High Availability Cluster ensures continuous system uptime by minimizing downtime through redundant components and failover mechanisms. This cluster architecture enhances your business continuity and data reliability, making critical services accessible even during hardware or software failures. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to implement and benefit from High Availability Clusters effectively.
Table of Comparison
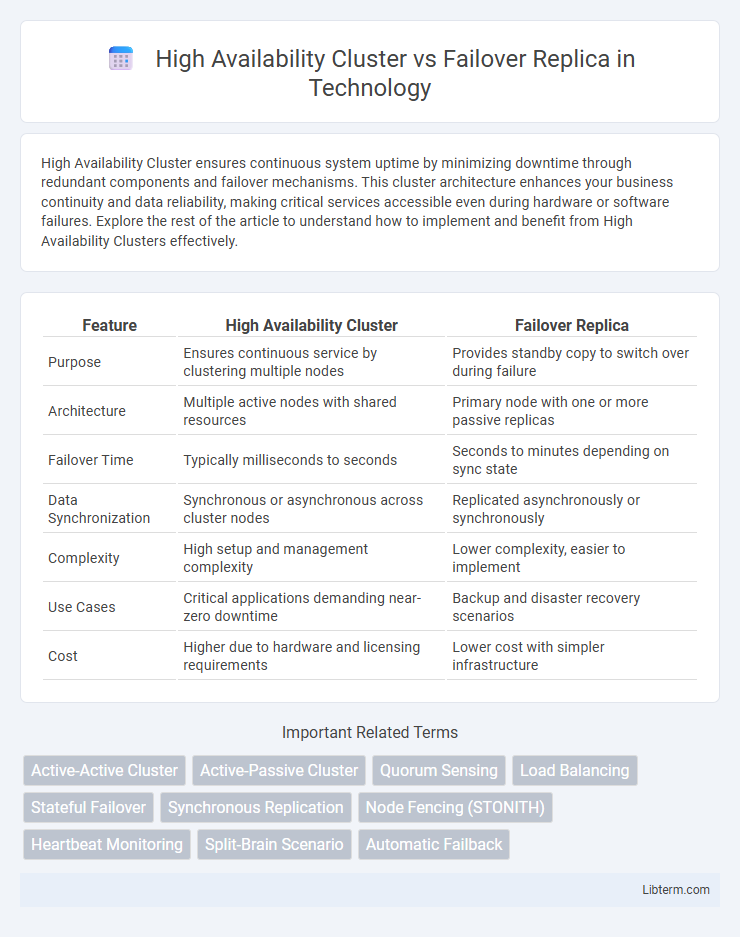
| Feature | High Availability Cluster | Failover Replica |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensures continuous service by clustering multiple nodes | Provides standby copy to switch over during failure |
| Architecture | Multiple active nodes with shared resources | Primary node with one or more passive replicas |
| Failover Time | Typically milliseconds to seconds | Seconds to minutes depending on sync state |
| Data Synchronization | Synchronous or asynchronous across cluster nodes | Replicated asynchronously or synchronously |
| Complexity | High setup and management complexity | Lower complexity, easier to implement |
| Use Cases | Critical applications demanding near-zero downtime | Backup and disaster recovery scenarios |
| Cost | Higher due to hardware and licensing requirements | Lower cost with simpler infrastructure |
Introduction to High Availability Solutions
High Availability (HA) solutions ensure continuous system operation and minimize downtime by using redundant server configurations. High Availability Clusters link multiple servers to work together, providing seamless workload distribution and immediate failover in case of hardware or software failures. Failover Replicas, often used in database environments, maintain synchronized copies of data to quickly switch to a standby server, preserving data integrity and operational continuity.
What is a High Availability Cluster?
A High Availability Cluster is a group of interconnected servers that work together to ensure continuous application uptime by automatically detecting and handling node failures. It uses heartbeat signals and failover mechanisms to maintain service availability and minimize downtime in critical environments. This cluster configuration supports resource sharing and load balancing to improve reliability and system resilience.
Defining Failover Replica Systems
Failover replica systems are designed to automatically switch to a standby database replica when the primary system fails, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss. These systems maintain continuous data synchronization between the primary and failover replicas using synchronous or asynchronous replication methods. Compared to high availability clusters, failover replicas emphasize data redundancy and quick recovery across distributed environments, optimizing fault tolerance in database infrastructures.
Key Differences: Architecture and Design
High Availability Clusters rely on multiple interconnected servers sharing storage and resources to provide continuous service, emphasizing redundancy and load balancing. Failover Replicas are designed with primary and secondary nodes, where the secondary remains passive until triggered by primary node failure, focusing on seamless failover without shared storage. The architecture of High Availability Clusters supports active-active configurations, while Failover Replicas typically use active-passive setups, influencing system complexity and resource utilization.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
High Availability Clusters provide robust fault tolerance by distributing workloads across multiple nodes, enhancing performance through parallel processing and ensuring minimal downtime during node failures. Failover Replicas primarily focus on data redundancy and automatic failover, which may introduce slight latency due to synchronization overhead, impacting real-time performance scalability. While clusters excel in scaling out resources dynamically to handle increased loads, failover replicas prioritize consistency and reliability over seamless performance scaling.
Data Consistency and Synchronization
High Availability Clusters ensure data consistency through synchronous replication across nodes, minimizing downtime by automatically redirecting workloads during failures. Failover Replicas rely on asynchronous replication that introduces slight latency, potentially causing brief data inconsistencies during failover events. Synchronization in High Availability Clusters is real-time and continuous, whereas Failover Replicas synchronize data periodically, affecting the immediacy of data consistency.
Downtime and Recovery Time Objectives
High Availability (HA) Clusters minimize downtime by using multiple nodes that continuously monitor each other, enabling near-instantaneous failover and targeting Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) of seconds to minutes. Failover Replicas rely on primary-secondary synchronization, often resulting in longer downtime during failover, with RTOs ranging from minutes to hours depending on data replication lag. HA Clusters provide superior rapid recovery capabilities suitable for mission-critical applications demanding minimal service interruption.
Cost Implications and Resource Utilization
High Availability Clusters often require substantial upfront investment in specialized hardware and software licenses, leading to higher capital costs compared to Failover Replicas, which typically leverage existing infrastructure with minimal additional resources. Resource utilization in High Availability Clusters is generally more efficient due to load balancing across multiple nodes, reducing idle capacity, whereas Failover Replicas maintain standby instances that consume resources without active workload. Organizations must weigh the trade-off between the continuous availability and optimized resource use of clusters against the simpler, cost-effective but less resource-efficient failover replica solutions.
Use Cases: When to Choose Each Solution
High Availability Clusters are optimal for environments requiring continuous system uptime and automatic failover, such as critical enterprise applications and financial services where downtime directly impacts operations. Failover Replicas are best suited for disaster recovery scenarios and read-intensive workloads, providing a standby server to take over during primary server failure without complex cluster configurations. Choosing between the two depends on the specific need for real-time redundancy or recovery and the complexity of infrastructure management desired.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Approach
High Availability Clusters provide continuous service by distributing workloads across multiple nodes, ensuring minimal downtime through active redundancy. Failover Replicas prioritize data integrity and recovery by maintaining synchronized standby copies that activate upon primary node failure. Choosing between these approaches depends on organizational priorities: High Availability Clusters suit environments demanding uninterrupted operation, whereas Failover Replicas excel in scenarios emphasizing data protection and disaster recovery.
High Availability Cluster Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com