Data marts streamline data access by focusing on specific business areas, enhancing query performance and decision-making. They enable your teams to quickly retrieve relevant insights without navigating the complexities of enterprise-wide data warehouses. Explore the rest of this article to understand how data marts can transform your data strategy.
Table of Comparison
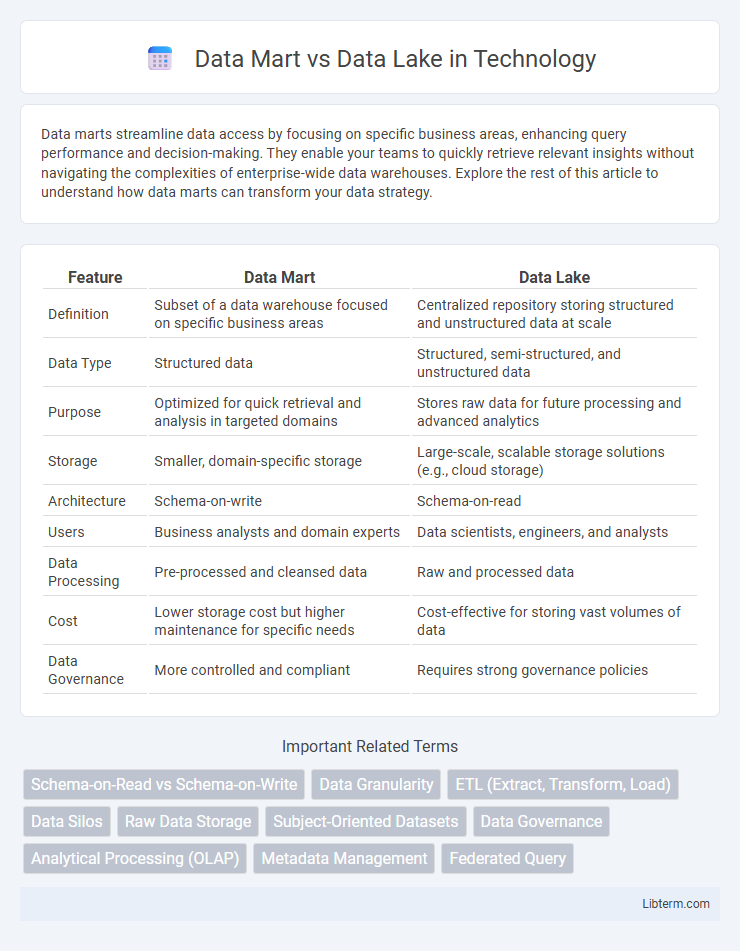
| Feature | Data Mart | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Subset of a data warehouse focused on specific business areas | Centralized repository storing structured and unstructured data at scale |
| Data Type | Structured data | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data |
| Purpose | Optimized for quick retrieval and analysis in targeted domains | Stores raw data for future processing and advanced analytics |
| Storage | Smaller, domain-specific storage | Large-scale, scalable storage solutions (e.g., cloud storage) |
| Architecture | Schema-on-write | Schema-on-read |
| Users | Business analysts and domain experts | Data scientists, engineers, and analysts |
| Data Processing | Pre-processed and cleansed data | Raw and processed data |
| Cost | Lower storage cost but higher maintenance for specific needs | Cost-effective for storing vast volumes of data |
| Data Governance | More controlled and compliant | Requires strong governance policies |
Introduction to Data Mart and Data Lake
Data marts are specialized subsets of data warehouses designed to serve specific business units or functions with structured, processed data for faster analytics. Data lakes store vast volumes of raw, unstructured, and semi-structured data from diverse sources, enabling flexible analytics and machine learning at scale. Understanding the distinction between data marts' curated datasets and data lakes' comprehensive data repositories is essential for optimized data management strategies.
What is a Data Mart?
