The PACELC theorem extends the CAP theorem by considering system behavior during both network partitions and normal operation, emphasizing trade-offs between latency and consistency even when no partition occurs. It highlights how distributed systems must balance these factors to optimize performance and reliability based on specific application requirements. Discover how PACELC principles affect your system design and decision-making by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
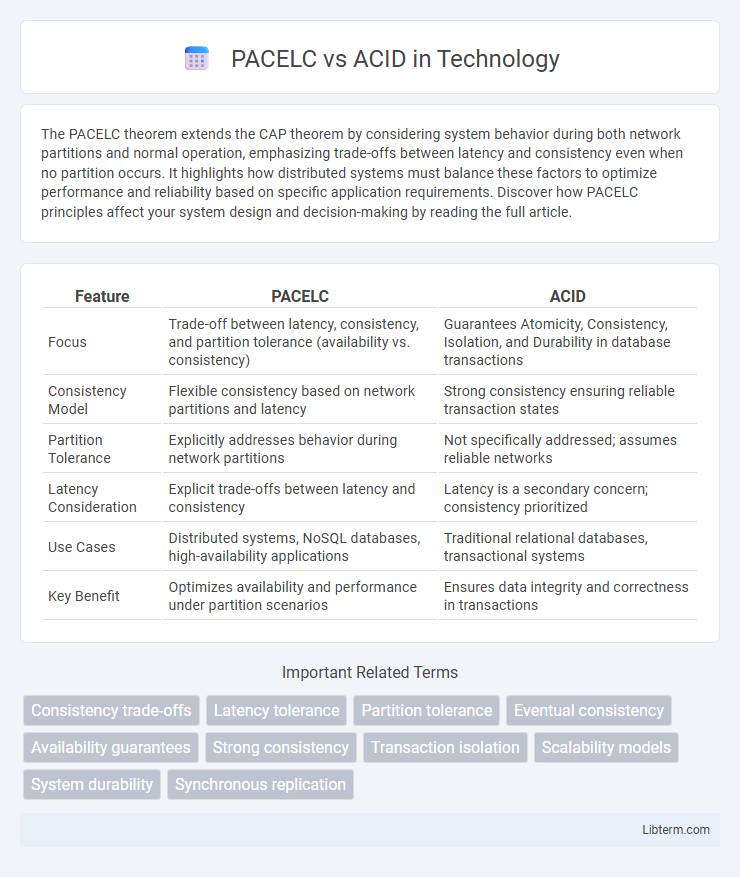
| Feature | PACELC | ACID |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Trade-off between latency, consistency, and partition tolerance (availability vs. consistency) | Guarantees Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability in database transactions |
| Consistency Model | Flexible consistency based on network partitions and latency | Strong consistency ensuring reliable transaction states |
| Partition Tolerance | Explicitly addresses behavior during network partitions | Not specifically addressed; assumes reliable networks |
| Latency Consideration | Explicit trade-offs between latency and consistency | Latency is a secondary concern; consistency prioritized |
| Use Cases | Distributed systems, NoSQL databases, high-availability applications | Traditional relational databases, transactional systems |
| Key Benefit | Optimizes availability and performance under partition scenarios | Ensures data integrity and correctness in transactions |
Introduction to PACELC and ACID
PACELC and ACID are foundational models in distributed database theory, defining consistency, availability, and partition tolerance trade-offs. ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) guarantees reliable transactions in traditional databases through strict consistency and isolation. PACELC extends CAP theorem by addressing latency in normal operations, stating "if a Partition occurs, choose between Availability and Consistency; Else choose between Latency and Consistency.
Understanding the PACELC Model
The PACELC model extends the CAP theorem by addressing latency and consistency trade-offs during network partitions and normal operation, emphasizing that systems balance between consistency and latency both when partitions occur and when they don't. Unlike ACID, which ensures atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability within a single transaction, PACELC evaluates distributed systems' consistency and availability across different states. Understanding PACELC helps architects design databases that optimize for latency or consistency depending on system requirements and network conditions.
