Failover routing ensures continuous network availability by automatically redirecting traffic to backup servers when the primary server fails. This mechanism minimizes downtime and maintains seamless access to your services. Explore the rest of the article to understand how failover routing can enhance your network reliability.
Table of Comparison
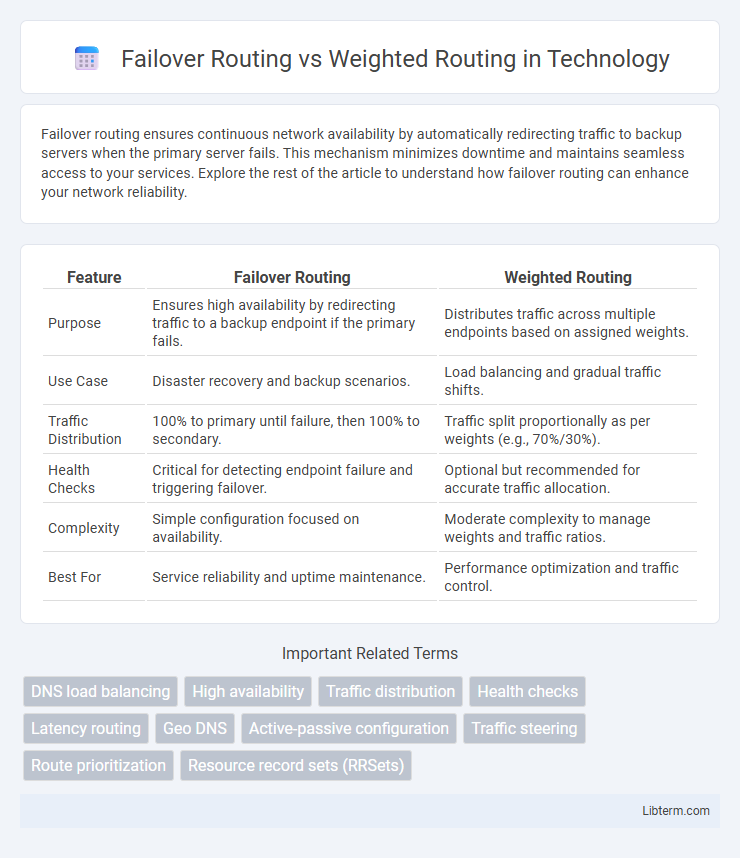
| Feature | Failover Routing | Weighted Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensures high availability by redirecting traffic to a backup endpoint if the primary fails. | Distributes traffic across multiple endpoints based on assigned weights. |
| Use Case | Disaster recovery and backup scenarios. | Load balancing and gradual traffic shifts. |
| Traffic Distribution | 100% to primary until failure, then 100% to secondary. | Traffic split proportionally as per weights (e.g., 70%/30%). |
| Health Checks | Critical for detecting endpoint failure and triggering failover. | Optional but recommended for accurate traffic allocation. |
| Complexity | Simple configuration focused on availability. | Moderate complexity to manage weights and traffic ratios. |
| Best For | Service reliability and uptime maintenance. | Performance optimization and traffic control. |
Introduction to Load Balancing in DNS
Failover Routing and Weighted Routing are critical DNS load balancing strategies designed to optimize traffic management and ensure high availability. Failover Routing automatically redirects traffic to a backup server when the primary server fails, minimizing downtime and service disruption. Weighted Routing distributes traffic across multiple servers based on predefined weights, enabling efficient resource utilization and improved response times.
What is Failover Routing?
Failover Routing directs traffic to a primary resource under normal conditions and switches to a backup resource when the primary becomes unavailable, ensuring high availability and resilience. It relies on health checks to monitor endpoint status and automatically reroutes traffic to maintain uninterrupted service. This method is crucial for disaster recovery and minimizing downtime in cloud infrastructure.
How Weighted Routing Works
Weighted Routing distributes traffic across multiple resources based on assigned weights, allowing precise control over traffic percentages directed to each endpoint. Each resource is assigned a numeric weight, and requests are routed proportionally, optimizing load balancing and resource utilization. This method enables gradual traffic shifts during deployments or testing by adjusting weights without downtime.
Key Differences Between Failover and Weighted Routing
Failover routing directs traffic to a primary resource and switches to a secondary only when the primary fails, ensuring high availability. Weighted routing distributes traffic across multiple resources based on assigned weights, optimizing load balancing and resource utilization. The key difference lies in failover routing's focus on redundancy and uptime versus weighted routing's emphasis on proportional traffic distribution.
Use Cases for Failover Routing
Failover Routing is primarily used to ensure high availability and reliability by automatically redirecting traffic to a healthy backup resource when the primary endpoint fails. Common use cases include disaster recovery for critical applications, maintaining website uptime during server outages, and automatically switching to a standby database to prevent data loss. This routing policy is crucial for businesses requiring uninterrupted service and minimal downtime.
Scenarios Suited for Weighted Routing
Weighted Routing is ideal for scenarios requiring traffic distribution across multiple resources based on specified weights, such as load balancing between servers or gradual migration of traffic during deployment. This method allows precise control over traffic proportions directed to each endpoint, optimizing resource utilization and improving application performance. It is particularly effective in scenarios involving A/B testing, multi-region failover, or gradual feature rollouts where traffic segmentation is crucial.
Performance and Reliability Comparison
Failover routing prioritizes reliability by automatically redirecting traffic to a backup endpoint during an outage, ensuring minimal downtime and maintaining service availability. Weighted routing optimizes performance by distributing traffic among multiple endpoints based on assigned weights, allowing better load balancing and resource utilization. Failover routing excels in failproof continuity, while weighted routing enhances overall performance through intelligent traffic distribution.
Pros and Cons of Failover Routing
Failover Routing in DNS ensures high availability by automatically redirecting traffic to a secondary server if the primary server fails, minimizing downtime and improving service reliability. However, it may lead to uneven load distribution since traffic only shifts when an outage occurs, potentially overloading the backup server during failover events. Weighted Routing, by contrast, distributes traffic based on assigned weights, offering better load balancing but lacking the automatic failure detection and immediate rerouting capabilities of Failover Routing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Weighted Routing
Weighted Routing enables traffic distribution across multiple resources based on assigned weights, offering fine control over load balancing and resource utilization. It allows for optimal bandwidth use and improved redundancy but can introduce complexity in managing and adjusting weight values. Unlike Failover Routing, which prioritizes availability and triggers only during failures, Weighted Routing continuously balances loads, which may lead to uneven performance if weights are not correctly configured.
Choosing the Right Routing Policy for Your Needs
Failover Routing prioritizes high availability by directing traffic to a primary resource and automatically switching to a backup during failures, making it ideal for critical applications requiring maximum uptime. Weighted Routing distributes traffic across multiple resources based on assigned weights, offering fine-tuned load balancing and gradual migration options for scalable environments. Selecting the right routing policy depends on your specific needs for reliability versus traffic distribution, ensuring optimal performance and user experience.
Failover Routing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com