A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a secure, isolated environment within a public cloud infrastructure that allows you to run resources in a logically separated network. It offers control over IP address ranges, subnets, and network gateways, providing enhanced security and flexibility for your cloud deployments. Discover how a VPC can optimize your cloud architecture by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
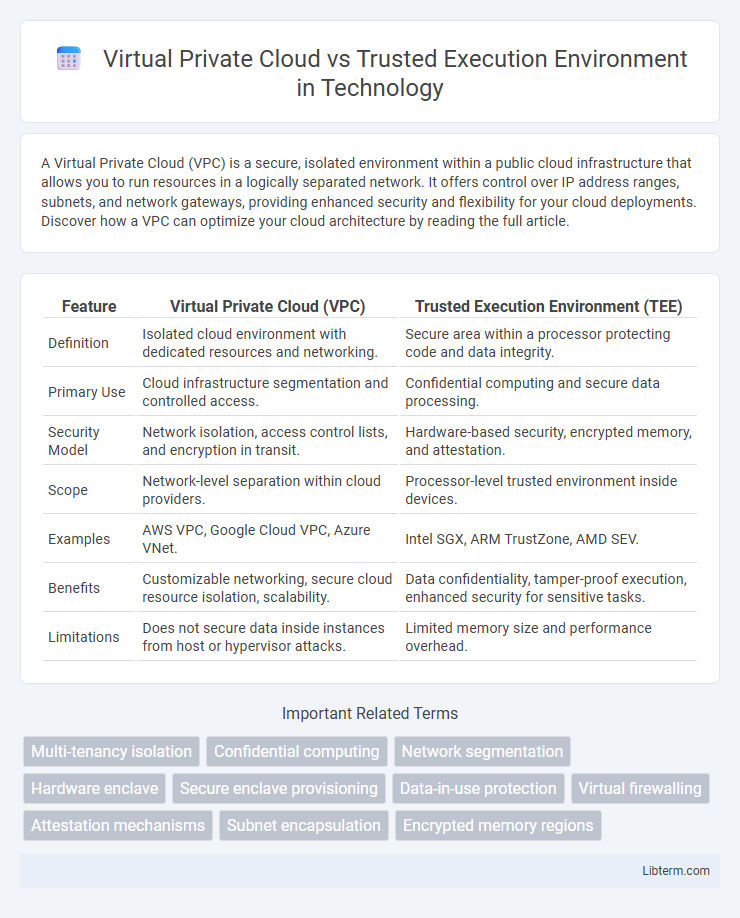
| Feature | Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) | Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Isolated cloud environment with dedicated resources and networking. | Secure area within a processor protecting code and data integrity. |
| Primary Use | Cloud infrastructure segmentation and controlled access. | Confidential computing and secure data processing. |
| Security Model | Network isolation, access control lists, and encryption in transit. | Hardware-based security, encrypted memory, and attestation. |
| Scope | Network-level separation within cloud providers. | Processor-level trusted environment inside devices. |
| Examples | AWS VPC, Google Cloud VPC, Azure VNet. | Intel SGX, ARM TrustZone, AMD SEV. |
| Benefits | Customizable networking, secure cloud resource isolation, scalability. | Data confidentiality, tamper-proof execution, enhanced security for sensitive tasks. |
| Limitations | Does not secure data inside instances from host or hypervisor attacks. | Limited memory size and performance overhead. |
Introduction to Virtual Private Cloud and Trusted Execution Environment
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) provides a logically isolated section of a public cloud environment, enabling users to launch resources in a secure, virtual network that mimics traditional on-premises infrastructure. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) is a secure area within a main processor that ensures sensitive data is stored, processed, and protected in an isolated and trusted environment. While VPC focuses on network-level security and resource isolation in cloud platforms, TEE emphasizes hardware-based security for data integrity and confidentiality during computation.