The Fundamentals of the ACID Properties
The ACID properties--Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability--define the fundamental principles ensuring reliable database transactions by guaranteeing complete success or failure, maintaining data integrity, preventing concurrent access conflicts, and safeguarding data against system failures. PACELC extends the CAP theorem by emphasizing the trade-offs between latency and consistency not only during network partitions but also in normal operation. Understanding ACID is crucial for evaluating transaction reliability, while PACELC provides a broader perspective on system behavior under varying availability and consistency demands.
Key Differences Between PACELC and ACID
PACELC and ACID are fundamental models for understanding distributed database consistency and reliability, with PACELC addressing trade-offs between latency, consistency, and partition tolerance, while ACID focuses on atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability within single-node transactions. PACELC expands upon the CAP theorem by incorporating latency and consistency trade-offs even outside network partitions, making it crucial for distributed systems performance optimization. ACID ensures data integrity during transactions but may sacrifice availability and latency in distributed environments where PACELC provides a more holistic framework for balancing these factors.
Strengths and Weaknesses of PACELC
PACELC offers a more nuanced approach than ACID by addressing trade-offs not only during network partitions but also in latency and consistency under normal operations, enabling better optimization for distributed database performance. Its strength lies in balancing availability, consistency, and latency based on specific application requirements across various states, making it ideal for highly distributed systems with complex consistency needs. However, PACELC's complexity can introduce challenges in design and implementation, as developers must carefully choose trade-offs that suit their workload, which may lead to increased system complexity compared to the straightforward guarantees of ACID properties.
Advantages and Limitations of ACID
ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) ensures reliable transaction processing with strong data integrity and fault tolerance, making it ideal for systems requiring strict consistency and correctness, such as banking or financial applications. Its limitations include reduced scalability and performance in distributed systems due to the need for strict locking and synchronization, which can lead to increased latency and resource contention. In contrast, PACELC addresses trade-offs between latency and consistency in distributed databases but may sacrifice strong consistency to achieve higher availability and partition tolerance.
Use Cases for PACELC vs ACID
PACELC is ideal for distributed databases requiring high availability and low latency, balancing consistency during partition (P) and latency under normal conditions (ELC), making it suitable for real-time applications like online gaming and financial trading. ACID transactions provide strict consistency, atomicity, isolation, and durability, which are crucial for traditional relational databases used in banking systems and order processing where data integrity is paramount. Use cases requiring flexible trade-offs between consistency and performance benefit from PACELC, while those demanding absolute consistency and fault tolerance rely on ACID compliance.
Choosing the Right Consistency Model
Choosing the right consistency model involves understanding PACELC and ACID trade-offs in distributed databases. PACELC emphasizes latency and consistency during partitions and normal operation, categorizing systems by trade-offs made in these conditions. In contrast, ACID focuses on atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability within single-node transactions, making PACELC more relevant for distributed system consistency choices.
Real-World Database Examples
PACELC and ACID are critical models for understanding database consistency and availability in distributed systems. Amazon DynamoDB exemplifies PACELC by prioritizing availability and partition tolerance while making latency trade-offs during normal operation, contrasting with traditional ACID-compliant systems like PostgreSQL, which emphasize strong consistency and atomicity. Cassandra demonstrates PACELC's flexibility by allowing tunable consistency levels to balance latency and consistency based on application needs, diverging from ACID's strict transaction guarantees found in relational databases such as Oracle DB.
Conclusion: PACELC or ACID for Your Application
Choosing between PACELC and ACID depends on your application's specific needs for consistency, availability, and latency under network partitions. PACELC provides more flexibility by addressing trade-offs during normal operation and failures, making it ideal for distributed, high-availability systems. ACID ensures strong consistency and transactional integrity, which suits applications requiring strict data accuracy and reliability.
PACELC Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com