Dynamic typing allows variables to change types during program execution, offering flexibility and faster development cycles. This type system adapts automatically without the need for explicit type declarations, which can simplify coding but may lead to runtime errors. Explore the rest of the article to understand how dynamic typing can impact your programming approach.
Table of Comparison
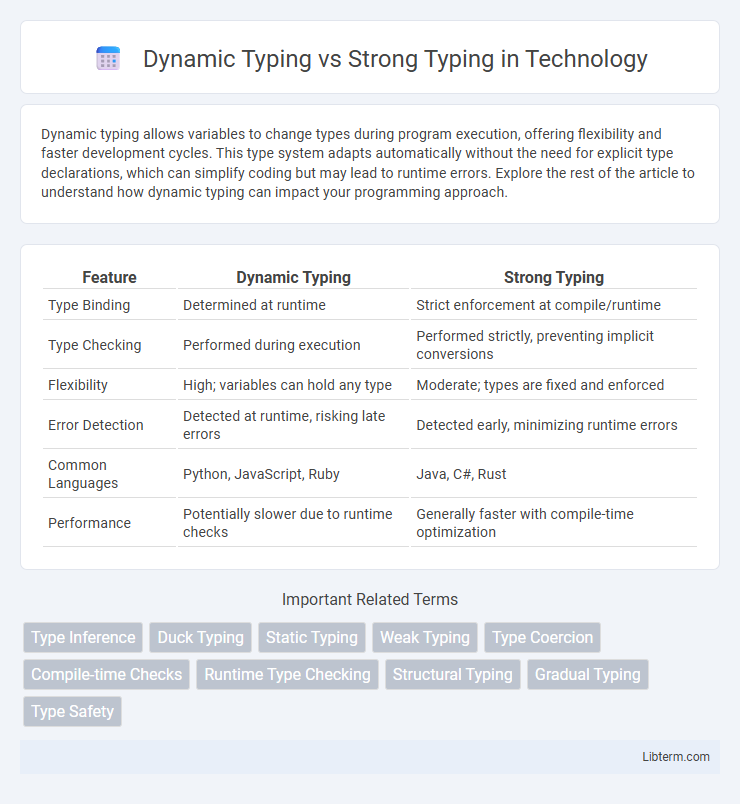
| Feature | Dynamic Typing | Strong Typing |
|---|---|---|
| Type Binding | Determined at runtime | Strict enforcement at compile/runtime |
| Type Checking | Performed during execution | Performed strictly, preventing implicit conversions |
| Flexibility | High; variables can hold any type | Moderate; types are fixed and enforced |
| Error Detection | Detected at runtime, risking late errors | Detected early, minimizing runtime errors |
| Common Languages | Python, JavaScript, Ruby | Java, C#, Rust |
| Performance | Potentially slower due to runtime checks | Generally faster with compile-time optimization |
Understanding Dynamic Typing
Dynamic typing allows variables to hold values of any type during runtime without explicit type declarations, enabling flexible and rapid development. This approach relies on type checking at runtime, which can lead to increased software agility but may introduce type-related errors that are only detected during execution. Languages like Python, JavaScript, and Ruby exemplify dynamic typing, providing programmers with ease of code modification and prototyping capabilities.
What Is Strong Typing?
Strong typing enforces strict rules on how data types are used, preventing implicit type conversions that can lead to unexpected behavior or errors. Languages with strong typing, such as Python and Java, require explicit operations between compatible types, enhancing code reliability and reducing runtime bugs. This type safety ensures that values are treated consistently according to their data type throughout program execution.
Key Differences Between Dynamic and Strong Typing
Dynamic typing refers to determining variable types at runtime, allowing flexibility and rapid development, while strong typing enforces strict type rules preventing unintended operations between incompatible types. Dynamic typing can lead to runtime type errors due to lack of compile-time checks, whereas strong typing guarantees greater type safety by catching errors during compilation or execution. Languages like Python exemplify dynamic typing, whereas languages such as Haskell demonstrate strong typing characteristics, highlighting a primary difference in how type constraints are applied and enforced.
Advantages of Dynamic Typing
Dynamic typing allows variables to hold values of any type without explicit declarations, enhancing coding flexibility and rapid prototyping. It facilitates quicker development cycles by reducing verbosity and enabling programmers to write generic functions that handle diverse data types effortlessly. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in scripting, web development, and situations requiring frequent changes to data structures.
Benefits of Strong Typing
Strong typing enhances code reliability by enforcing strict type rules, reducing runtime errors and unexpected behavior. It improves maintainability and readability by clearly defining variable types, facilitating easier debugging and collaboration. Languages like Rust, Haskell, and Ada leverage strong typing to ensure robust and secure software development.
Common Languages Using Dynamic Typing
Common languages using dynamic typing include Python, JavaScript, Ruby, and PHP, enabling variables to hold different data types without explicit declarations. Dynamic typing enhances flexibility and rapid development by resolving type checks at runtime rather than compile time. Strong typing, often contrasted with dynamic typing, enforces strict type rules but can also appear in dynamically typed languages, ensuring safer operations despite type flexibility.
Popular Languages With Strong Typing
Popular languages with strong typing include Java, Python, and C#. These languages enforce strict data type rules at compile time or runtime, preventing type errors and promoting code reliability. Strong typing enhances debugging and maintainability by catching type mismatches early in development.
Real-World Use Cases and Examples
Dynamic typing allows variables to hold multiple data types during runtime, enabling rapid development and flexibility ideal for prototyping, scripting, and web development in languages like Python and JavaScript. Strong typing enforces strict type rules, reducing runtime errors and enhancing reliability in complex applications such as banking software and system programming, commonly seen in languages like Java and Rust. Real-world examples demonstrate dynamic typing's effectiveness in fast-paced environments with changing data structures, whereas strong typing excels in scenarios demanding robust type safety and maintainability.
Performance and Error Handling Considerations
Dynamic typing offers flexibility by determining variable types at runtime, which can lead to slower performance due to additional type checking during execution. Strong typing enforces strict type rules, reducing runtime errors by catching type mismatches early, often at compile time, thus improving code safety. Performance in strongly typed languages typically benefits from optimized memory allocation and faster execution, while dynamic typing may introduce overhead through continuous type validation and potential runtime exceptions.
Choosing the Right Typing System for Your Project
Dynamic typing offers flexibility by allowing variables to change types at runtime, which can speed up development in prototyping and small projects. Strong typing enforces strict type rules, reducing runtime errors and improving code reliability, particularly in large-scale or safety-critical applications. Choosing the right typing system depends on project goals, team expertise, and the need for error prevention versus development speed.
Dynamic Typing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com