Cloud computing revolutionizes data storage and processing by delivering scalable resources over the internet, enabling businesses to reduce IT costs and improve operational efficiency. With on-demand access to vast computing power, you can quickly adapt to changing market demands and enhance collaboration across teams. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how cloud computing can transform your organization's digital strategy.
Table of Comparison
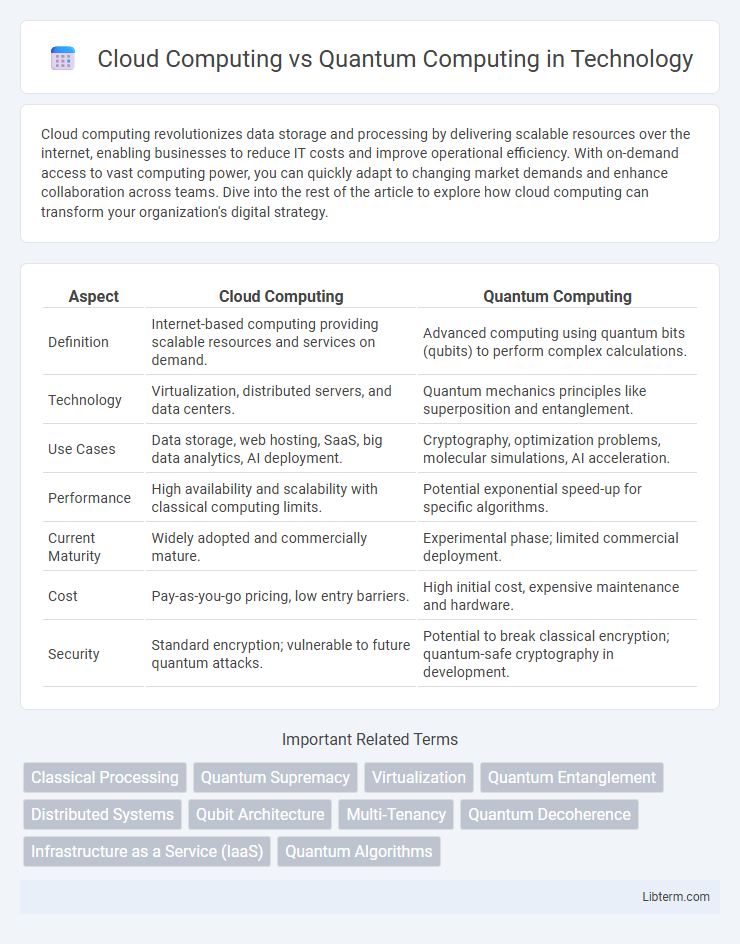
| Aspect | Cloud Computing | Quantum Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internet-based computing providing scalable resources and services on demand. | Advanced computing using quantum bits (qubits) to perform complex calculations. |
| Technology | Virtualization, distributed servers, and data centers. | Quantum mechanics principles like superposition and entanglement. |
| Use Cases | Data storage, web hosting, SaaS, big data analytics, AI deployment. | Cryptography, optimization problems, molecular simulations, AI acceleration. |
| Performance | High availability and scalability with classical computing limits. | Potential exponential speed-up for specific algorithms. |
| Current Maturity | Widely adopted and commercially mature. | Experimental phase; limited commercial deployment. |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go pricing, low entry barriers. | High initial cost, expensive maintenance and hardware. |
| Security | Standard encryption; vulnerable to future quantum attacks. | Potential to break classical encryption; quantum-safe cryptography in development. |
Introduction to Cloud Computing and Quantum Computing
Cloud computing delivers on-demand computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, over the internet, enabling scalable and flexible IT solutions for businesses and individuals. Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics, leveraging qubits to perform complex calculations exponentially faster than classical computers. While cloud computing excels in accessibility and cost-efficiency for conventional tasks, quantum computing promises breakthroughs in cryptography, optimization, and simulation by solving problems beyond the reach of classical algorithms.
