Artificial Intelligence revolutionizes industries by enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. This technology enhances efficiency, accuracy, and innovation across various sectors, from healthcare to finance. Explore the rest of the article to discover how AI can transform your world and what future advancements lie ahead.
Table of Comparison
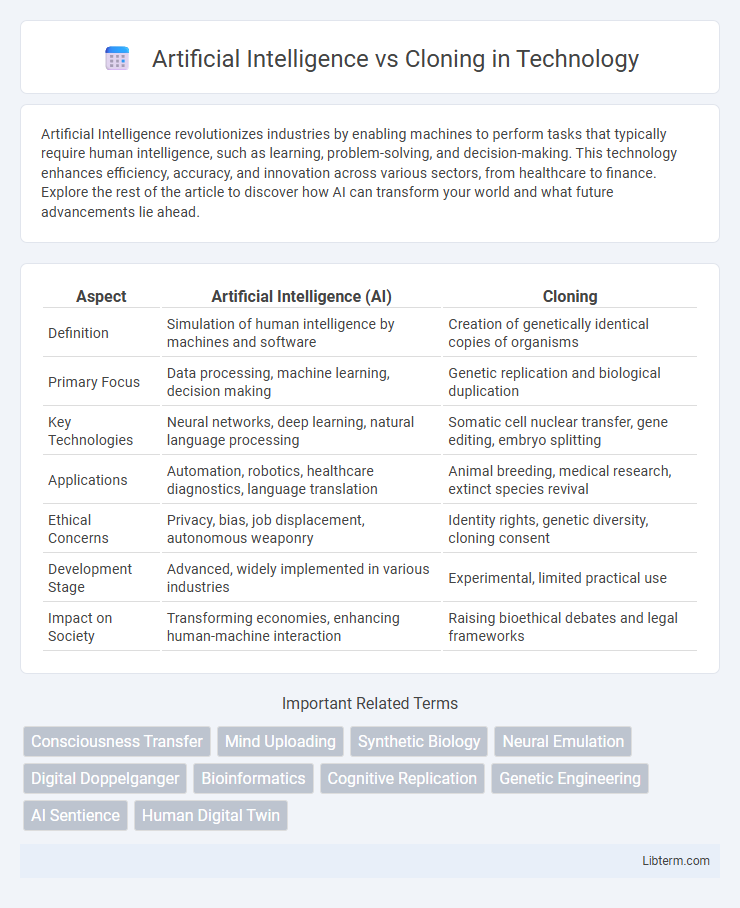
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Cloning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simulation of human intelligence by machines and software | Creation of genetically identical copies of organisms |
| Primary Focus | Data processing, machine learning, decision making | Genetic replication and biological duplication |
| Key Technologies | Neural networks, deep learning, natural language processing | Somatic cell nuclear transfer, gene editing, embryo splitting |
| Applications | Automation, robotics, healthcare diagnostics, language translation | Animal breeding, medical research, extinct species revival |
| Ethical Concerns | Privacy, bias, job displacement, autonomous weaponry | Identity rights, genetic diversity, cloning consent |
| Development Stage | Advanced, widely implemented in various industries | Experimental, limited practical use |
| Impact on Society | Transforming economies, enhancing human-machine interaction | Raising bioethical debates and legal frameworks |
Understanding Artificial Intelligence: Definition and Scope
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, including learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and natural language processing. The scope of AI encompasses machine learning, neural networks, robotics, and computer vision, enabling automation and decision-making across various industries. Unlike cloning, which involves creating genetically identical organisms, AI focuses on simulating cognitive functions through algorithms and data-driven models.
Cloning Explained: Concepts and Ethical Dilemmas
Cloning involves creating genetically identical copies of organisms or cells, employing techniques like somatic cell nuclear transfer to replicate DNA precisely. Ethical dilemmas surrounding cloning include concerns about identity, individuality, and potential harm to clones, raising debates about human rights and the moral implications of recreating life. The scientific promise of cloning for medical therapies contrasts sharply with societal worries about misuse and the consequences of tampering with natural biological processes.
Core Differences: AI vs. Cloning Technologies
Artificial Intelligence involves creating algorithms and systems that simulate human intelligence through data processing and machine learning, whereas cloning focuses on producing genetically identical organisms using biological and genetic replication techniques. AI emphasizes computational models and software-driven decision-making, while cloning is rooted in molecular biology and DNA manipulation. The core difference lies in AI's synthetic cognition capabilities versus cloning's replication of biological entities.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Society
Artificial Intelligence drives innovation in sectors like healthcare, finance, and transportation by enabling predictive analytics, automated decision-making, and personalized user experiences. AI-powered technologies such as machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and computer vision transform industries through enhanced efficiency, improved diagnostics, and autonomous systems. These applications accelerate advancements in smart cities, medical imaging, fraud detection, and autonomous vehicles, significantly shaping modern society's technological landscape.
Cloning in Medicine and Agriculture: Current Uses
Cloning in medicine enables the reproduction of genetically identical cells and tissues for regenerative therapies and organ transplantation, improving treatment outcomes for diseases like Parkinson's and diabetes. In agriculture, cloning ensures the propagation of high-yield, disease-resistant livestock and crops, enhancing food security and farming efficiency. Current applications focus on therapeutic cloning for personalized medicine and agricultural cloning for sustainable production and genetic conservation.
Ethical Concerns: AI versus Cloning
Ethical concerns surrounding artificial intelligence center on issues like privacy invasion, algorithmic bias, and the potential loss of human autonomy, raising debates about accountability and surveillance. In cloning, ethical dilemmas focus on identity, the morality of replicating life, and the implications of genetic manipulation on individuality and biodiversity. Both fields challenge societal norms by questioning the limits of human intervention in natural processes and the definition of personhood.
Human Identity: Impacts of AI and Cloning
Artificial Intelligence challenges human identity by enabling machines to mimic cognitive functions, raising questions about consciousness and self-awareness. Cloning directly confronts individuality by replicating genetic material, complicating concepts of uniqueness and personal identity. Both technologies provoke ethical debates on what it means to be human in an era where artificial and biological boundaries blur.
Legal Frameworks Governing AI and Cloning
Legal frameworks governing Artificial Intelligence prioritize data privacy, algorithmic accountability, and ethical use, enforcing regulations such as the GDPR in the EU and the AI Act's provisions for transparency and risk management. In contrast, cloning legislation centers on bioethics, genetic safety, and human rights protections, with strict bans or regulatory controls found in countries like the United States under the Dickey-Wicker Amendment and international agreements like the Oviedo Convention. Both domains require evolving legal standards to address rapid technological advancements while balancing innovation with societal and moral responsibilities.
Future Potential: AI and Cloning Innovations
Artificial intelligence advancements are rapidly enhancing automation, data processing, and decision-making capabilities, promising breakthroughs in healthcare, robotics, and personalized technology. Cloning innovations hold transformative potential in regenerative medicine, species preservation, and genetic research, enabling new approaches to organ transplantation and biodiversity conservation. The convergence of AI and cloning technologies may accelerate future innovations, driving unprecedented progress in bioengineering and synthetic biology.
Society’s Choice: Balancing Progress and Morality
Society faces complex ethical dilemmas when balancing progress in artificial intelligence and cloning, as both technologies offer transformative benefits yet raise profound moral questions about identity, privacy, and human dignity. The advancement of AI challenges norms around decision-making autonomy and surveillance, while cloning provokes debates on individuality and the sanctity of life. Effective regulation and public discourse are essential to navigate these tensions, ensuring technological innovation aligns with societal values and human rights.
Artificial Intelligence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com