Replication ensures data consistency and availability by creating exact copies of information across multiple servers or locations. This process safeguards against data loss and enhances system reliability, crucial for business continuity. Discover how effective replication strategies can protect Your data and improve system performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
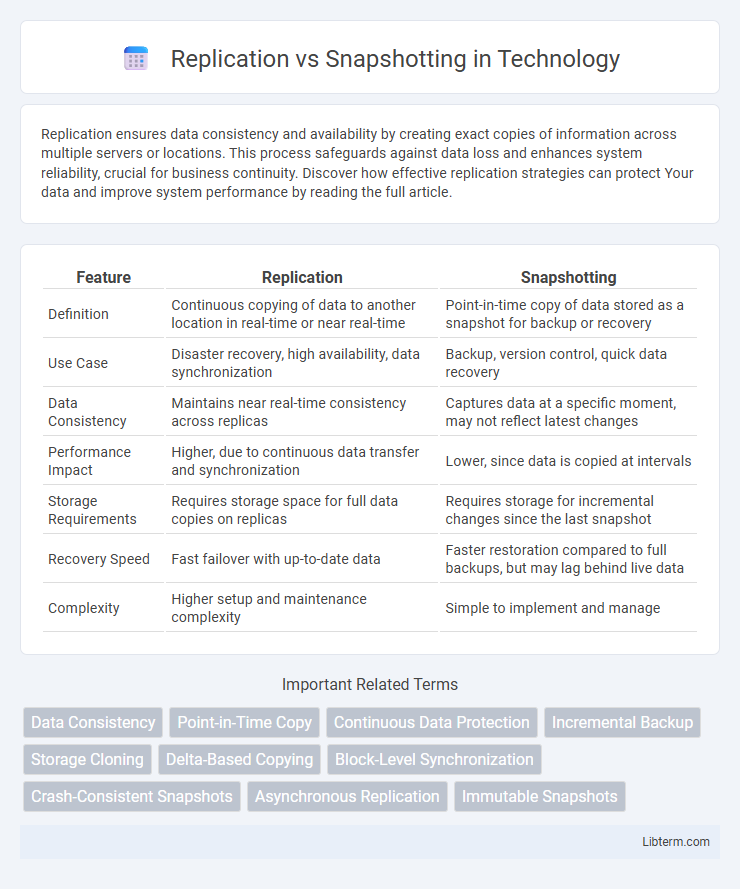
| Feature | Replication | Snapshotting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous copying of data to another location in real-time or near real-time | Point-in-time copy of data stored as a snapshot for backup or recovery |
| Use Case | Disaster recovery, high availability, data synchronization | Backup, version control, quick data recovery |
| Data Consistency | Maintains near real-time consistency across replicas | Captures data at a specific moment, may not reflect latest changes |
| Performance Impact | Higher, due to continuous data transfer and synchronization | Lower, since data is copied at intervals |
| Storage Requirements | Requires storage space for full data copies on replicas | Requires storage for incremental changes since the last snapshot |
| Recovery Speed | Fast failover with up-to-date data | Faster restoration compared to full backups, but may lag behind live data |
| Complexity | Higher setup and maintenance complexity | Simple to implement and manage |
Understanding Data Replication
Data replication involves continuously copying data from one database or server to another to ensure consistency and availability across systems. This process supports real-time data synchronization, disaster recovery, and load balancing, making it crucial for high-availability environments. Unlike snapshotting, which captures a static point-in-time copy, replication maintains an ongoing, dynamic data flow between sources.
What is Data Snapshotting?
Data snapshotting captures the exact state of a dataset at a specific point in time, creating a read-only copy that preserves consistency and facilitates quick data recovery. Unlike replication, which continuously duplicates data across systems for redundancy and high availability, snapshotting stores a static image useful for backup and archival purposes. This method minimizes performance impact on the original data source by using techniques like copy-on-write or redirect-on-write.
Key Differences Between Replication and Snapshotting
Replication involves continuously copying data in real-time or near-real-time to ensure high availability and disaster recovery, often used in databases and storage systems. Snapshotting captures the state of a system or dataset at a specific point in time, enabling quick rollback or backup without ongoing data duplication. Replication supports immediate failover with synchronized data, while snapshotting provides historical versions for recovery and auditing purposes.
Use Cases for Replication
Replication is essential for disaster recovery and high availability by continuously copying data to multiple locations, ensuring minimal downtime in case of system failure. It supports load balancing and scalability by distributing read operations across replicated servers, enhancing performance for large-scale applications. In contrast to snapshotting, which captures point-in-time data states for backups or testing, replication maintains real-time data synchronization for operational continuity.
Use Cases for Snapshotting
Snapshotting is ideal for backup and recovery scenarios, enabling quick restoration points without interrupting ongoing operations. It efficiently supports test and development environments by creating exact, consistent copies of data for experimentation or updates. Snapshots also facilitate data archiving and compliance by preserving system states at specific moments for auditing and historical analysis.
Performance Impact: Replication vs Snapshotting
Replication maintains real-time data synchronization, often resulting in higher network and system resource consumption due to continuous data transfers, which may impact performance during heavy transaction loads. Snapshotting captures data states at specific intervals, minimizing immediate performance overhead but introducing latency in data availability and potential storage spikes during snapshot creation. Choosing between replication and snapshotting depends on balancing the need for up-to-date data access against acceptable resource utilization and storage efficiency.
Data Consistency and Availability Comparison
Replication ensures high data availability by continuously copying data across multiple nodes, maintaining strong consistency especially in synchronous configurations. Snapshotting captures data states at specific points in time, providing quick recovery options but potentially introducing data inconsistency between snapshots due to asynchronous updates. While replication supports real-time data consistency and availability, snapshotting optimizes recovery speed with occasional consistency trade-offs.
Cost Implications in Replication and Snapshotting
Replication typically incurs higher costs due to continuous data transfer, increased storage requirements, and ongoing network usage, especially in multi-site setups. Snapshotting reduces expenses by capturing incremental data changes at specific intervals, minimizing storage consumption and bandwidth use. However, frequent snapshots can lead to storage overhead, making it essential to balance snapshot frequency with resource allocation for cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Replication continuously copies data from a primary source to a secondary location, ensuring real-time synchronization for disaster recovery and high availability. Snapshotting captures point-in-time copies of data, offering efficient storage and quick restoration for backup and version control. Choosing between replication and snapshotting depends on your requirements for data currency, recovery speed, storage capacity, and system complexity to optimize performance and resource utilization.
Future Trends in Data Backup and Recovery
Replication and snapshotting are evolving with advancements in cloud computing and AI-driven automation, enhancing real-time data protection and reducing recovery point objectives (RPOs). Future trends emphasize continuous data replication combined with instant snapshotting to enable near-zero downtime disaster recovery and improved data integrity. Integration of machine learning algorithms will optimize backup scheduling and anomaly detection, making data backup and recovery more resilient and efficient.
Replication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com