Row lock mechanisms provide secure and stable support for your rowing machine, enhancing workout safety and efficiency. They are essential for maintaining proper form and preventing machine movement during intense exercise sessions. Discover the benefits of choosing the right row lock and how it can improve your rowing experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
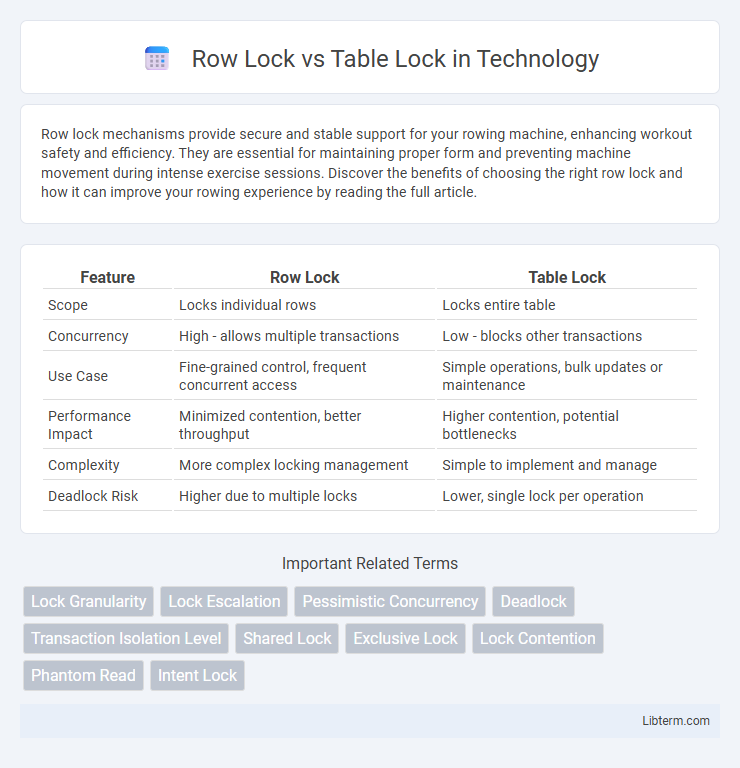
| Feature | Row Lock | Table Lock |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Locks individual rows | Locks entire table |
| Concurrency | High - allows multiple transactions | Low - blocks other transactions |
| Use Case | Fine-grained control, frequent concurrent access | Simple operations, bulk updates or maintenance |
| Performance Impact | Minimized contention, better throughput | Higher contention, potential bottlenecks |
| Complexity | More complex locking management | Simple to implement and manage |
| Deadlock Risk | Higher due to multiple locks | Lower, single lock per operation |
Introduction to Database Locking Mechanisms
Database locking mechanisms control concurrent data access to ensure transaction consistency and prevent conflicts. Row locks restrict access to individual records, allowing higher concurrency and minimizing contention, while table locks reserve the entire table, simplifying lock management but reducing parallelism. Effective use of row locks and table locks depends on workload characteristics, balancing performance and data integrity in multi-user environments.
Understanding Row Locks
Row locks restrict access to specific rows within a table, enabling multiple transactions to modify different rows concurrently without conflict. This lock type improves transaction throughput and reduces contention by allowing fine-grained control over data access. Understanding row locks is essential for optimizing database performance and maintaining data integrity in multi-user environments.
Exploring Table Locks
Table locks prevent multiple transactions from modifying or reading a table simultaneously, ensuring data consistency by locking the entire table during operations. In high-concurrency environments, table locks can cause significant contention and reduce performance due to blocking other queries until the lock is released. Understanding table locking mechanisms is crucial for optimizing database throughput and avoiding bottlenecks in applications with heavy read/write demands.
Key Differences Between Row Lock and Table Lock
Row locks restrict access to specific rows during transactions, allowing higher concurrency by letting multiple users modify different rows simultaneously. Table locks apply to the entire table, blocking access for other transactions until the lock is released, which can reduce concurrency but ensures data consistency for bulk operations. Row locks generally incur higher overhead compared to table locks, making table locks more suitable for operations that affect large portions of data.
Performance Impact: Row Lock vs Table Lock
Row locks improve database concurrency by allowing multiple transactions to access different rows simultaneously, reducing wait times and enhancing throughput. Table locks restrict access to the entire table, causing significant performance bottlenecks during high transaction volumes due to increased contention and longer wait periods. In systems with frequent updates or reads, row-level locking offers superior performance by minimizing lock contention and optimizing resource utilization.
Data Consistency and Concurrency Control
Row lock allows multiple transactions to access different rows of a table simultaneously, enhancing concurrency while maintaining data consistency by isolating changes at the row level. Table lock restricts access to the entire table, ensuring stronger data consistency during complex operations but significantly reducing concurrency by blocking other transactions. Effective concurrency control strategies balance the granularity of locks to optimize performance and maintain data integrity under concurrent workloads.
Use Cases: When to Use Row Locks
Row locks are ideal for high-concurrency environments where multiple transactions access different rows simultaneously, such as in online transaction processing (OLTP) systems. They enhance performance by minimizing lock contention and allowing finer granularity of data manipulation, making them suitable for applications like banking systems or e-commerce platforms handling numerous concurrent updates. Use row locks when precise data integrity is crucial without compromising system throughput and responsiveness.
Use Cases: When to Opt for Table Locks
Table locks are ideal for bulk operations such as batch updates, schema modifications, or data imports where concurrent access can be temporarily suspended to ensure data integrity. In environments with low concurrency or read-heavy workloads, table locks minimize overhead by avoiding the complexity of managing numerous row-level locks. Opting for table locks enhances performance during maintenance tasks and reduces the risk of deadlocks in scenarios requiring exclusive access to the entire table.
Best Practices for Efficient Lock Management
Implement fine-grained row locks to minimize contention and enhance concurrency, especially in high-transaction environments, whereas table locks should be reserved for bulk operations or maintenance tasks to avoid excessive blocking. Utilize lock escalation cautiously, monitoring databases like SQL Server or Oracle to prevent unnecessary escalation from row to table locks that degrade performance. Implement automated deadlock detection and timeout settings to optimize resource usage and ensure transaction efficiency while maintaining data integrity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Locking Strategy
Selecting the appropriate locking strategy depends on the specific database workload and concurrency requirements, with row locks offering finer granularity and better throughput for high-concurrency environments by locking individual rows. Table locks provide a simpler, more efficient option for bulk operations or scenarios with low contention, minimizing overhead but reducing parallelism. Balancing the trade-offs between data consistency, performance, and concurrency control is essential for optimizing database locking strategies.
Row Lock Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com