Multi-domain (SAN) certificates secure multiple domain names and subdomains under a single SSL certificate, simplifying management and reducing costs for businesses. By including Subject Alternative Names (SANs), these certificates enhance security and streamline website trust across various web properties. Explore this article to understand how a multi-domain (SAN) certificate can protect your online presence efficiently.
Table of Comparison
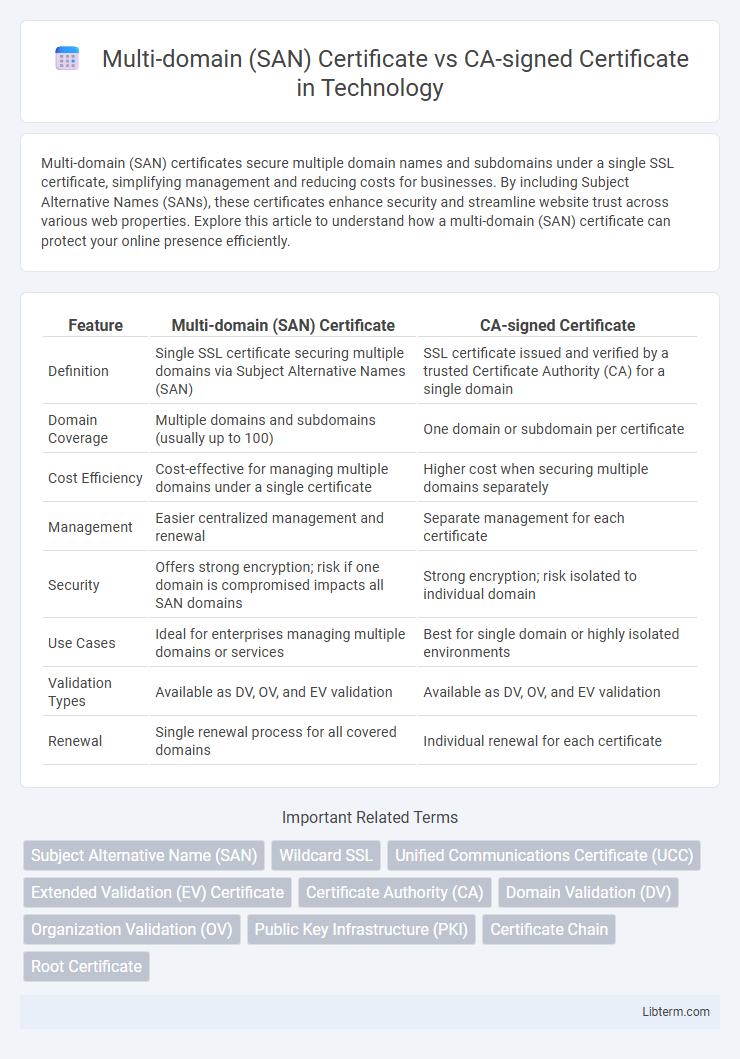
| Feature | Multi-domain (SAN) Certificate | CA-signed Certificate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single SSL certificate securing multiple domains via Subject Alternative Names (SAN) | SSL certificate issued and verified by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) for a single domain |
| Domain Coverage | Multiple domains and subdomains (usually up to 100) | One domain or subdomain per certificate |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for managing multiple domains under a single certificate | Higher cost when securing multiple domains separately |
| Management | Easier centralized management and renewal | Separate management for each certificate |
| Security | Offers strong encryption; risk if one domain is compromised impacts all SAN domains | Strong encryption; risk isolated to individual domain |
| Use Cases | Ideal for enterprises managing multiple domains or services | Best for single domain or highly isolated environments |
| Validation Types | Available as DV, OV, and EV validation | Available as DV, OV, and EV validation |
| Renewal | Single renewal process for all covered domains | Individual renewal for each certificate |
Understanding Multi-domain (SAN) Certificates
Multi-domain (SAN) certificates allow securing multiple domain names within a single SSL/TLS certificate by listing each domain as a Subject Alternative Name, simplifying certificate management and reducing costs for businesses with various websites. Unlike traditional CA-signed certificates issued for a single domain or subdomain, SAN certificates provide flexibility by covering diverse domains, subdomains, or services under one trusted certificate. This approach enhances website security across multiple platforms while maintaining compliance with Certificate Authority guidelines.
