A VPN encrypts your internet connection, ensuring online privacy and protecting sensitive data from hackers and surveillance. It allows you to access restricted content by masking your IP address and bypassing geo-blocks. Discover how a VPN can enhance your digital security and freedom by reading the rest of the article.
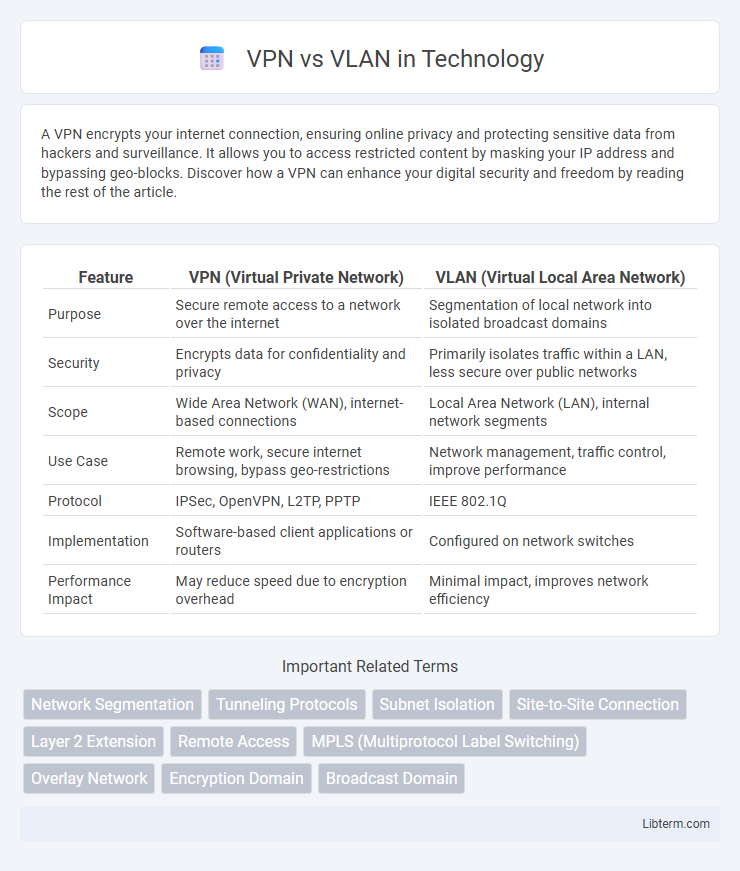
Table of Comparison
| Feature | VPN (Virtual Private Network) | VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Secure remote access to a network over the internet | Segmentation of local network into isolated broadcast domains |
| Security | Encrypts data for confidentiality and privacy | Primarily isolates traffic within a LAN, less secure over public networks |
| Scope | Wide Area Network (WAN), internet-based connections | Local Area Network (LAN), internal network segments |
| Use Case | Remote work, secure internet browsing, bypass geo-restrictions | Network management, traffic control, improve performance |
| Protocol | IPSec, OpenVPN, L2TP, PPTP | IEEE 802.1Q |
| Implementation | Software-based client applications or routers | Configured on network switches |
| Performance Impact | May reduce speed due to encryption overhead | Minimal impact, improves network efficiency |
Introduction to VPN and VLAN
VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates a secure, encrypted connection over the internet, enabling private communication between remote devices and networks. VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) segments a physical network into multiple logical networks, improving security and traffic management within the same infrastructure. Both technologies enhance network security but serve different purposes: VPN protects data over public networks, while VLAN organizes internal network traffic.
Core Differences Between VPN and VLAN
VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates secure, encrypted connections over public networks to ensure privacy and remote access, while VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) segments a physical network into multiple logical networks to improve performance and security within a local environment. VPN operates at the network layer by tunneling data across the internet, whereas VLAN functions at the data link layer by tagging Ethernet frames for traffic separation. The core difference lies in VPN's role in extending secure private networks over wide area connections, contrasted with VLAN's focus on traffic isolation and network management within localized infrastructure.
How VPNs Work: Key Features Explained
VPNs create secure, encrypted tunnels over public networks to connect remote users or sites, ensuring data privacy and protection from cyber threats. Key features include authentication protocols, encryption standards like AES-256, and secure tunneling methods such as OpenVPN or IPsec. These elements work together to maintain confidentiality, integrity, and secure access to private networks from anywhere in the world.
How VLANs Work: Essential Concepts
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) segment a physical network into multiple logical networks by assigning devices to different broadcast domains, enhancing security and traffic management. Each VLAN is identified by a unique VLAN ID, enabling switches to tag and isolate traffic using IEEE 802.1Q protocol. This segmentation reduces network congestion and improves performance by limiting broadcast traffic to devices within the same VLAN.
Security Implications: VPN vs VLAN
VPNs create encrypted tunnels over public networks, ensuring secure remote access by protecting data confidentiality and integrity from external threats. VLANs segment network traffic within a local environment to reduce broadcast domains and limit access but lack inherent encryption, making them vulnerable to internal attacks if the network is compromised. For robust security, combining VPN encryption with VLAN segmentation offers comprehensive protection against both external and internal threats.
Use Cases: When to Choose VPN or VLAN
VPNs are ideal for securely connecting remote users or branch offices over the internet, providing encrypted access to corporate networks and protecting data from interception. VLANs are best suited for segmenting local area networks within an organization to enhance security, manage traffic, and isolate sensitive data or departments. Choose VPN when secure, encrypted communication between geographically dispersed locations is needed, and opt for VLAN when optimizing network performance and segmentation within a single physical infrastructure.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
VPNs deliver secure remote access by encrypting data, which can introduce latency and reduce overall throughput, affecting performance especially on high-traffic networks. VLANs enhance local network efficiency by segmenting traffic within the same physical infrastructure, minimizing broadcast domains and improving scalability for large enterprise environments. While VPN scalability depends on encryption overhead and server capacity, VLAN scalability relies on switch hardware limits and network design complexity, making VLANs generally more efficient for internal segmentation but VPNs essential for secure external connectivity.
Cost Considerations: VPN vs VLAN
VPNs generally offer lower upfront costs as they utilize existing internet infrastructure, making them cost-effective for remote connectivity without the need for dedicated hardware. VLANs require investments in managed network switches and ongoing maintenance, leading to higher initial expenses but providing enhanced internal network segmentation and security. Businesses must weigh the operational savings of VPNs against the infrastructure costs of VLANs based on their scale and security requirements.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
VPN implementation challenges include complex configuration, ensuring robust encryption, and managing latency across dispersed networks. Solutions involve deploying automated configuration tools, adopting advanced encryption standards like AES-256, and optimizing routing protocols to minimize latency. VLAN implementation difficulties stem from VLAN sprawl, misconfiguration risks, and troubleshooting segmentation issues, addressed through consistent VLAN documentation, automated configuration management, and enhanced network monitoring tools.
VPN vs VLAN: Which is Right for Your Network?
VPN and VLAN serve distinct functions in network management, with VPN providing secure remote access by encrypting internet connections, ideal for safeguarding data over public networks. VLAN segments a local network into separate, isolated broadcast domains, enhancing internal network efficiency and security without encrypting data. Choosing between VPN and VLAN depends on your network requirements: VPN suits remote access and secure communication across the internet, while VLAN optimizes local traffic management and internal network segmentation.
VPN Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com