Mirror Backup creates an exact replica of your data by copying files and folders in real time, ensuring zero data loss and quick recovery during system failures. This method is essential for maintaining up-to-date information without the need for compression or encryption, making restoration straightforward and efficient. Discover how Mirror Backup can protect your critical files and streamline your data security by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
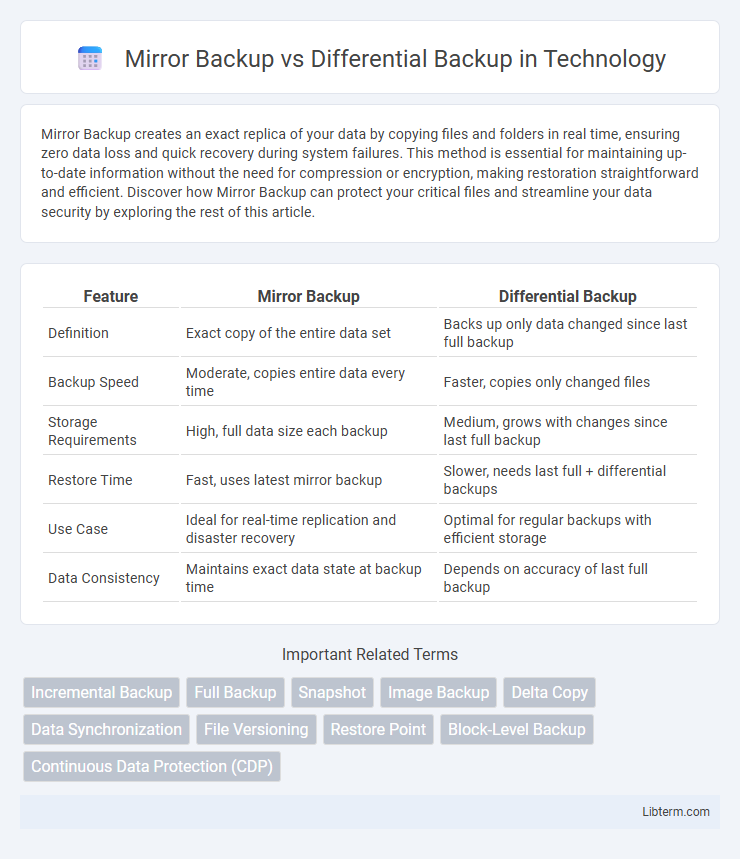
| Feature | Mirror Backup | Differential Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exact copy of the entire data set | Backs up only data changed since last full backup |
| Backup Speed | Moderate, copies entire data every time | Faster, copies only changed files |
| Storage Requirements | High, full data size each backup | Medium, grows with changes since last full backup |
| Restore Time | Fast, uses latest mirror backup | Slower, needs last full + differential backups |
| Use Case | Ideal for real-time replication and disaster recovery | Optimal for regular backups with efficient storage |
| Data Consistency | Maintains exact data state at backup time | Depends on accuracy of last full backup |
Introduction to Backup Strategies
Mirror backup creates an exact copy of the source data, ensuring real-time synchronization and instant recovery with minimal data loss. Differential backup saves only the changes made since the last full backup, optimizing storage space while reducing restoration time compared to incremental backups. Both strategies enhance data protection but vary significantly in backup speed, storage consumption, and recovery complexity.
What is Mirror Backup?
Mirror Backup creates an exact, real-time replica of a source folder or drive, ensuring every file is duplicated and updated continuously to reflect changes. This method allows quick restoration since the backup is an identical copy without compression or versioning, making it ideal for disaster recovery. Unlike differential backup, which saves only changes since the last full backup, mirror backup maintains a direct match with the original data at all times.
What is Differential Backup?
Differential backup captures all changes made since the last full backup, storing only modified files to save space and reduce backup time. Unlike mirror backup, which creates an exact replica of the source data, differential backup does not overwrite previous changes but accumulates them until the next full backup. This method enables faster recovery by restoring the last full backup plus the latest differential data.
Key Differences Between Mirror and Differential Backups
Mirror backups create an exact replica of the source data at a specific point in time, including deleted files, ensuring immediate restoration with identical folder structure. Differential backups, however, store only the changes made since the last full backup, resulting in progressively larger backup sizes until the next full backup occurs. Mirror backups consume more storage and provide faster recovery, while differential backups optimize storage efficiency and backup speed but require the last full backup plus the differential data for full restoration.
Advantages of Mirror Backup
Mirror backup offers the advantage of creating an exact replica of the source data, enabling immediate data recovery without the need for additional restoration processes. It simplifies file management by maintaining up-to-date copies that reflect real-time changes, reducing the risk of data loss. This method enhances backup efficiency by minimizing storage requirements compared to full backups while providing faster access to the latest data versions than differential backups.
Advantages of Differential Backup
Differential backup offers faster data restoration compared to mirror backup by saving only the changes made since the last full backup, reducing recovery time significantly. This backup method consumes less storage space than mirror backup, making it cost-effective for managing large volumes of data. Differential backups also minimize the risk of data redundancy, improving backup efficiency without compromising data integrity.
Use Cases for Mirror Backup
Mirror backup is ideal for users needing an exact, real-time replica of their data, ensuring immediate recovery without complex restoration processes. It suits environments requiring constant data availability, such as business servers or active workstations with sensitive information. This backup type supports rapid disaster recovery by maintaining up-to-date file copies, minimizing data loss during system failures.
Use Cases for Differential Backup
Differential backup is ideal for environments requiring efficient restoration without the overhead of full backups, such as frequently changing databases and active file servers. It stores all changes made since the last full backup, enabling quicker recovery times compared to incremental backups while consuming less storage than multiple full backups. This approach suits businesses needing reliable point-in-time recovery and minimal downtime during backup operations.
Performance and Storage Considerations
Mirror Backup creates an exact copy of the source data, allowing fast restoration but consuming significantly more storage since every change results in a new full mirror. Differential Backup stores only the changes made since the last full backup, improving storage efficiency but requiring more time to restore as it depends on the last full backup and the accumulated changes. Performance-wise, Mirror Backups offer quicker recovery times with higher storage costs, whereas Differential Backups balance moderate storage usage with longer restoration processes.
Choosing the Right Backup Method for Your Needs
Mirror backups create an exact replica of your data, allowing for quick recovery of entire systems, while differential backups save changes made since the last full backup, optimizing storage space and recovery time. Selecting the right backup method depends on factors such as data change frequency, available storage, and recovery speed requirements. For environments needing rapid restoration and minimal data loss, mirror backups are ideal, whereas differential backups suit scenarios prioritizing efficient storage and backup speed.
Mirror Backup Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com