DNS Unicast ensures direct communication between DNS servers using a single IP address, enhancing the reliability of name resolution. This method reduces the complexity found in multicast DNS by simplifying traffic flow and improving network performance. Discover how DNS Unicast can optimize your network's efficiency by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
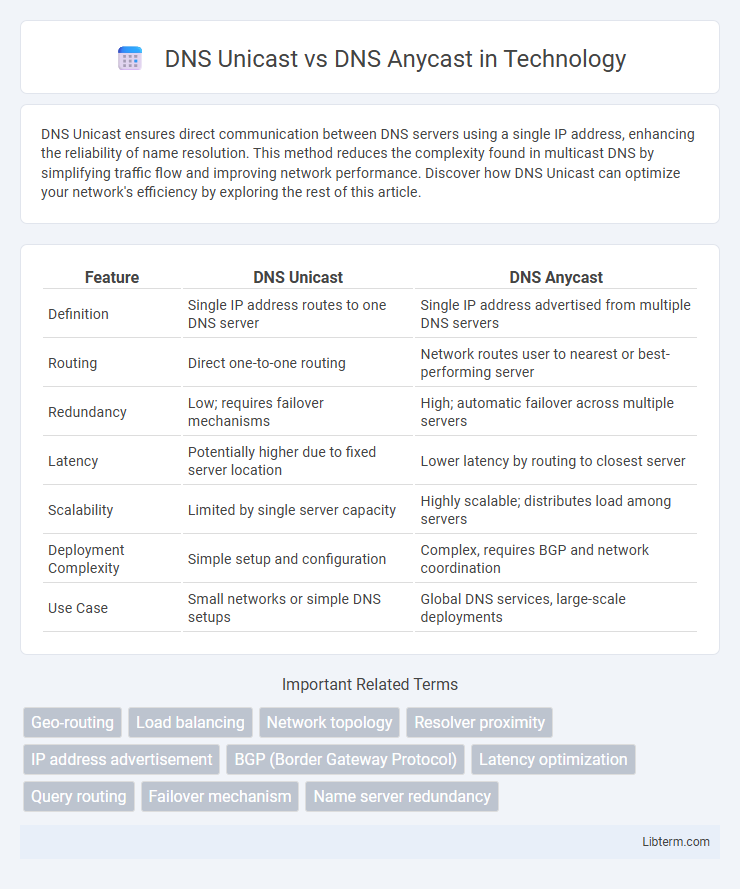
| Feature | DNS Unicast | DNS Anycast |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single IP address routes to one DNS server | Single IP address advertised from multiple DNS servers |
| Routing | Direct one-to-one routing | Network routes user to nearest or best-performing server |
| Redundancy | Low; requires failover mechanisms | High; automatic failover across multiple servers |
| Latency | Potentially higher due to fixed server location | Lower latency by routing to closest server |
| Scalability | Limited by single server capacity | Highly scalable; distributes load among servers |
| Deployment Complexity | Simple setup and configuration | Complex, requires BGP and network coordination |
| Use Case | Small networks or simple DNS setups | Global DNS services, large-scale deployments |
Introduction to DNS Unicast and Anycast
DNS Unicast involves assigning a single IP address to a DNS server, directing all queries for a domain to that specific server, which can lead to slower response times and a single point of failure. DNS Anycast assigns the same IP address to multiple servers distributed globally, allowing queries to be routed to the nearest or fastest server, enhancing performance and redundancy. This approach improves DNS query resolution speed and resilience by leveraging geographic distribution and routing protocols.
How DNS Unicast Works
DNS Unicast directs queries to a single, specific server IP address, ensuring that all DNS requests are handled by that particular node. This method establishes a one-to-one relationship between the client and the DNS server, relying on server responsiveness and network latency to maintain performance. Unicast DNS is straightforward but can become a bottleneck during high traffic or server failure, lacking the load distribution and redundancy features inherent in anycast configurations.
How DNS Anycast Functions
DNS Anycast functions by assigning the same IP address to multiple DNS servers distributed across different geographic locations, enabling user queries to be routed to the nearest or fastest server based on network topology and routing protocols. This method enhances DNS response times, reduces latency, and improves redundancy by allowing the Domain Name System infrastructure to handle high traffic loads and mitigate distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Unlike DNS Unicast, which directs queries to a single IP address and server, Anycast ensures more efficient load balancing and fault tolerance within DNS services.
Key Differences Between DNS Unicast and Anycast
DNS Unicast directs queries to a single, specific server IP address ensuring targeted and straightforward resolution, while DNS Anycast uses multiple geographically dispersed servers sharing the same IP address to route queries to the nearest or best-performing node. Unicast offers simplicity and precise control but can create single points of failure, whereas Anycast enhances redundancy, load balancing, and reduced latency by distributing traffic across multiple servers. The key differences lie in network architecture, fault tolerance, and performance optimization, with Anycast providing improved scalability and resilience compared to the single-target nature of Unicast.
Advantages of Using DNS Unicast
DNS unicast ensures precise control over server responses by directing queries to a specific, unique IP address, enhancing predictability and troubleshooting efficiency. It simplifies network management by allowing administrators to configure and monitor a single server endpoint without the complexities of multiple routing paths. This method offers stable and consistent latency, ideal for applications requiring reliable and steady DNS resolution.
Benefits of DNS Anycast Deployment
DNS Anycast deployment enhances global DNS query resolution by routing user requests to the nearest or best-performing DNS server, reducing latency and improving response times. It increases redundancy and fault tolerance since multiple servers share the same IP address, ensuring continuous DNS service even during server outages or DDoS attacks. By distributing traffic efficiently, DNS Anycast minimizes network congestion and bolsters overall DNS infrastructure resilience compared to traditional Unicast configurations.
Performance Comparison: Unicast vs Anycast
DNS Anycast improves performance by routing user queries to the nearest DNS server, reducing latency and enhancing load distribution across multiple servers. DNS Unicast directs queries to a single specific server address, which can lead to higher latency during peak traffic or server outages. Anycast's ability to provide faster query responses and improved redundancy in global DNS infrastructure makes it a preferred choice for large-scale, high-availability environments.
Security Implications for Each Approach
DNS Unicast routes queries to a single, specific IP address, making it simpler to monitor and secure but vulnerable to targeted DDoS attacks and single points of failure. DNS Anycast distributes traffic across multiple geographically dispersed servers sharing the same IP, enhancing resilience and mitigating DDoS impacts but complicating source verification and increasing risks from route hijacking or BGP attacks. Effective security for Anycast requires strong network-level protections and continuous traffic anomaly detection, while Unicast demands robust endpoint security and failover mechanisms.
Use Cases and Real-World Applications
DNS Unicast delivers queries to a single, specific IP address, making it ideal for environments requiring precise control and straightforward traffic management, such as small business networks with a centralized DNS server. DNS Anycast routes queries to the nearest or best-performing server based on network topology, optimizing response times and load distribution, which is essential for global content delivery networks (CDNs) and large-scale public DNS services like Google Public DNS and Cloudflare. Enterprises leverage DNS Anycast for improved redundancy and DDoS mitigation, while DNS Unicast suits simpler setups with predictable traffic patterns and localized infrastructure.
Choosing the Right DNS Architecture for Your Needs
Choosing the right DNS architecture depends on factors like geographic distribution, latency requirements, and redundancy needs. DNS Unicast directs queries to a single, specific server IP address, offering simplicity but limited fault tolerance. DNS Anycast routes queries to the nearest or best-performing server from multiple nodes sharing the same IP, improving load balancing, resilience, and response times for globally distributed users.
DNS Unicast Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com