A honeypot is a cybersecurity mechanism designed to attract and trap malicious actors by mimicking vulnerable systems, thus gathering critical data on attack methods and sources. This proactive defense strategy enhances your network's security by identifying threats before they cause real damage. Explore the rest of the article to learn how honeypots can fortify your cyber defenses effectively.
Table of Comparison
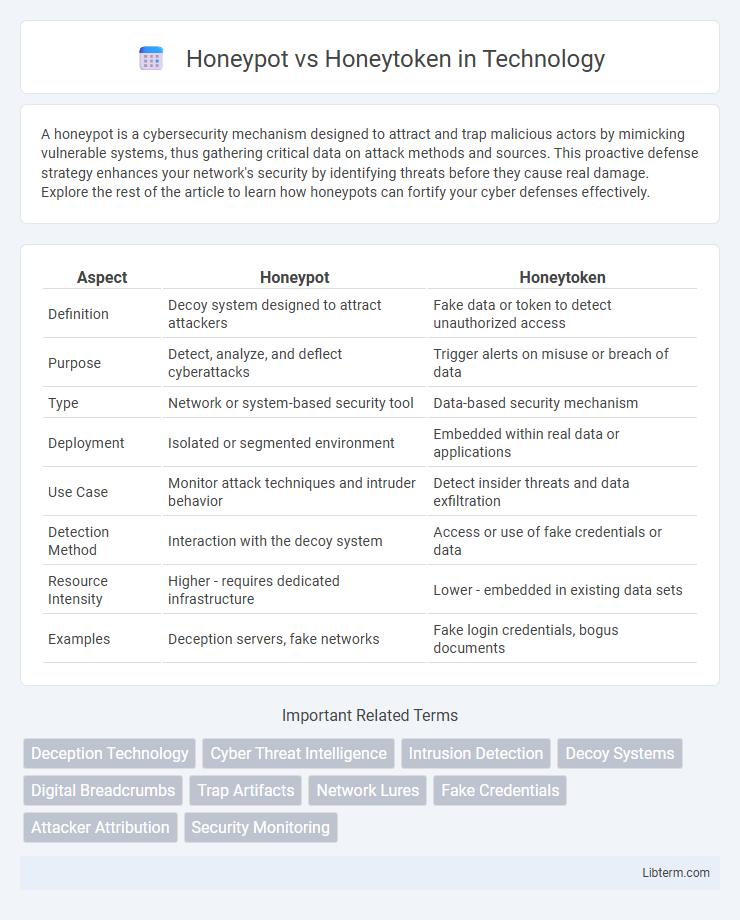
| Aspect | Honeypot | Honeytoken |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decoy system designed to attract attackers | Fake data or token to detect unauthorized access |
| Purpose | Detect, analyze, and deflect cyberattacks | Trigger alerts on misuse or breach of data |
| Type | Network or system-based security tool | Data-based security mechanism |
| Deployment | Isolated or segmented environment | Embedded within real data or applications |
| Use Case | Monitor attack techniques and intruder behavior | Detect insider threats and data exfiltration |
| Detection Method | Interaction with the decoy system | Access or use of fake credentials or data |
| Resource Intensity | Higher - requires dedicated infrastructure | Lower - embedded in existing data sets |
| Examples | Deception servers, fake networks | Fake login credentials, bogus documents |
Introduction to Honeypot and Honeytoken
Honeypots are cybersecurity traps designed to mimic vulnerable systems, attracting attackers and analyzing their behavior to improve network defenses. Honeytokens are strategically placed fake data or credentials that alert security teams upon unauthorized use, serving as early warning signals for compromised environments. Both honeypots and honeytokens play crucial roles in threat detection and incident response by deceiving attackers and gathering intelligence.
What is a Honeypot?
A honeypot is a cybersecurity mechanism designed to mimic a real system or network to attract attackers and detect unauthorized access. It collects data on hacking attempts, allowing organizations to analyze attack methods and improve defense strategies. Unlike honeytokens, which are discrete pieces of data such as fake credentials or files, honeypots provide an interactive environment to monitor adversary behavior in real time.
What is a Honeytoken?
A honeytoken is a digital or physical bait designed to detect unauthorized access by triggering alerts when accessed or used illicitly. Unlike honeypots, which are entire decoy systems or networks mimicking real environments, honeytokens are individual data elements such as fake credentials, documents, or database records embedded strategically to identify insider threats or external breaches. Honeytokens provide granular insight into attacker behavior and can be integrated seamlessly into existing systems for proactive threat detection.
Core Differences Between Honeypot and Honeytoken
Honeypots are decoy systems or networks designed to attract cyber attackers and study their behavior by simulating real resources, whereas honeytokens are digital artifacts such as fake credentials or documents embedded within systems to detect unauthorized access. Honeypots actively engage attackers by providing an interactive environment, while honeytokens are passive triggers that alert defenders upon use or access. Core differences lie in deployment scope, with honeypots mimicking entire systems and honeytokens targeting localized assets to enhance threat detection and incident response.
Use Cases for Honeypots
Honeypots are primarily used in cybersecurity to attract and analyze malicious activities by mimicking vulnerable systems, enabling organizations to detect, study, and mitigate threats in real time. Common use cases include early threat detection, incident response training, and gathering intelligence on attacker methods, tools, and behaviors. Unlike honeytokens, which are digital traps like fake credentials or database entries, honeypots involve interactive systems that simulate real network environments for deeper attacker engagement.
Use Cases for Honeytokens
Honeytokens serve as deceptive data tokens that alert organizations to unauthorized access by mimicking valuable or sensitive information such as fake credentials, documents, or database entries. Use cases for honeytokens include detecting insider threats by embedding fake user accounts or triggering alerts when decoy API keys are used, enabling early warning for data breaches or malicious activities. Deploying honeytokens in cloud environments or databases improves threat intelligence by providing actionable insights into attacker behavior without exposing real assets.
Advantages of Honeypots
Honeypots provide a controlled environment to attract and analyze cyber attackers, enabling security teams to identify attack patterns and tools in real time. They offer detailed intelligence on malicious behavior without affecting production systems, enhancing proactive threat detection and response capabilities. By diverting attackers, honeypots reduce risks to critical assets and strengthen overall network defense strategies.
Benefits of Honeytokens
Honeytokens offer targeted threat detection by embedding deceptive data elements such as fake credentials or files within real systems, enabling precise identification of unauthorized access without deploying full-scale decoys. They enhance security visibility by triggering alerts when malicious actors interact with these planted items, reducing false positives common in traditional honeypot setups. This low-maintenance approach integrates seamlessly into existing environments, providing early warning signs and forensic value that help organizations quickly respond to insider threats and external breaches.
Limitations and Risks of Each Approach
Honeypots face limitations such as high maintenance costs and risk of becoming attack targets, potentially exposing sensitive network information if improperly isolated. Honeytokens, while easier to deploy, risk false positives that can lead to alert fatigue and may be detected and bypassed by sophisticated attackers. Both strategies require careful implementation to balance detection effectiveness against the potential for introducing new vulnerabilities.
Choosing the Right Deception Technique
Selecting between a honeypot and a honeytoken depends on the specific security goals and infrastructure of an organization. Honeypots are designed as decoy systems that attract attackers to analyze their tactics, while honeytokens are discrete data artifacts embedded within legitimate environments to detect unauthorized access or data breaches. Evaluating factors such as deployment complexity, monitoring capabilities, and the desired granularity of threat intelligence helps determine the most effective deception technique for enhanced cybersecurity defense.
Honeypot Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com