Bandwidth determines the maximum data transfer capacity of your internet connection, directly influencing download speeds and streaming quality. Higher bandwidth enables smoother online gaming, faster file downloads, and efficient handling of multiple devices simultaneously. Discover how to optimize your bandwidth for the best internet experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
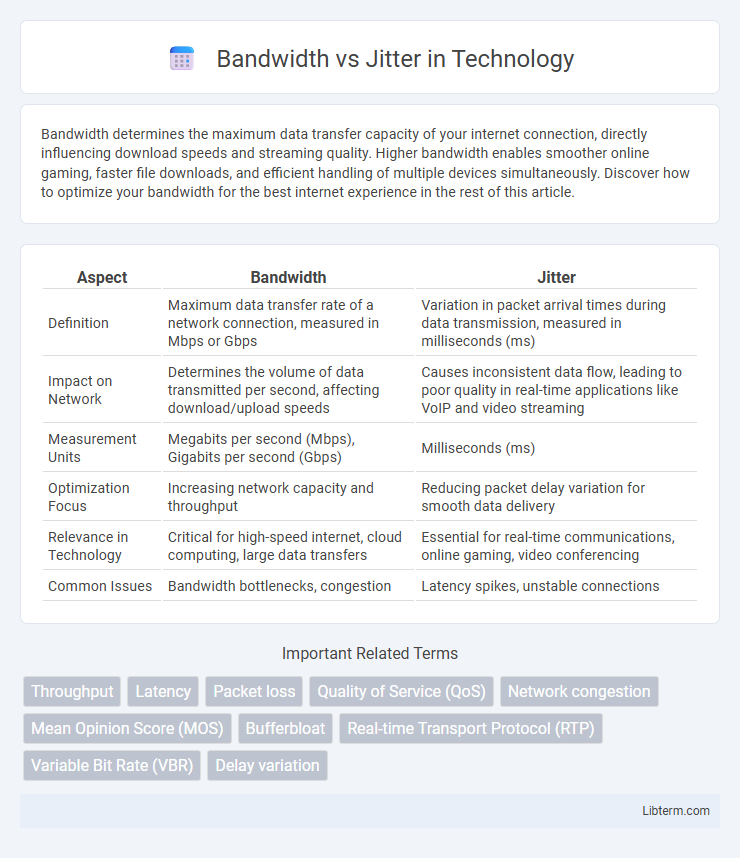
| Aspect | Bandwidth | Jitter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maximum data transfer rate of a network connection, measured in Mbps or Gbps | Variation in packet arrival times during data transmission, measured in milliseconds (ms) |
| Impact on Network | Determines the volume of data transmitted per second, affecting download/upload speeds | Causes inconsistent data flow, leading to poor quality in real-time applications like VoIP and video streaming |
| Measurement Units | Megabits per second (Mbps), Gigabits per second (Gbps) | Milliseconds (ms) |
| Optimization Focus | Increasing network capacity and throughput | Reducing packet delay variation for smooth data delivery |
| Relevance in Technology | Critical for high-speed internet, cloud computing, large data transfers | Essential for real-time communications, online gaming, video conferencing |
| Common Issues | Bandwidth bottlenecks, congestion | Latency spikes, unstable connections |
Understanding Bandwidth: Definition and Importance
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection in a given time, typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps). It is crucial for determining the capacity and speed of internet connections, directly impacting how quickly data such as video streams, downloads, and online games are delivered. High bandwidth ensures smooth performance and efficient handling of multiple devices, whereas low bandwidth can lead to slow transfer rates and degraded user experiences.
What is Jitter in Networking?
Jitter in networking refers to the variation in packet arrival times, causing inconsistent latency that can disrupt the smooth delivery of data streams. It is a critical metric for real-time applications like VoIP and online gaming, where stable timing is essential for quality. While bandwidth measures the maximum data transfer rate, jitter specifically impacts the reliability and performance of time-sensitive communication.
How Bandwidth and Jitter Affect Network Performance
Bandwidth determines the maximum data transmission capacity of a network, directly influencing speed and the ability to handle multiple simultaneous connections. Jitter refers to the variability in packet delay, causing irregular data flow that can disrupt real-time applications like VoIP and video conferencing. High bandwidth with low jitter ensures smooth data transfer, while high jitter can degrade the quality of services despite sufficient bandwidth.
Key Differences Between Bandwidth and Jitter
Bandwidth measures the maximum data transfer rate of a network connection, quantified in bits per second (bps), determining how much data can be sent over a network at one time. Jitter refers to the variability in packet delay time over a network, affecting the consistency of data transmission and causing disruptions in real-time applications like VoIP or video streaming. While bandwidth influences the volume of data transmitted, jitter impacts the stability and quality of data delivery, making both critical factors for network performance assessment.
Impact of Bandwidth on Data Transmission
Bandwidth directly influences data transmission speed by determining the maximum rate at which data can be transferred over a network. Higher bandwidth allows more data to pass through per second, reducing delays and improving overall performance. In contrast, insufficient bandwidth can lead to congestion, causing packet loss and increasing jitter, which disrupts smooth communication.
The Role of Jitter in Voice and Video Communication
Jitter significantly impacts voice and video communication by causing packet arrival time variations that disrupt audio and video quality, leading to choppy sound or pixelated images. While bandwidth determines the maximum data transmission rate, jitter affects the consistency and smoothness of real-time communication streams. Managing jitter through jitter buffers and quality of service (QoS) mechanisms is essential to maintain seamless voice and video calls over IP networks.
Measuring Bandwidth: Tools and Techniques
Measuring bandwidth accurately involves tools like speed tests, packet analyzers, and network monitoring software that evaluate data transfer rates in Mbps or Gbps. Techniques such as active probing, which sends test packets through the network, and passive monitoring, which captures real traffic, provide insights into available bandwidth and performance. Understanding these measurement methods helps distinguish bandwidth capacity from jitter, which refers to latency variation affecting real-time data transmission.
Jitter Measurement and Troubleshooting Methods
Jitter measurement involves assessing variations in packet delay within a network, typically using tools like packet analyzers and network performance monitors to quantify delay spikes and ensure quality of service. Troubleshooting jitter requires isolating network congestion, optimizing buffer sizes, and implementing Quality of Service (QoS) policies to stabilize packet timing. Understanding jitter's impact on real-time applications such as VoIP and video conferencing is critical for maintaining consistent network performance and user experience.
Bandwidth vs Jitter: Which Matters More?
Bandwidth determines the maximum data transfer capacity of a network, while jitter measures the variability in packet delay during transmission. For real-time applications like VoIP or video conferencing, low jitter is often more critical than high bandwidth to ensure smooth and uninterrupted communication. Prioritizing jitter reduction improves user experience by minimizing call drops and latency spikes, despite the available bandwidth.
Optimizing Networks to Minimize Jitter and Maximize Bandwidth
Optimizing networks to minimize jitter and maximize bandwidth involves implementing Quality of Service (QoS) protocols that prioritize time-sensitive traffic and allocate sufficient bandwidth for critical applications. Techniques such as traffic shaping, load balancing, and upgrading to higher-capacity infrastructure reduce packet delay variation and prevent congestion. Monitoring tools that analyze real-time network performance data help identify bottlenecks, enabling proactive adjustments to maintain low jitter and consistently high bandwidth.
Bandwidth Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com