Authorization is the process of granting or denying specific permissions to users or systems based on their identity and roles. It ensures that Your access to resources, data, or functions is appropriately controlled and secure, preventing unauthorized actions. Discover more about how effective authorization strategies protect your systems and enhance security throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
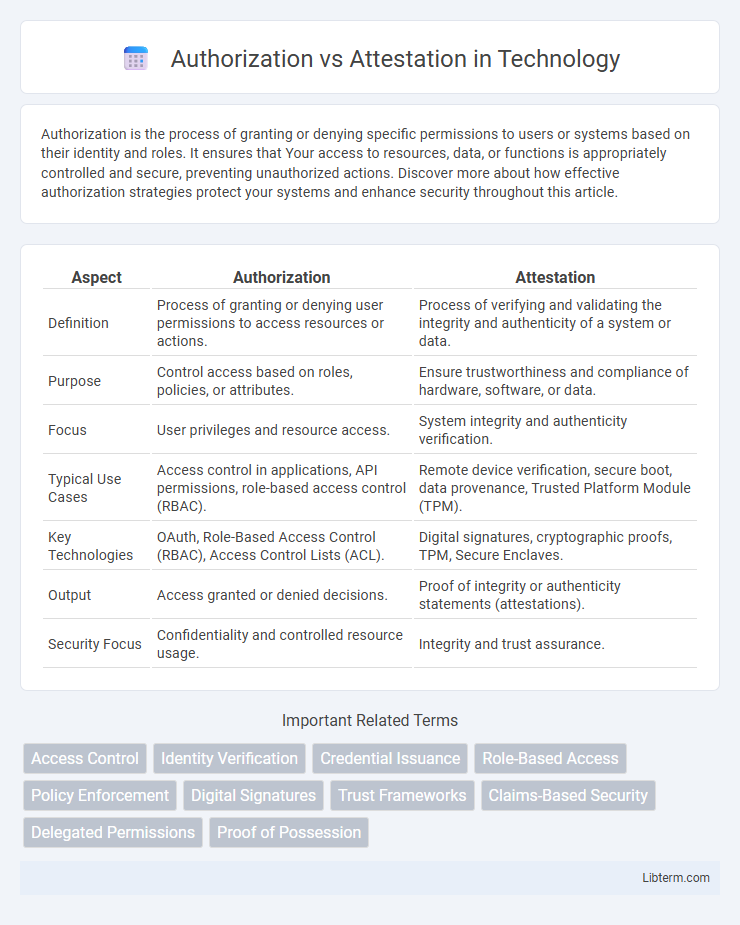
| Aspect | Authorization | Attestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of granting or denying user permissions to access resources or actions. | Process of verifying and validating the integrity and authenticity of a system or data. |
| Purpose | Control access based on roles, policies, or attributes. | Ensure trustworthiness and compliance of hardware, software, or data. |
| Focus | User privileges and resource access. | System integrity and authenticity verification. |
| Typical Use Cases | Access control in applications, API permissions, role-based access control (RBAC). | Remote device verification, secure boot, data provenance, Trusted Platform Module (TPM). |
| Key Technologies | OAuth, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Access Control Lists (ACL). | Digital signatures, cryptographic proofs, TPM, Secure Enclaves. |
| Output | Access granted or denied decisions. | Proof of integrity or authenticity statements (attestations). |
| Security Focus | Confidentiality and controlled resource usage. | Integrity and trust assurance. |
Understanding Authorization and Attestation
Authorization is the process of granting or denying access rights to resources based on predefined policies, ensuring that users or systems have appropriate permissions. Attestation involves verifying the integrity and authenticity of systems or data, confirming that they meet security standards before access or processing. Understanding both concepts is crucial for implementing robust security frameworks that control access and validate trustworthiness in digital environments.
Defining Authorization: Key Concepts
Authorization defines the process of granting or denying user access to resources based on predefined policies and roles, ensuring security compliance and operational efficiency. Key concepts include access control mechanisms, role-based access control (RBAC), and policy enforcement points that validate user permissions. Authorization systems integrate with identity management frameworks to systematically manage user privileges and prevent unauthorized actions.
What is Attestation? Core Principles
Attestation is the process of verifying and validating the integrity and authenticity of data, systems, or identities by a trusted third party or system component. Core principles of attestation include trustworthiness, ensuring that the entity performing attestation is reliable; integrity, confirming that data or systems have not been tampered with; and non-repudiation, providing proof that an attestation event occurred and cannot be denied later. Attestation often involves cryptographic techniques to securely measure and report the state of software or hardware components.
Differences Between Authorization and Attestation
Authorization involves granting official permission or approval to perform specific actions based on predefined criteria, while attestation is the formal declaration or verification that certain facts or conditions are true. Authorization focuses on controlling access and rights within systems or processes, whereas attestation emphasizes validation and evidence to confirm authenticity or compliance. Differences between authorization and attestation are critical in security frameworks, with authorization managing permissions and attestation providing proof or certification.
Use Cases: When to Use Authorization
Authorization is essential for controlling access to resources based on user roles, permissions, and policies in environments like cloud platforms, enterprise systems, and secure applications. It ensures only authorized users can perform specific actions such as accessing sensitive data, executing transactions, or modifying configurations. Common use cases include role-based access control (RBAC), API access management, and enforcing compliance requirements within regulated industries.
Use Cases: When to Use Attestation
Attestation is ideal for verifying the integrity and authenticity of data or actions, such as confirming software authenticity during secure boot processes or validating user identity in zero-trust security models. It is commonly used in scenarios requiring proof of compliance with security policies, like enterprise device management and remote system integrity checks. Unlike authorization, which grants access rights, attestation provides cryptographic assurance that a system or component meets predefined security standards before access is granted.
The Role of Authorization in Security Protocols
Authorization plays a crucial role in security protocols by defining and enforcing access controls, ensuring that only authenticated users can perform specific actions or access certain resources. It operates by evaluating permissions against predefined policies, which limits the potential for unauthorized data exposure or modification. Effective authorization mechanisms help maintain system integrity, confidentiality, and compliance with security standards.
The Importance of Attestation in Trust Management
Attestation plays a critical role in trust management by providing verifiable proof that a system or entity meets specified security criteria, enhancing confidence in digital interactions. Unlike authorization, which controls access based on predefined policies, attestation verifies the integrity and authenticity of a system's state, ensuring that trusted components are in place before granting access. This verification process strengthens overall security frameworks by enabling dynamic trust decisions based on real-time evidence rather than static permissions.
Common Authorization and Attestation Mechanisms
Common authorization mechanisms include role-based access control (RBAC), attribute-based access control (ABAC), and OAuth, which define user permissions based on roles, attributes, or tokenized consent. Attestation mechanisms often rely on digital signatures, Trusted Platform Modules (TPM), or certificate-based validation to verify the integrity and authenticity of devices or software. Both authorization and attestation are critical for secure access management, ensuring that only validated users or devices can interact with sensitive systems.
Choosing Between Authorization and Attestation
Choosing between authorization and attestation depends on the context of access control and verification needs within an organization. Authorization determines user permissions and access levels based on roles and policies, ensuring secure resource management. Attestation involves validating the integrity and authenticity of systems or data, commonly through cryptographic proofs, to confirm trustworthiness before granting access.
Authorization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com