A platform serves as a foundational technology that enables users to build, deploy, and manage applications or services efficiently. By leveraging a versatile platform, businesses can streamline operations and enhance user engagement with scalable and customizable solutions. Discover how adopting the right platform can transform Your digital strategy and drive success in the following article.
Table of Comparison
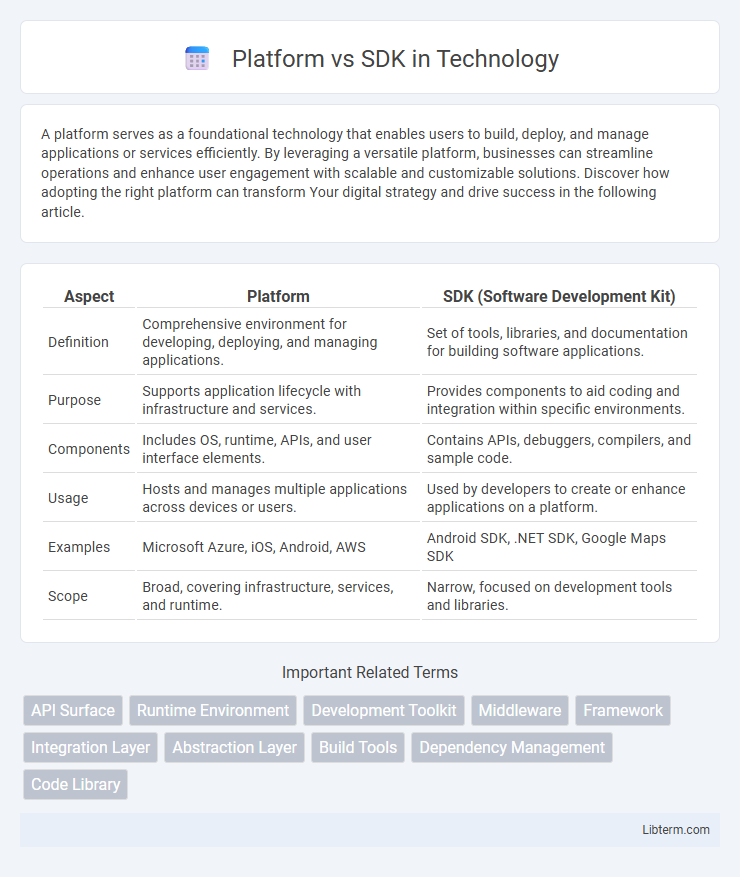
| Aspect | Platform | SDK (Software Development Kit) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive environment for developing, deploying, and managing applications. | Set of tools, libraries, and documentation for building software applications. |
| Purpose | Supports application lifecycle with infrastructure and services. | Provides components to aid coding and integration within specific environments. |
| Components | Includes OS, runtime, APIs, and user interface elements. | Contains APIs, debuggers, compilers, and sample code. |
| Usage | Hosts and manages multiple applications across devices or users. | Used by developers to create or enhance applications on a platform. |
| Examples | Microsoft Azure, iOS, Android, AWS | Android SDK, .NET SDK, Google Maps SDK |
| Scope | Broad, covering infrastructure, services, and runtime. | Narrow, focused on development tools and libraries. |
Introduction to Platforms and SDKs
Platforms provide a foundational environment enabling developers to build, deploy, and manage applications, often including operating systems, cloud services, or hardware ecosystems. SDKs (Software Development Kits) consist of tools, libraries, and documentation designed to facilitate development within a specific platform or for a particular technology. Understanding the distinction between platforms and SDKs helps developers choose the appropriate resources for efficient application development and integration.
Defining a Platform: Key Characteristics
A platform provides a comprehensive environment that supports the execution, development, and management of applications through integrated tools, services, and infrastructure. It offers scalability, interoperability, and user interface components, enabling developers to build, deploy, and maintain software efficiently. Core characteristics include an extensive API ecosystem, support for third-party integrations, and built-in security features that facilitate seamless application lifecycle management.
What is an SDK? Core Components and Functions
An SDK (Software Development Kit) is a comprehensive set of tools, libraries, documentation, and code samples designed to facilitate the creation of applications for specific platforms or frameworks. Core components of an SDK typically include application programming interfaces (APIs), debugging tools, and integrated development environment (IDE) plugins, which together streamline coding, testing, and deployment processes. SDKs function as essential resources that enable developers to efficiently build, customize, and maintain software tailored to particular hardware, operating systems, or service ecosystems.
Platform vs SDK: Fundamental Differences
A platform provides a comprehensive environment including hardware, software, and tools designed to support the development and execution of applications, while an SDK (Software Development Kit) offers a set of specific tools, libraries, and documentation to aid in building software for a particular platform or framework. Platforms like iOS or Android encompass operating systems, app stores, and user interfaces, whereas SDKs such as the iOS SDK or Android SDK focus on facilitating developers with APIs, debuggers, and emulators. The fundamental difference lies in scope: platforms deliver an all-encompassing ecosystem, whereas SDKs serve as focused development kits within those ecosystems.
Use Cases: When to Choose a Platform
A platform is ideal for businesses seeking comprehensive solutions that integrate multiple tools, services, and environments to streamline workflows and scale operations effectively. Use cases include enterprise software development where collaboration, deployment, and maintenance require unified management and standardized APIs. Platforms support long-term projects demanding extensibility, cross-functional compatibility, and centralized data control, unlike SDKs that focus primarily on specific feature integrations within individual applications.
Use Cases: When to Choose an SDK
Choose an SDK when you need a set of pre-built tools, libraries, and documentation to develop applications for a specific platform efficiently. SDKs are ideal for building custom features or integrating APIs within an app, such as adding payment processing, social media login, or augmented reality capabilities. For projects requiring full control over app development and rapid implementation of platform-specific functionalities, SDKs offer a streamlined, developer-friendly environment.
Integration: How Platforms and SDKs Work Together
Platforms provide comprehensive environments that support multiple tools and services, enabling seamless integration across different applications. SDKs (Software Development Kits) offer developers specific libraries and APIs to build and customize functionalities within these platforms efficiently. Together, platforms and SDKs create synergistic ecosystems that streamline development workflows and enhance application interoperability.
Benefits and Limitations of Platforms
Platforms provide a comprehensive environment with integrated tools and services, allowing developers to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently within a unified ecosystem. They offer scalability, security features, and seamless compatibility but may impose constraints on customization and platform dependency, potentially limiting flexibility. While platforms accelerate development and maintenance, the reliance on proprietary frameworks can create challenges in migration and integration with external systems.
Advantages and Drawbacks of SDKs
SDKs offer developers a comprehensive set of tools, libraries, and documentation designed to streamline application development and ensure compatibility with specific platforms or services. They provide accelerated development cycles and enhanced functionality integration, but may introduce limitations due to platform dependency, potential for increased complexity, and the need for ongoing updates to remain compatible. Organizations must weigh the benefits of rapid deployment and tailored features against challenges such as restricted flexibility and maintenance overhead inherent in SDK usage.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Selecting between a platform and an SDK depends on your project's scope, flexibility requirements, and integration needs. Platforms offer comprehensive environments with built-in tools and services ideal for end-to-end development, while SDKs provide specific libraries and APIs for targeted functionality integration. For projects needing full-stack solutions and minimal setup, platforms are optimal; SDKs work best when customizing features within existing infrastructures is a priority.
Platform Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com