Core Concepts: Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing enables on-demand access to shared computing resources via the internet, supporting scalable infrastructure, platforms, and software services. It utilizes virtualization, distributed storage, and multi-tenant architectures to optimize resource allocation and cost efficiency. Key models include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), facilitating flexible and remote computing environments.
Core Concepts: Understanding Quantum Computing
Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform complex calculations exponentially faster than classical cloud computing systems. Unlike cloud computing, which relies on classical bits that represent either 0 or 1, quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits, enabling parallel computation and enhanced processing power for specific algorithms. Understanding these core quantum concepts is essential to distinguishing quantum computing's potential advantages over traditional cloud-based computing architectures.
Key Differences Between Cloud and Quantum Computing
Cloud computing delivers scalable, on-demand access to shared computing resources over the internet, leveraging data centers to process and store vast amounts of information efficiently. Quantum computing utilizes quantum bits (qubits) to perform complex computations at unprecedented speeds by exploiting quantum phenomena like superposition and entanglement, targeting specific problems such as cryptography and optimization. The fundamental difference lies in cloud computing's classical architecture designed for versatility and broad application, whereas quantum computing's specialized quantum mechanics-based approach aims to solve problems infeasible for classical systems.
Infrastructure and Technology Stack Comparison
Cloud computing infrastructure relies on distributed servers, virtual machines, and scalable storage systems hosted in data centers, utilizing technologies such as virtualization, containers, and orchestration tools like Kubernetes. Quantum computing infrastructure consists of quantum processors (qubits), cryogenic systems to maintain ultra-low temperatures, and quantum error correction mechanisms, which require specialized hardware vastly different from classical servers. The technology stack for cloud computing includes APIs, SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS layers built on classical computing architectures, while quantum computing stacks involve quantum algorithms, quantum programming languages (like Qiskit or Cirq), and quantum hardware control systems optimized for quantum coherence and entanglement.
Performance and Scalability Aspects
Cloud computing offers high scalability by leveraging distributed servers to handle varying workloads efficiently, enabling rapid resource allocation and elastic performance improvements. Quantum computing, while currently limited by qubit coherence and error rates, promises exponential performance gains for specific complex problems but remains constrained in practical scalability and widespread deployment. Performance in cloud environments excels for general-purpose applications, whereas quantum computing targets niche tasks with potentially transformative speedups once hardware scalability challenges are resolved.
Security Implications of Cloud vs Quantum Computing
Cloud computing relies on encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication to secure data but remains vulnerable to cyber attacks such as DDoS and data breaches due to centralized servers. Quantum computing introduces the potential to crack traditional cryptographic algorithms through quantum attacks, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant encryption standards. The evolving threat landscape demands integrating post-quantum cryptography in cloud infrastructures to ensure long-term data security against quantum-enabled exploits.
Real-World Applications: Cloud Computing vs Quantum Computing
Cloud computing powers real-world applications like data storage, web hosting, and artificial intelligence through scalable infrastructure and on-demand resources, widely used in industries such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce. Quantum computing targets complex problem solving in cryptography, optimization, and drug discovery, offering potential breakthroughs but remaining largely experimental with limited commercial deployment. Enterprises currently rely on cloud computing for reliable and accessible solutions while exploring quantum computing for future advancements in computational power and algorithmic efficiency.
Cost Considerations and Accessibility
Cloud computing offers scalable resources with cost-effective pay-as-you-go models, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes without significant upfront investment in hardware. Quantum computing, still in experimental stages, involves substantial costs related to specialized hardware, maintenance, and limited access through select providers, restricting widespread availability. The affordability and ease of access to cloud services contrast sharply with the high expenses and niche accessibility of quantum computing technologies.
Future Trends and Industry Impacts
Cloud computing will continue to evolve with increased adoption of edge computing, AI integration, and multi-cloud strategies, driving enhanced scalability and real-time data processing across industries. Quantum computing promises breakthroughs in solving complex problems related to cryptography, drug discovery, and optimization algorithms, potentially disrupting sectors like finance, healthcare, and materials science. The convergence of cloud and quantum computing technologies is expected to create hybrid platforms, accelerating innovation and enabling unprecedented computational power for enterprise applications.
Cloud Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com