Manual server configuration allows you to customize settings to optimize performance and security according to your specific needs. It involves adjusting parameters such as IP addresses, firewall rules, and software environments without relying on automated tools. Explore the rest of this article to learn how manual server configuration can enhance your system's efficiency and reliability.
Table of Comparison
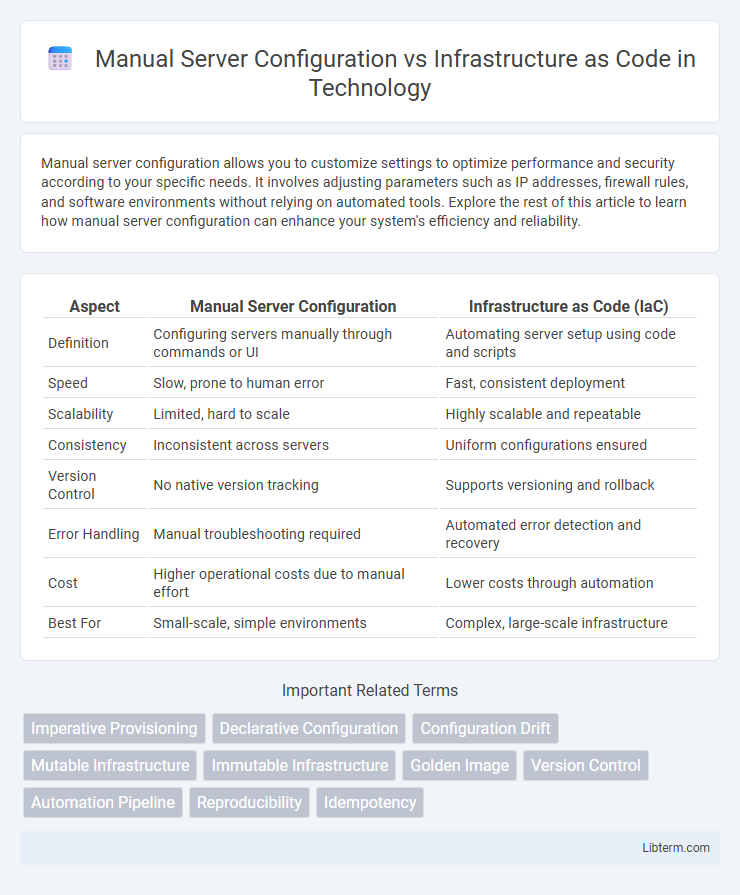
| Aspect | Manual Server Configuration | Infrastructure as Code (IaC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Configuring servers manually through commands or UI | Automating server setup using code and scripts |
| Speed | Slow, prone to human error | Fast, consistent deployment |
| Scalability | Limited, hard to scale | Highly scalable and repeatable |
| Consistency | Inconsistent across servers | Uniform configurations ensured |
| Version Control | No native version tracking | Supports versioning and rollback |
| Error Handling | Manual troubleshooting required | Automated error detection and recovery |
| Cost | Higher operational costs due to manual effort | Lower costs through automation |
| Best For | Small-scale, simple environments | Complex, large-scale infrastructure |
Introduction to Server Configuration Approaches
Manual server configuration involves direct, hands-on setup of hardware and software components, relying on administrator expertise for each server environment. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) automates this process using code templates and scripts, enabling consistent, repeatable, and scalable deployments across multiple servers. These contrasting approaches highlight the shift from error-prone, time-consuming manual tasks to efficient, automated infrastructure management using tools like Terraform, Ansible, and CloudFormation.
What is Manual Server Configuration?
Manual server configuration involves physically setting up and managing server hardware and software by system administrators through direct interaction with the server environment. This process includes installing operating systems, configuring network settings, updating software, and applying security patches without the use of automation tools. It often leads to inconsistencies, human errors, and difficulties in scaling compared to automated approaches like Infrastructure as Code.
What is Infrastructure as Code (IaC)?
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a modern IT practice that automates the provisioning and management of infrastructure through machine-readable configuration files rather than manual setup. IaC enables consistent, repeatable, and scalable deployments by defining resources like servers, networks, and storage using code, often with tools like Terraform, Ansible, or AWS CloudFormation. This approach reduces human errors, accelerates deployment times, and enhances collaboration across development and operations teams.
Key Differences: Manual Configuration vs IaC
Manual server configuration involves configuring systems through direct, manual intervention such as command-line inputs or graphical interfaces, leading to inconsistencies and human errors. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) uses version-controlled scripts to automate and standardize the deployment of infrastructure, enabling repeatability, scalability, and improved disaster recovery. Key differences include automation level, consistency, and ease of auditing, with IaC providing enhanced traceability compared to the error-prone and time-consuming manual setup.
Pros and Cons of Manual Server Configuration
Manual server configuration allows for granular control and immediate customization of server settings, making it suitable for small-scale or unique environments where automation may be excessive. However, it is prone to human error, lacks scalability, and can lead to inconsistent configurations across multiple servers, increasing maintenance complexity. Compared to Infrastructure as Code (IaC), manual processes are time-consuming and harder to document, limiting repeatability and automation potential.
Benefits of Adopting Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enables rapid, consistent server provisioning and configuration, significantly reducing human errors inherent in manual setups. By automating infrastructure deployment with tools like Terraform or Ansible, IaC enhances scalability, version control, and repeatability across cloud environments such as AWS and Azure. Organizations adopting IaC benefit from improved collaboration, faster recovery times, and streamlined compliance through auditable, codified infrastructure changes.
Common Tools for Infrastructure as Code
Popular tools for Infrastructure as Code include Terraform, Ansible, and AWS CloudFormation, widely recognized for automating server and infrastructure provisioning. These tools enable version control, automated deployment, and consistency across environments, reducing human errors compared to manual server configuration. Leveraging these solutions improves scalability, repeatability, and maintainability in modern cloud and on-premises infrastructure setups.
Automation, Scalability, and Consistency Comparison
Manual server configuration often leads to errors and inconsistencies due to its reliance on human intervention, limiting automation capabilities. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enables automated deployments, ensuring consistent environments and rapid scalability by defining infrastructure through version-controlled code. IaC dramatically reduces configuration drift and accelerates infrastructure provisioning, making it ideal for dynamic, large-scale environments.
Security Implications for Both Methods
Manual server configuration often increases the risk of human error, leading to inconsistent security settings and vulnerabilities due to lack of standardized enforcement. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enables automated, repeatable deployments with integrated security policies, enhancing compliance and reducing attack surfaces through version-controlled configurations. However, both methods require rigorous security audits and proper management of credentials to mitigate risks from misconfiguration or exposed secrets.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Manual server configuration offers granular control and immediate adjustments, suited for small-scale or legacy systems with limited automation needs. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) provides scalability, consistency, and version control by automating deployment through code, ideal for dynamic, large-scale cloud environments. Organizations should evaluate factors such as team expertise, infrastructure complexity, and deployment frequency to select the approach that best aligns with their operational goals and resource availability.
Manual Server Configuration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com