Avro and Thrift are powerful data serialization frameworks designed to facilitate efficient cross-language data exchange and storage. Both support schema evolution and provide compact binary formats, making them ideal for high-performance applications and large-scale distributed systems. Explore the rest of the article to understand how choosing between Avro and Thrift can optimize your data handling strategies.
Table of Comparison
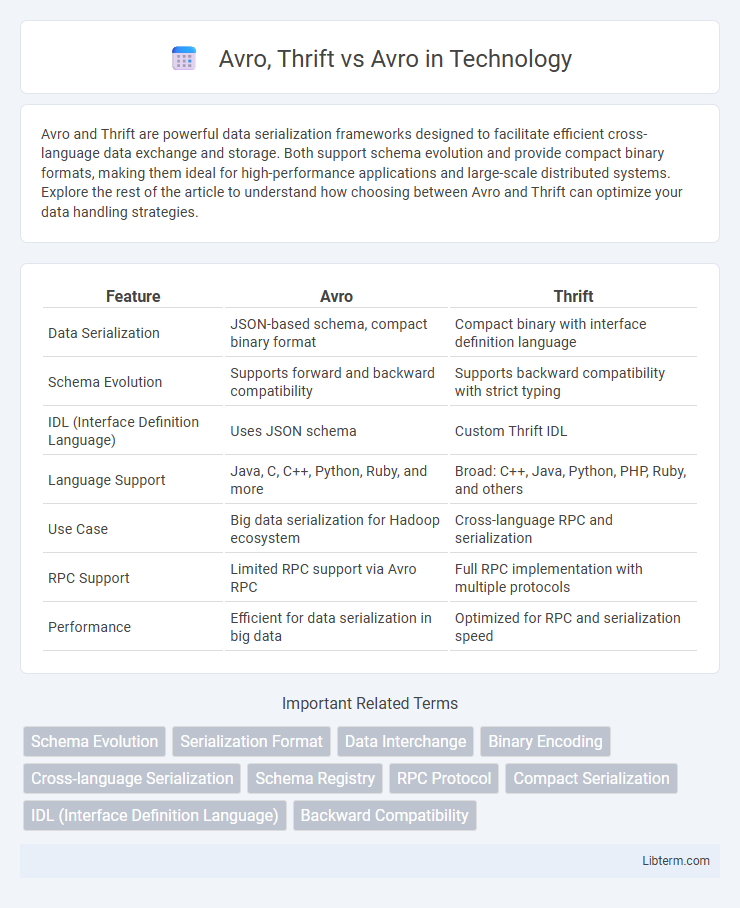
| Feature | Avro | Thrift |
|---|---|---|
| Data Serialization | JSON-based schema, compact binary format | Compact binary with interface definition language |
| Schema Evolution | Supports forward and backward compatibility | Supports backward compatibility with strict typing |
| IDL (Interface Definition Language) | Uses JSON schema | Custom Thrift IDL |
| Language Support | Java, C, C++, Python, Ruby, and more | Broad: C++, Java, Python, PHP, Ruby, and others |
| Use Case | Big data serialization for Hadoop ecosystem | Cross-language RPC and serialization |
| RPC Support | Limited RPC support via Avro RPC | Full RPC implementation with multiple protocols |
| Performance | Efficient for data serialization in big data | Optimized for RPC and serialization speed |
Introduction to Data Serialization
Avro and Thrift are popular data serialization frameworks designed for efficient data exchange and storage across distributed systems. Avro uses JSON for defining schemas and supports dynamic typing, enabling seamless integration with big data tools like Apache Hadoop, while Thrift combines a code generation engine with a compact binary protocol for cross-language RPC and data serialization. Choosing between Avro and Thrift depends on factors such as schema evolution requirements, language support, and integration with existing data processing ecosystems.
What is Avro?
Avro is a data serialization system developed within the Apache Hadoop project, designed for efficient, compact, and fast serialization of data. It uses JSON for defining data types and protocols, enabling robust schema evolution and cross-language serialization compatibility. Avro's binary serialization format supports dynamic schemas, making it ideal for big data processing and streaming applications.
