Compression optimizes file sizes or data streams by reducing redundancy, which enhances storage efficiency and accelerates transmission speeds. This technique is essential in many fields such as multimedia, software development, and data management to save bandwidth and resources. Discover how mastering compression can improve Your digital experience in the detailed insights ahead.
Table of Comparison
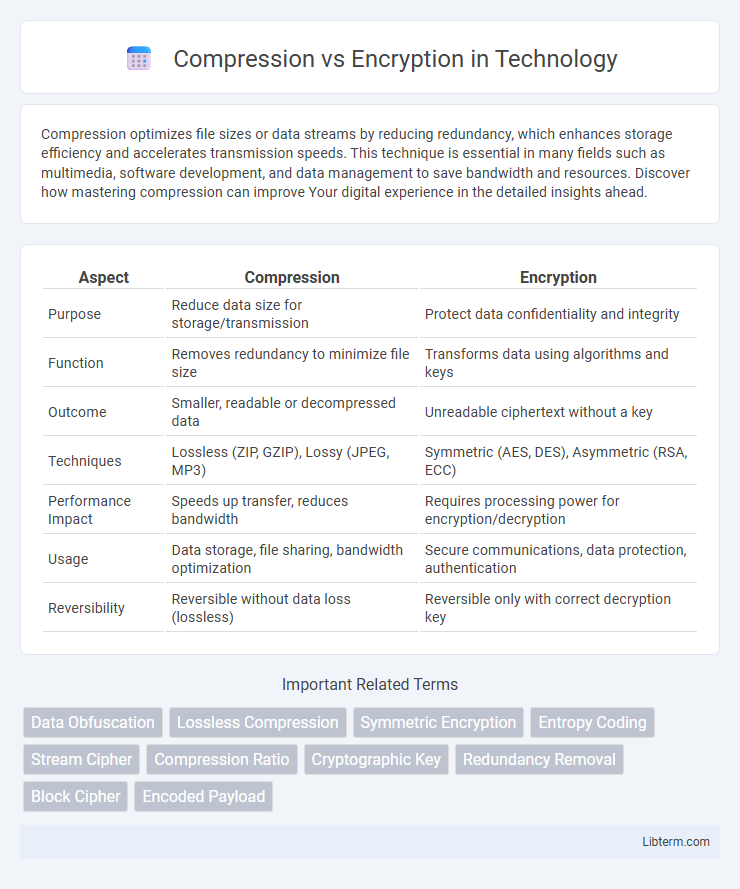
| Aspect | Compression | Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduce data size for storage/transmission | Protect data confidentiality and integrity |
| Function | Removes redundancy to minimize file size | Transforms data using algorithms and keys |
| Outcome | Smaller, readable or decompressed data | Unreadable ciphertext without a key |
| Techniques | Lossless (ZIP, GZIP), Lossy (JPEG, MP3) | Symmetric (AES, DES), Asymmetric (RSA, ECC) |
| Performance Impact | Speeds up transfer, reduces bandwidth | Requires processing power for encryption/decryption |
| Usage | Data storage, file sharing, bandwidth optimization | Secure communications, data protection, authentication |
| Reversibility | Reversible without data loss (lossless) | Reversible only with correct decryption key |
Introduction to Compression and Encryption
Compression reduces file size by removing redundant data patterns, allowing more efficient storage and faster transmission. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format using algorithms and keys to ensure confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access. Both processes are essential for optimizing data handling but serve distinct purposes: compression enhances efficiency, while encryption secures information.
What is Compression?
Compression reduces the size of data by removing redundancy and encoding information more efficiently using algorithms like Huffman coding or LZW. It enhances storage and transmission efficiency without necessarily securing the data. Lossless and lossy are primary types of compression, with lossless preserving original data perfectly and lossy sacrificing some fidelity for higher compression ratios.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of converting plaintext data into a coded format called ciphertext, ensuring that only authorized parties with the correct decryption key can access the original information. It uses algorithms such as AES, RSA, and DES to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, maintaining confidentiality and data integrity. Encryption is essential in securing communications, safeguarding personal data, and preventing cyberattacks in various applications like online banking, messaging, and cloud storage.
Key Differences Between Compression and Encryption
Compression reduces file size by eliminating redundancy and encoding data more efficiently, while encryption transforms data into an unreadable format to ensure confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access. Compression aims to optimize storage and transmission efficiency, whereas encryption prioritizes data security and privacy. Key differences include compression being reversible without a key, while encryption requires a cryptographic key for both encoding and decoding the information.
Common Types of Compression Algorithms
Lossless compression algorithms such as Huffman coding, Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW), and DEFLATE are commonly used for reducing file size without data loss, making them ideal for text and executable files. Lossy compression methods like JPEG and MP3 are applied primarily to images and audio, sacrificing some quality to achieve higher compression ratios. These compression techniques differ fundamentally from encryption, which focuses on data security rather than size reduction.
Popular Encryption Methods
Popular encryption methods include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA), and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), each offering strong data protection through different algorithms suitable for various security needs. Compression reduces data size by removing redundancy, whereas encryption transforms data into an unreadable format to ensure confidentiality. Understanding that compression typically occurs before encryption enhances system efficiency without compromising security in data transmission and storage.
Use Cases: When to Compress vs. Encrypt
Compression is ideal for reducing file sizes in data storage, transmitting large media files, and optimizing network bandwidth during file transfers. Encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information, securing online communications, and ensuring data privacy in financial transactions, healthcare records, and personal identification. Businesses should compress data when efficiency and speed are priorities, while encryption must be prioritized when confidentiality and data security are critical.
Performance Implications: Speed and Efficiency
Compression reduces file size by eliminating redundancy, significantly enhancing data transmission speed and storage efficiency, which lowers bandwidth and disk usage. Encryption, while securing data through algorithms like AES or RSA, typically adds computational overhead that can decrease processing speed and increase latency. Balancing these methods often involves compressing data before encryption to optimize overall system performance without compromising security.
Security Considerations and Data Integrity
Encryption ensures data confidentiality by transforming information into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access, while compression reduces file size by eliminating redundancies without inherently securing the data. Compression algorithms focus on lossless or lossy data reduction, which may affect integrity if not properly managed, whereas encryption maintains data integrity through cryptographic hashes and checksums. Combining compression and encryption requires careful sequencing; compressing before encrypting helps preserve data integrity and optimizes security by preventing pattern exposure in encrypted data.
Combining Compression and Encryption: Best Practices
Combining compression and encryption enhances data security and efficiency by reducing file size before encrypting, which minimizes processing time and storage requirements. Best practices include compressing data first to avoid loss of compression efficiency caused by encrypted, seemingly random data, and then applying strong encryption algorithms like AES to protect the compressed data. Implementing secure key management and validating compression algorithms ensures data integrity and maximizes overall system performance.
Compression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com