Key Differences Between VPC and TEE
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) provides isolated cloud resources within a public cloud environment, offering network-level segmentation, secure IP address ranges, and customizable routing controls. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) ensures hardware-based secure enclaves for sensitive code execution, isolating data and processes even from privileged software on the same device. VPC focuses on virtual network isolation and resource segregation in the cloud, while TEE emphasizes hardware-rooted security for confidential computing at the processor level.
Core Components of Virtual Private Cloud
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) core components include subnets, route tables, internet gateways, and network access control lists (ACLs), which collectively enable secure and isolated cloud network environments. VPCs allocate IP address ranges and control traffic flow through virtual firewalls, ensuring segmented workloads and controlled connectivity. Unlike Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) that protect data at the hardware level, VPCs provide comprehensive network-level security and infrastructure isolation within public clouds.
Essential Features of Trusted Execution Environment
Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) provides a secure area within a main processor, safeguarding sensitive data through isolated execution, hardware-based cryptographic operations, and secure key management. Unlike Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), which offers network isolation for cloud resources, TEE ensures confidentiality and integrity at the hardware level, preventing unauthorized access even from the operating system or hypervisor. Essential features of TEE include memory encryption, secure boot, attestation, and resistance to physical and software attacks, enabling trusted application execution in untrusted environments.
Security Approaches: VPC vs TEE
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) provides network-level security by isolating resources within a virtual network, using firewalls, subnets, and access control lists to prevent unauthorized access. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) secures data by creating a hardware-isolated enclave within the CPU, ensuring code and data integrity with encryption and tamper resistance during processing. While VPC focuses on perimeter defense for cloud resources, TEE emphasizes protecting sensitive computations and data at the hardware level against insider and external threats.
Performance Considerations in VPC and TEE
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) offers scalable network isolation with minimal latency impact, relying on robust cloud infrastructure to maintain high throughput for enterprise workloads. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) provides strong security by enabling isolated execution of sensitive code, but its hardware-based encryption and integrity checks introduce performance overhead that can slow compute-intensive tasks. Balancing VPC's network efficiency against TEE's security-driven latency is critical for optimizing performance in cloud environments.
Use Cases for Virtual Private Cloud
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is primarily used for creating isolated network environments within public cloud infrastructure, enabling secure hosting of applications, databases, and development environments with customizable network configurations. It facilitates scalable multi-tenant architectures and supports hybrid cloud models by connecting on-premises data centers to cloud resources through VPN or dedicated links. These use cases highlight VPC's role in controlling network traffic, enhancing security, and ensuring compliance in shared public cloud settings.
Applications of Trusted Execution Environment
Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) provides hardware-isolated secure areas within a main processor, enabling sensitive applications like cryptographic key management, secure payment processing, and DRM content protection to run with enhanced security. Unlike Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), which isolates resources at the network level for scalable cloud infrastructure and multi-tenant data segregation, TEE focuses on protecting code and data confidentiality and integrity in real-time on individual devices. Applications of TEE span IoT security, mobile authentication, secure enclave computing, and blockchain consensus mechanisms, offering robust defense against software and physical tampering.
Cost Implications: VPC vs TEE
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) typically incurs costs related to network infrastructure, data transfer, and resource allocation within cloud environments, which can scale with usage and complexity. Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) often involves expenses tied to specialized hardware, licensing, and limited computation capacity, potentially increasing upfront investment but reducing long-term security risks. Evaluating cost implications depends on workload requirements, with VPC favored for scalable network isolation and TEE prioritized for high-assurance security in sensitive data processing.
Choosing the Right Solution: VPC or TEE
Choosing between a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) depends on whether the primary need is network isolation or secure computation. VPC provides isolated cloud resources with customizable security controls, ideal for segregating workloads and managing access in multi-tenant environments. TEEs offer hardware-based security for executing sensitive code and data in an encrypted environment, essential for protecting against insider threats and ensuring data confidentiality at runtime.
Virtual Private Cloud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com