Avro’s Key Features
Avro offers seamless schema evolution, compact binary serialization, and rich data structures, making it ideal for big data processing and streaming applications. Unlike Thrift, Avro embeds schemas directly within messages, eliminating schema negotiation overhead and enhancing compatibility across diverse systems. Its dynamic typing and JSON integration provide flexibility for rapid development while ensuring efficient data serialization in Apache Hadoop ecosystems.
Thrift Overview
Thrift is a high-performance, scalable cross-language serialization framework developed by Apache, enabling seamless communication between services written in different programming languages through its Interface Definition Language (IDL) and binary protocol. Unlike Avro, which excels in schema evolution and compact data serialization primarily for Hadoop ecosystems, Thrift offers a rich ecosystem with built-in RPC capabilities, supporting a wide range of transport and protocol options for flexible service development. Thrift's design focuses on efficient network communication and pluggable serialization protocols, making it a robust choice for microservices and distributed systems requiring cross-language interoperability.
Architecture Comparison: Thrift vs Avro
Thrift features a compact binary protocol and supports multiple languages with a service definition interface (IDL), enabling RPC calls and complex data structures. Avro employs JSON-based schemas and dynamic typing, focusing on data serialization with schema evolution support, making it ideal for big data environments like Hadoop. Architecturally, Thrift combines serialization with RPC capabilities, while Avro primarily emphasizes efficient serialization and schema management without integrated RPC support.
Data Modeling and Schema Evolution
Avro uses JSON-based schemas enabling flexible data modeling with support for schema evolution through backward and forward compatibility, allowing seamless updates to data structures without breaking existing consumers. Thrift employs an Interface Definition Language (IDL) with strong typing, offering rigid schema enforcement but limited schema evolution capabilities, often requiring client and server coordination for changes. Avro's dynamic schema resolution makes it more adaptable for data pipelines requiring frequent schema modifications, whereas Thrift is better suited for tightly-coupled RPC systems with stable data models.
Performance Benchmark: Serialization and Deserialization
Avro outperforms Thrift in serialization speed due to its schema-based binary encoding, achieving lower latency and smaller payload sizes in real-time data processing. Thrift offers faster deserialization in some scenarios by using a compact binary protocol but can introduce overhead with complex data structures. Performance benchmarks indicate Avro is preferable for systems requiring high-throughput streaming and minimal serialization overhead, while Thrift suits applications needing flexible protocol options.
Language and Platform Support
Avro supports dynamic languages like Python, Ruby, and Java along with JVM-based environments, enabling seamless integration across big data ecosystems such as Hadoop. Thrift offers comprehensive support for multiple languages, including C++, Java, Python, PHP, Ruby, and more, facilitating cross-platform RPC and serialization in distributed systems. Avro's strong focus on schema evolution suits data serialization within the Apache stack, while Thrift excels in multi-language RPC communication with broad platform compatibility.
Use Cases: When to Choose Avro or Thrift
Avro excels in big data ecosystems, particularly with Apache Hadoop and Kafka, due to its compact binary serialization and seamless schema evolution, making it ideal for batch processing and streaming data pipelines. Thrift is better suited for cross-language service communication, offering both serialization and RPC capabilities that support complex service architectures and real-time RPC calls in microservices. Choose Avro for data-intensive analytics and storage with schema evolution needs, while Thrift is preferred for scalable, high-performance RPC services requiring multi-language support.
Conclusion: Avro vs Thrift – Which is Better?
Avro excels in schema evolution and seamless integration with the Hadoop ecosystem, making it ideal for big data serialization and streaming applications. Thrift offers a robust cross-language RPC framework with extensive language support, suited for microservices and distributed systems requiring compact data serialization. Choosing between Avro and Thrift depends on the specific use case: prefer Avro for efficient serialization within data pipelines and analytics, while Thrift is better for versatile RPC communication across heterogeneous environments.
Avro, Thrift Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com