Bandwidth determines the maximum data transfer rate of your internet connection, directly affecting download and streaming speeds. Higher bandwidth allows for smoother online experiences, especially when multiple devices are connected simultaneously. Explore the article to understand how to optimize your bandwidth for improved performance.
Table of Comparison
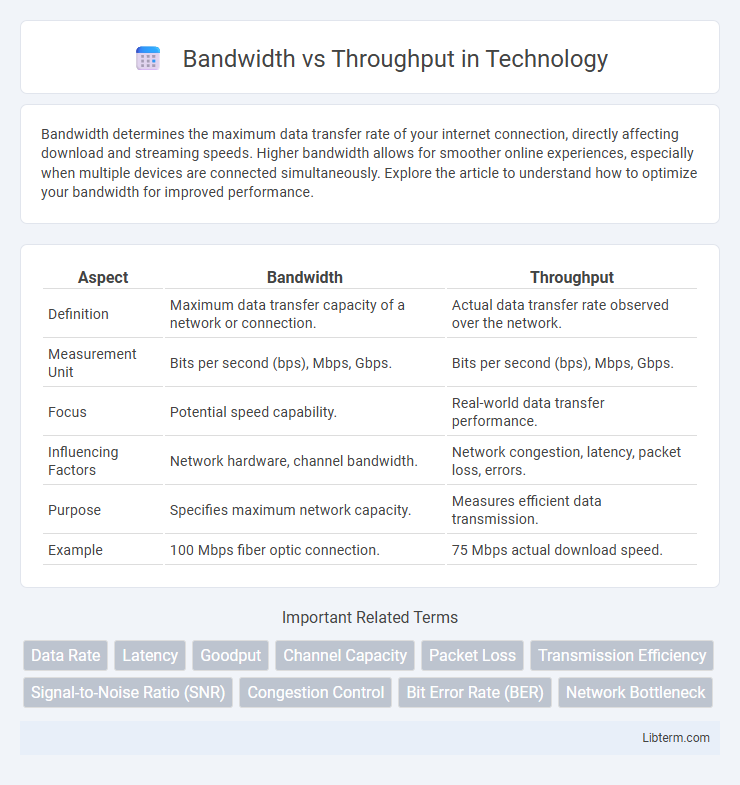
| Aspect | Bandwidth | Throughput |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maximum data transfer capacity of a network or connection. | Actual data transfer rate observed over the network. |
| Measurement Unit | Bits per second (bps), Mbps, Gbps. | Bits per second (bps), Mbps, Gbps. |
| Focus | Potential speed capability. | Real-world data transfer performance. |
| Influencing Factors | Network hardware, channel bandwidth. | Network congestion, latency, packet loss, errors. |
| Purpose | Specifies maximum network capacity. | Measures efficient data transmission. |
| Example | 100 Mbps fiber optic connection. | 75 Mbps actual download speed. |
Understanding Bandwidth: Definition and Importance
Bandwidth refers to the maximum data transfer capacity of a network connection, measured in bits per second (bps). It determines the potential speed at which data can be transmitted, making it a critical factor for network performance and capacity planning. Understanding bandwidth helps organizations ensure they allocate enough resources to meet demand and avoid bottlenecks.
What is Throughput? Key Concepts Explained
Throughput refers to the actual amount of data successfully transmitted over a network within a specific time, typically measured in bits per second (bps). It reflects real-world network performance, accounting for factors like latency, packet loss, and network congestion that reduce the effective data transfer rate compared to theoretical bandwidth. Understanding throughput is crucial for optimizing network efficiency, as it represents the true speed at which data is delivered to end-users.
Bandwidth vs Throughput: Core Differences
Bandwidth represents the maximum data transfer capacity of a network connection measured in bits per second (bps), indicating the potential speed available. Throughput reflects the actual data successfully transmitted over the network within a specific time frame, often lower than bandwidth due to factors like latency, packet loss, and network congestion. Understanding the core difference between bandwidth and throughput is critical for optimizing network performance and accurately assessing effective data transmission rates.
How Bandwidth Impacts Network Performance
Bandwidth determines the maximum data transfer rate that a network can handle, directly influencing the capacity to support multiple simultaneous connections and high-demand applications. Higher bandwidth allows more data to flow through the network per second, reducing potential bottlenecks and improving overall responsiveness. However, actual throughput depends on factors like network congestion, latency, and hardware efficiency, meaning bandwidth alone does not guarantee optimal network performance.
Measuring Throughput: Techniques and Tools
Measuring throughput involves assessing the actual data transfer rate achieved over a network, reflecting real-world performance rather than theoretical limits. Techniques such as packet analysis, protocol-specific counters, and traffic generators are commonly employed to capture throughput metrics accurately. Tools like Wireshark, iPerf, and NetFlow provide detailed insights into data flow, helping identify bottlenecks and optimize network efficiency.
Factors Affecting Bandwidth and Throughput
Bandwidth represents the maximum data transfer capacity of a network, while throughput measures the actual data successfully transmitted over a given time period. Factors affecting bandwidth include channel width, signal-to-noise ratio, and network hardware capabilities, whereas throughput is influenced by network congestion, protocol overhead, and packet loss. Optimizing both requires addressing physical infrastructure limitations, minimizing interference, and implementing efficient network protocols to maximize data transmission efficiency.
Real-World Examples: Bandwidth vs Throughput
Bandwidth represents the maximum data transfer capacity of a network, such as a 1 Gbps Ethernet connection, while throughput reflects the actual data transfer rate experienced, often lower due to network congestion or hardware limitations. For instance, a home Internet plan may offer 100 Mbps bandwidth, but real-world throughput might only reach 80 Mbps during peak hours because of ISP traffic management. Data centers also demonstrate this gap as fiber-optic cables provide high bandwidth, but throughput can be reduced by server processing speed and network switch performance.
Optimizing Network Throughput
Network throughput optimization involves maximizing the actual data transfer rate within the constraints of bandwidth, which represents the maximum potential capacity of a network. Efficient throughput depends on minimizing latency, packet loss, and jitter while employing techniques such as traffic shaping, Quality of Service (QoS), and congestion control protocols. Monitoring real-time network performance and adjusting configurations ensures that throughput approaches the theoretical bandwidth limits for improved application responsiveness and user experience.
Common Misconceptions About Bandwidth and Throughput
Bandwidth is often mistaken for throughput, but bandwidth represents the maximum data transfer capacity of a network connection, measured in bits per second (bps), while throughput is the actual data successfully transmitted over the network in a given time. Many believe higher bandwidth guarantees higher throughput, but factors like network congestion, latency, and hardware limitations often reduce throughput below the bandwidth limit. Understanding that throughput reflects real-world performance and bandwidth only the potential capacity is critical for accurate network analysis and optimization.
Choosing the Right Solution: Bandwidth or Throughput?
Selecting the right solution between bandwidth and throughput depends on your specific network demands and performance goals. Bandwidth refers to the maximum data transfer capacity of a connection, measured in bits per second (bps), while throughput indicates the actual data successfully transmitted over the network. Prioritize bandwidth when planning for high data volume capacity and throughput when the efficiency of data transfer and low latency are critical for applications such as streaming or online gaming.
Bandwidth Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com