Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) and Test-Driven Development (TDD) are software development methodologies that enhance code quality and ensure functionality meets requirements through automated testing. While TDD focuses on writing tests before code to drive implementation, BDD emphasizes collaboration and shared understanding by using natural language descriptions of expected behavior. Explore the article to learn how these methodologies can improve your development process and boost software reliability.
Table of Comparison
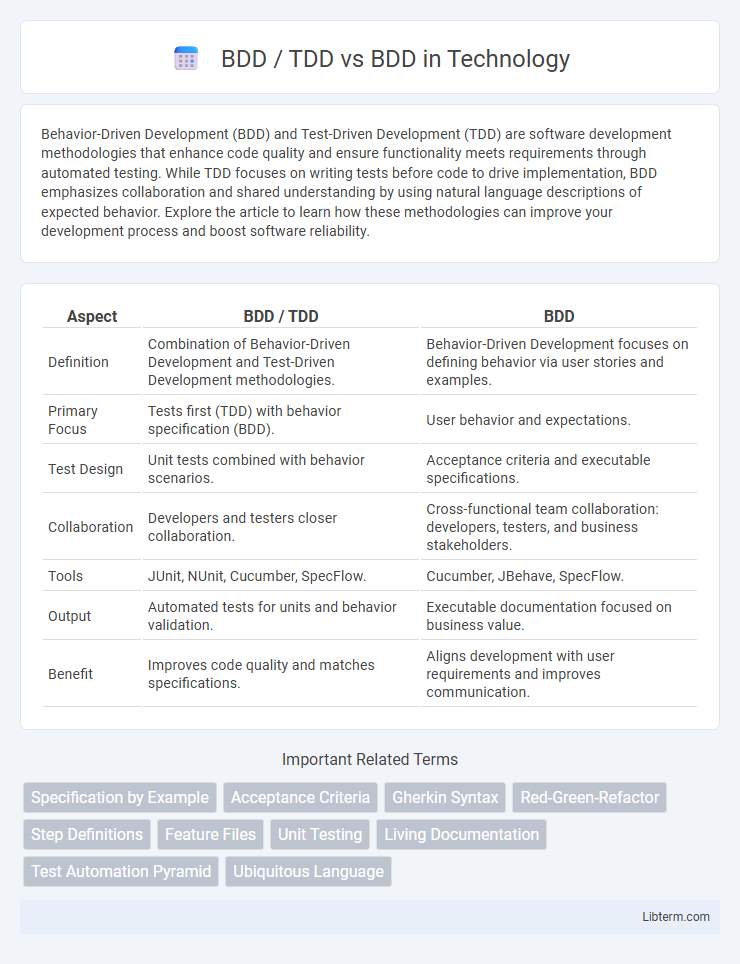
| Aspect | BDD / TDD | BDD |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of Behavior-Driven Development and Test-Driven Development methodologies. | Behavior-Driven Development focuses on defining behavior via user stories and examples. |
| Primary Focus | Tests first (TDD) with behavior specification (BDD). | User behavior and expectations. |
| Test Design | Unit tests combined with behavior scenarios. | Acceptance criteria and executable specifications. |
| Collaboration | Developers and testers closer collaboration. | Cross-functional team collaboration: developers, testers, and business stakeholders. |
| Tools | JUnit, NUnit, Cucumber, SpecFlow. | Cucumber, JBehave, SpecFlow. |
| Output | Automated tests for units and behavior validation. | Executable documentation focused on business value. |
| Benefit | Improves code quality and matches specifications. | Aligns development with user requirements and improves communication. |
Introduction to BDD and TDD
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) and Test-Driven Development (TDD) are agile software methodologies focused on improving code quality and collaboration. TDD emphasizes writing unit tests before code implementation to ensure functionality correctness, while BDD extends this concept by using natural language descriptions to define software behavior, enhancing communication between developers, testers, and business stakeholders. BDD frameworks like Cucumber and SpecFlow facilitate scenarios that align software development with business requirements more effectively than traditional TDD.
What is Test-Driven Development (TDD)?
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a software development methodology where developers write automated test cases before writing the actual code, ensuring that code functionality meets the specified requirements. TDD emphasizes short development cycles, with tests driving design decisions and promoting cleaner, more reliable codebases. While Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) focuses on collaboration and shared understanding through natural language scenarios, TDD centers on code correctness and unit-level test creation early in the development process.
What is Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)?
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) is a software development approach that emphasizes collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders through shared language and examples to define application behavior. BDD extends Test-Driven Development (TDD) by focusing on the expected behavior and user outcomes rather than just testing individual units of code. The practice utilizes natural language constructs, such as Gherkin syntax, to write executable specifications that improve communication and ensure alignment with business requirements.
Key Differences Between TDD and BDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) emphasizes writing tests before code with a focus on functionality validation at the unit level, while Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) centers on specifying application behavior through shared, human-readable scenarios that describe business outcomes. TDD uses technical tests written in programming languages often by developers, whereas BDD encourages collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders using domain-specific languages like Gherkin. The key difference lies in TDD's focus on how code works internally versus BDD's focus on what the system should do externally, promoting clearer communication and alignment with business objectives.
Advantages of TDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) enhances code quality by enforcing the creation of tests before implementation, which leads to early bug detection and more reliable software. TDD promotes simpler, cleaner, and more modular code, making maintenance and refactoring easier compared to Behavior-Driven Development (BDD). The strict test-first approach in TDD drives better developer discipline and more granular unit tests, resulting in faster feedback loops and improved overall development efficiency.
Advantages of BDD
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) enhances collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders by using natural language to define test scenarios, making requirements clearer and reducing misunderstandings. BDD fosters better communication through shared living documentation, which accelerates feedback loops and aligns development with business goals. This approach also improves test coverage and maintenance by focusing on user behavior and expected outcomes rather than low-level implementation details.
BDD vs TDD: Workflow Comparison
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) and Test-Driven Development (TDD) differ primarily in workflow focus, with BDD emphasizing collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders through natural language scenarios that drive development. TDD centers on writing unit tests before code implementation, guiding functionality by narrowly scoped tests to ensure correctness. BDD workflows integrate acceptance criteria early, promoting shared understanding and ensuring development aligns with business requirements, whereas TDD workflows prioritize technical correctness through iterative test-case creation and refactoring.
Use Cases: When to Choose TDD or BDD
TDD (Test-Driven Development) is ideal for low-level unit testing where defining precise behavior of functions or methods is crucial, especially in complex algorithmic or library code. BDD (Behavior-Driven Development) suits high-level acceptance criteria and user stories, focusing on system behavior and collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders. Choose TDD for technical correctness and implementation details, while BDD fits scenarios requiring communication of business rules and user experience validation.
Common Challenges in BDD and TDD Implementation
Common challenges in BDD and TDD implementation include unclear user stories and ambiguous acceptance criteria that hinder effective test creation, leading to gaps between requirements and tests. Maintaining test suites in rapidly evolving codebases often results in fragile tests prone to false positives or negatives, impacting developer confidence. Collaboration barriers between technical teams and business stakeholders can cause misaligned expectations, reducing the overall effectiveness of behavior-driven and test-driven development practices.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Approach for Your Project
Selecting the right testing methodology depends on project goals and team collaboration preferences. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) improves communication through shared language and focuses on user behavior, ideal for projects with diverse stakeholders. Test-Driven Development (TDD) emphasizes code correctness and rapid feedback, best suited for developer-centric environments targeting robust unit tests.
BDD / TDD Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com