Packet filtering is a fundamental network security technique that monitors incoming and outgoing data packets based on predefined rules, allowing or blocking traffic accordingly. It helps protect your network by preventing unauthorized access and controlling the flow of data between devices. Discover how packet filtering enhances security and what best practices you should follow in the full article.
Table of Comparison
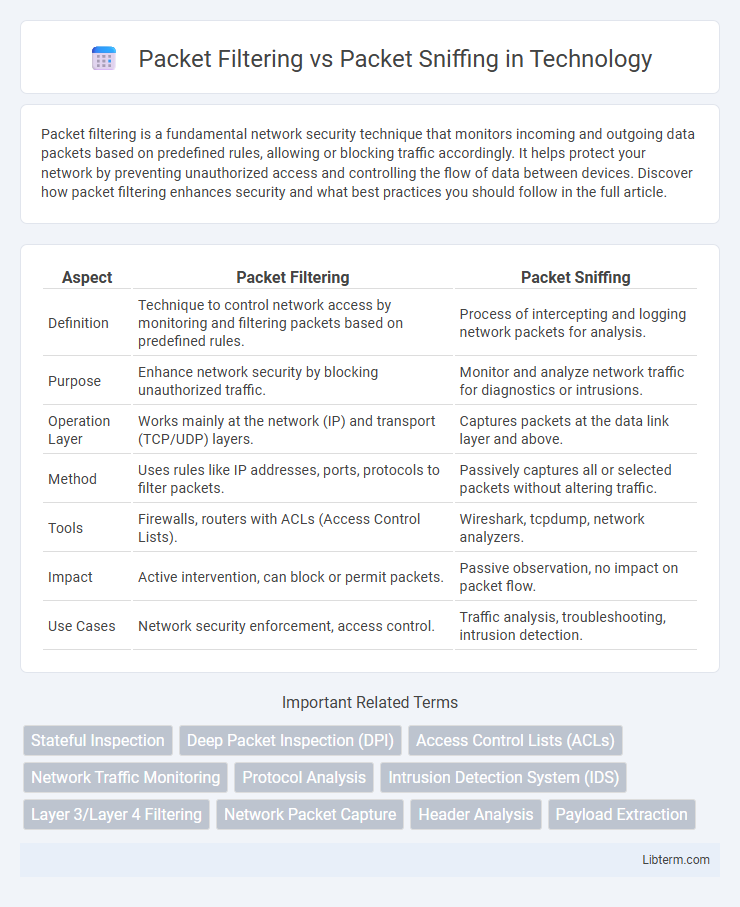
| Aspect | Packet Filtering | Packet Sniffing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique to control network access by monitoring and filtering packets based on predefined rules. | Process of intercepting and logging network packets for analysis. |
| Purpose | Enhance network security by blocking unauthorized traffic. | Monitor and analyze network traffic for diagnostics or intrusions. |
| Operation Layer | Works mainly at the network (IP) and transport (TCP/UDP) layers. | Captures packets at the data link layer and above. |
| Method | Uses rules like IP addresses, ports, protocols to filter packets. | Passively captures all or selected packets without altering traffic. |
| Tools | Firewalls, routers with ACLs (Access Control Lists). | Wireshark, tcpdump, network analyzers. |
| Impact | Active intervention, can block or permit packets. | Passive observation, no impact on packet flow. |
| Use Cases | Network security enforcement, access control. | Traffic analysis, troubleshooting, intrusion detection. |
Introduction to Packet Filtering and Packet Sniffing
Packet filtering is a network security technique that controls data flow by inspecting packets based on predefined rules such as IP addresses, protocols, or ports to allow or block traffic. Packet sniffing involves capturing and analyzing network packets in real-time to monitor data transmission, diagnose network issues, or intercept sensitive information. Both techniques are essential for network management but serve fundamentally different purposes: packet filtering enforces access control, while packet sniffing focuses on traffic observation and analysis.