A Data Mart is a focused subset of a data warehouse designed to serve specific business lines or teams by providing quick and easy access to relevant, curated data. It integrates structured data from various sources optimized for analysis, reporting, and decision-making within specialized domains like sales, finance, or marketing. Unlike Data Lakes, Data Marts emphasize clean, processed, and organized datasets tailored for user-specific queries and performance efficiency.
What is a Data Lake?
A Data Lake is a centralized repository that stores vast amounts of raw, unstructured, and structured data at any scale, enabling advanced analytics and machine learning. Unlike Data Marts, which contain curated and subject-specific datasets designed for quick querying and reporting, Data Lakes retain data in its native format, facilitating flexible schema-on-read processing. This architecture supports diverse data types--from logs and social media feeds to transactional databases--making Data Lakes essential for big data analytics and real-time data exploration.
Key Differences Between Data Mart and Data Lake
Data marts are specialized subsets of data warehouses designed for specific business lines or departments, optimized for quick query performance and structured data storage. Data lakes store vast amounts of raw, unstructured, and semi-structured data in native formats, enabling flexible analysis and supporting machine learning workloads. The key differences lie in data structure, purpose, and processing speed: data marts emphasize structured, processed data for specific user groups, while data lakes prioritize vast, diverse, and detailed datasets for broad and exploratory analytics.
Data Structure and Storage Approaches
Data marts employ structured storage optimized for specific business functions, often using relational databases and schema-on-write techniques to ensure data is cleaned, organized, and query-ready. In contrast, data lakes store vast amounts of raw, unstructured, or semi-structured data using schema-on-read, leveraging scalable object storage systems like Hadoop or cloud-based platforms. This fundamental difference allows data marts to support fast, specific analytics, while data lakes offer flexibility for big data processing and data science experimentation.
Use Cases: When to Choose Data Mart vs Data Lake
Data marts are ideal for business departments requiring fast, specific data insights such as sales, finance, or marketing, enabling targeted reporting and analysis with structured, cleaned data. Data lakes support big data analytics, machine learning, and raw data storage, making them suitable for data scientists and organizations needing flexibility in handling unstructured or semi-structured data. Choose data marts for high-performance query environments and data lakes for scalable storage of diverse data types for advanced analytics and exploration.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Data marts offer optimized performance for specific business units by focusing on structured, curated data, enabling faster query response times compared to the vast, unstructured storage in data lakes. Data lakes provide superior scalability by accommodating large volumes of diverse data types, but this flexibility often leads to slower performance during complex analytics without dedicated processing layers. Enterprises must balance the high-performance, user-friendly environment of data marts with the expansive, scalable infrastructure of data lakes to meet varying analytical requirements.
Data Security and Governance in Both Systems
Data marts offer granular data security and governance with tailored access controls and compliance protocols specific to departmental needs, enabling stricter management of sensitive information. Data lakes handle vast volumes of raw data with enterprise-wide governance frameworks and advanced encryption, but face challenges in maintaining consistent security across diverse data types and formats. Effective data governance in data marts revolves around role-based access, while data lakes require automated metadata management and strong policy enforcement to ensure data integrity and compliance.
Integration with Analytics and BI Tools
Data marts provide streamlined integration with analytics and BI tools by offering curated, subject-specific datasets optimized for fast query performance and ease of use in reporting platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and Looker. Data lakes support integration with advanced analytics and machine learning frameworks such as Apache Spark and TensorFlow, enabling exploration of raw, unstructured data for deeper insights but requiring additional data processing layers. Choosing between data marts and data lakes depends on the analytics requirements: structured reporting and business dashboards favor data marts, while data lakes excel in flexible, large-scale data exploration and predictive analytics.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Solution for Your Needs
Choosing between a data mart and a data lake depends on your organization's data structure and analytics goals. Data marts offer streamlined, department-specific data repositories optimized for quick access and business intelligence, suitable for focused, high-performance analytics. Data lakes provide scalable storage for vast, raw data sets across various formats, ideal for advanced analytics and machine learning tasks requiring flexibility and comprehensive data integration.
Data Mart Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com