing user privacy with organizational security while maintaining effective device monitoring and incident response.
Compliance and Data Privacy Issues
Corporate-owned devices offer enhanced control over compliance and data privacy by enabling centralized management, strict security policies, and regular monitoring, reducing the risk of data breaches. BYOD policies pose significant challenges in enforcing uniform compliance and protecting sensitive information due to device diversity and user autonomy. Organizations must implement robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions and clear data privacy protocols to mitigate risks associated with BYOD environments.
Scalability and Flexibility for Businesses
Corporate-owned device programs offer businesses greater scalability by enabling centralized control over device deployment, security policies, and software management, ensuring consistent performance as the organization grows. In contrast, BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies provide enhanced flexibility by allowing employees to use personal devices, reducing hardware costs and accommodating diverse work styles but potentially complicating IT management and security enforcement. Balancing scalability and flexibility depends on the organization's size, security requirements, and operational priorities.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Organization
Choosing the right strategy between Corporate-Owned and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) depends on balancing security, cost, and employee flexibility. Corporate-Owned devices offer enhanced control and consistent security policies, reducing the risk of data breaches and compliance issues. BYOD can boost employee satisfaction and reduce hardware expenses but requires robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions to mitigate potential security vulnerabilities.
Corporate-Owned Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com