Defining Packet Filtering
Packet filtering is a network security mechanism that controls data flow by examining packet headers and allowing or blocking traffic based on predefined rules such as IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols. It operates at the network layer, providing a basic level of protection against unauthorized access by filtering incoming and outgoing packets according to security policies. Unlike packet sniffing, which passively intercepts and analyzes network traffic for monitoring or troubleshooting, packet filtering actively enforces access control and network traffic management.
Understanding Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing involves capturing and analyzing data packets traveling over a network to monitor and troubleshoot communication flow, detect security threats, or gather network performance metrics. Unlike packet filtering, which selectively allows or blocks packets based on predefined rules, packet sniffing passively intercepts all packets without altering network traffic. Tools like Wireshark and tcpdump enable detailed inspection of packet headers and payloads, providing insights into network protocols and potential vulnerabilities.
Key Differences Between Packet Filtering and Packet Sniffing
Packet filtering evaluates network packets based on predefined rules to allow or block traffic, enhancing network security by controlling data flow at the router or firewall level. Packet sniffing involves capturing and analyzing packets in real-time for monitoring or troubleshooting purposes without interfering with packet transmission. The key difference lies in packet filtering's active role in traffic control versus packet sniffing's passive role in data inspection.
Packet Filtering: How It Works
Packet filtering operates by examining the header information of each data packet, such as source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocol types, to determine whether to allow or block the packet based on predefined security rules. Routers and firewalls implement packet filtering to enforce access control policies and prevent unauthorized traffic from entering or leaving a network. This method efficiently enhances network security by filtering packets at the network layer without inspecting the packet payload, ensuring minimal impact on network performance.
Packet Sniffing: Techniques and Tools
Packet sniffing involves capturing and analyzing network traffic to monitor data packets for troubleshooting or security purposes. Techniques such as promiscuous mode enable network interface cards (NICs) to intercept all packets on the network segment, while deep packet inspection (DPI) provides detailed analysis by examining packet payloads. Popular tools for packet sniffing include Wireshark, Tcpdump, and Microsoft Network Monitor, which offer real-time data capture, filtering capabilities, and protocol decoding essential for network diagnostics and intrusion detection.
Use Cases: Packet Filtering vs Packet Sniffing
Packet filtering is essential for network security, controlling data flow by allowing or blocking packets based on IP addresses, protocols, and port numbers, commonly used in firewalls to prevent unauthorized access. Packet sniffing is primarily used for network monitoring and troubleshooting, capturing and analyzing data packets to detect anomalies, diagnose issues, or gather information for performance optimization. While packet filtering enforces security policies at the network perimeter, packet sniffing provides deep visibility into network traffic for IT administrators and cybersecurity professionals.
Security Implications of Packet Filtering
Packet filtering enhances network security by selectively allowing or blocking data packets based on predefined rules such as IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols, effectively preventing unauthorized access and mitigating potential threats like IP spoofing and Denial-of-Service attacks. This form of firewall operation inspects the header information of packets without altering the payload, enabling organizations to enforce granular control over inbound and outbound traffic. Compared to packet sniffing, which passively monitors and captures network data often for analysis or malicious interception, packet filtering actively controls and restricts network access to safeguard sensitive information and maintain system integrity.
Risks Associated with Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing poses significant security risks as it enables unauthorized interception and capture of sensitive data, including passwords, credit card information, and confidential communications, often without detection. Malicious actors can exploit sniffed data to launch identity theft, network breaches, and man-in-the-middle attacks, compromising both personal and organizational security. Unlike packet filtering, which controls traffic based on predefined rules to block unauthorized data packets, packet sniffing passively monitors network traffic, increasing vulnerability to data leakage and privacy violations.
Choosing the Right Network Security Approach
Packet filtering involves actively controlling network access by inspecting and permitting or blocking data packets based on predefined rules, making it essential for establishing perimeter defense in firewalls. Packet sniffing passively captures and analyzes network traffic to monitor, diagnose, or detect security threats, offering deep packet inspection capabilities critical for identifying stealthy intrusions. Selecting the right approach depends on security objectives: packet filtering is optimal for preventing unauthorized access, while packet sniffing is vital for real-time network monitoring and forensic analysis.
Packet Filtering Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com