What is a CA-signed Certificate?
A CA-signed certificate is a digital certificate issued and digitally signed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) that verifies the authenticity of the website or organization. It provides secure, encrypted communication between a user's browser and the server while ensuring trust through third-party validation. This type of certificate is essential for establishing secure HTTPS connections and protecting sensitive information online.
Key Differences Between SAN and CA-signed Certificates
Multi-domain (SAN) certificates allow multiple domain names to be secured under a single SSL certificate using Subject Alternative Names, enhancing flexibility and reducing management complexity. CA-signed certificates, issued by trusted Certificate Authorities, validate the legitimacy of a domain or organization, ensuring higher trust and security through thorough verification processes. The key difference lies in SAN certificates' support for multiple domains on one certificate, whereas CA-signed certificates refer broadly to certificates validated by Certificate Authorities, which can be single-domain, multi-domain (SAN), or wildcard.
Use Cases for Multi-domain (SAN) Certificates
Multi-domain (SAN) certificates enable securing multiple domain names and subdomains within a single SSL certificate, making them ideal for organizations managing diverse web properties or services under one certificate. These certificates streamline HTTPS deployment for businesses operating several brands or sites, reducing management complexity and costs compared to issuing individual CA-signed certificates for each domain. Use cases include multi-brand companies, agencies handling client portfolios, and businesses aiming to consolidate security for corporate networks with varying domain assets.
Advantages of Multi-domain (SAN) Certificates
Multi-domain (SAN) certificates enable securing multiple domain names and subdomains under a single SSL certificate, reducing management complexity and cost compared to obtaining individual CA-signed certificates for each domain. They simplify certificate administration by consolidating multiple domains, enhancing security with centralized control while maintaining trust through CA validation. SAN certificates improve scalability and flexibility for organizations managing diverse web assets, providing streamlined renewal processes and reducing potential downtime.
Limitations of Multi-domain (SAN) Certificates
Multi-domain (SAN) certificates support multiple domain names within a single SSL certificate but have limitations including a fixed maximum number of domains allowed, often capped at 100 SAN entries, which may be insufficient for large organizations with numerous domains. These certificates can complicate domain management and pose security risks if one domain is compromised, potentially affecting all domains under the same certificate. Additionally, multi-domain certificates may not support every domain validation method uniformly, limiting flexibility in some certificate authorities' validation processes.
Benefits of Traditional CA-signed Certificates
Traditional CA-signed certificates provide trusted authentication by major Certificate Authorities, ensuring widespread browser and device compatibility for secure communications. They offer strong validation levels, including Extended Validation (EV) and Organization Validation (OV), which enhance user trust through verified organizational identity. Additionally, CA-signed certificates simplify management with automated renewal options and comprehensive support, reducing administrative overhead for maintaining secure websites.
Security Considerations: SAN vs. CA-signed Certificates
Multi-domain (SAN) certificates enhance security by allowing multiple domain names to be protected under a single certificate, reducing management complexity and potential vulnerabilities from handling multiple certificates. CA-signed certificates ensure trustworthiness through rigorous validation by a Certificate Authority, providing strong authentication and preventing man-in-the-middle attacks. Security considerations emphasize that while SAN certificates centralize domain validation, using a reputable CA with strict issuance policies is critical to maintaining overall certificate integrity and trust in both types.
Cost Comparison: Multi-domain vs. CA-signed Certificates
Multi-domain (SAN) certificates offer cost efficiency by securing multiple domains under a single certificate, often reducing purchase and renewal fees compared to buying separate CA-signed certificates for each domain. CA-signed single-domain certificates can become expensive when managing multiple domains, as each requires individual procurement, increasing overall operational costs. For organizations with numerous domains, multi-domain SAN certificates provide a scalable and budget-friendly SSL solution while maintaining trusted validation standards.
Choosing the Right Certificate for Your Organization
Selecting the right certificate depends on organizational needs for security, cost, and domain management. Multi-domain (SAN) Certificates allow multiple domain names and subdomains to be secured under a single certificate, simplifying certificate management and reducing costs for businesses with diverse online properties. In contrast, CA-signed Certificates provide individual, trusted validation for each domain, offering a higher assurance level suitable for organizations requiring specific domain validation and enhanced security compliance.
Multi-domain (SAN) Certificate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com