A disaster recovery site ensures your business continuity by providing a secure location to restore critical systems and data after an unexpected event. It minimizes downtime and data loss, safeguarding your operations from disruptions caused by natural disasters or cyberattacks. Explore the rest of this article to understand how you can implement an effective disaster recovery site for maximum resilience.
Table of Comparison
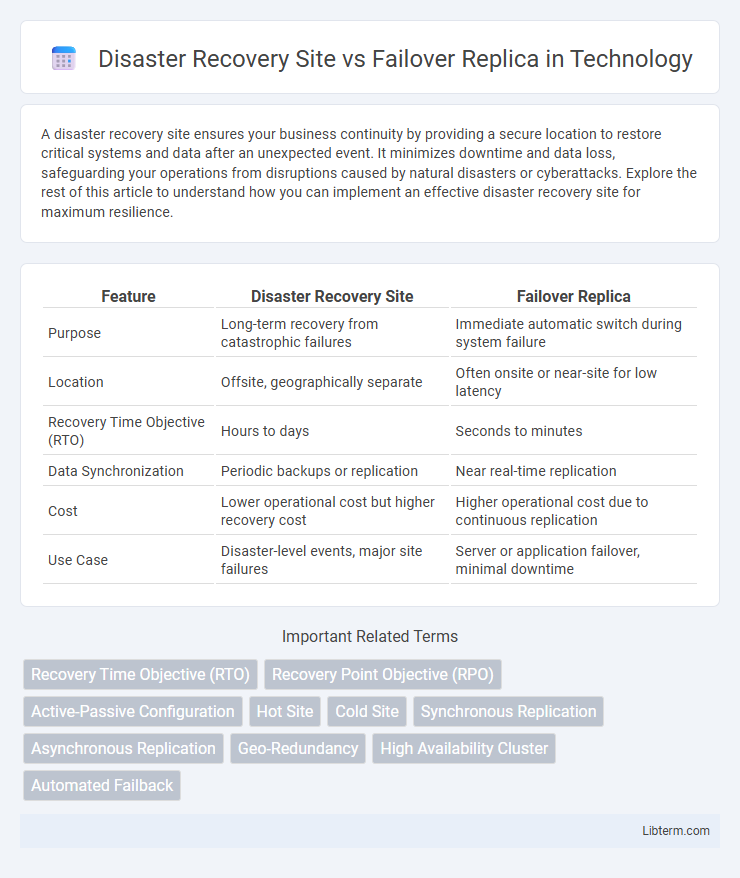
| Feature | Disaster Recovery Site | Failover Replica |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Long-term recovery from catastrophic failures | Immediate automatic switch during system failure |
| Location | Offsite, geographically separate | Often onsite or near-site for low latency |
| Recovery Time Objective (RTO) | Hours to days | Seconds to minutes |
| Data Synchronization | Periodic backups or replication | Near real-time replication |
| Cost | Lower operational cost but higher recovery cost | Higher operational cost due to continuous replication |
| Use Case | Disaster-level events, major site failures | Server or application failover, minimal downtime |
Introduction to Disaster Recovery Sites and Failover Replicas
Disaster recovery sites provide dedicated infrastructure located remotely to restore IT operations after catastrophic failures, ensuring business continuity through data backups and system redundancy. Failover replicas are synchronized copies of primary systems that enable instantaneous switching in case of system faults, minimizing downtime and data loss. Both strategies support resilience but differ in scope and activation speed, with disaster recovery sites often involving manual failover and failover replicas enabling automatic, near-instant failover.
Key Differences Between Disaster Recovery Sites and Failover Replicas
Disaster recovery sites are geographically separate locations equipped to take over operations after a catastrophic event, ensuring business continuity when the primary site fails, while failover replicas are synchronized copies of a primary system used to provide immediate switch-over with minimal downtime. Disaster recovery sites typically involve complex infrastructure setups, including data backups and restoration processes, designed for long-term recovery, whereas failover replicas focus on real-time or near-real-time replication to enable automatic failover. Key differences include recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO), with failover replicas offering lower RTO and RPO due to continuous synchronization, whereas disaster recovery sites often have higher RTO and RPO due to data restoration efforts.
How Disaster Recovery Sites Work
Disaster recovery sites function by maintaining a fully or partially operational copy of primary IT infrastructure at a geographically distant location, ensuring critical data and applications are accessible if the main site fails. These sites synchronize data through scheduled backups or real-time replication, enabling rapid recovery and minimizing downtime during disasters like hardware failures or cyberattacks. Disaster recovery sites are often categorized as hot, warm, or cold based on their readiness level, impacting recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO).
Operational Mechanisms of Failover Replicas
Failover replicas operate by continuously synchronizing data with the primary system to enable immediate switchover during failures, minimizing downtime and data loss. They use automated failover mechanisms that monitor system health and trigger seamless transitions to replica sites without manual intervention. This real-time data replication and automatic recovery process ensures high availability and business continuity in critical IT environments.
Deployment Considerations for Disaster Recovery Sites
Disaster recovery site deployment requires comprehensive infrastructure setup, including dedicated hardware, secure data replication channels, and geographic diversity to ensure resilience against regional outages. Failover replicas typically emphasize synchronous or asynchronous data replication for near-instant failover but may demand less physical infrastructure compared to full disaster recovery sites. Evaluating recovery point objectives (RPO), recovery time objectives (RTO), and budget constraints are critical for determining the deployment complexity and scalability of a disaster recovery site versus a failover replica.
Performance and Latency: DR Site vs Failover Replica
Failover replicas offer near-instantaneous failover with minimal latency due to synchronous or asynchronous replication within the same or nearby data centers, ensuring high performance during disaster recovery. Disaster recovery (DR) sites typically involve longer distances, resulting in higher latency and slower recovery times because data synchronization relies on periodic backups or asynchronous replication. Choosing between a failover replica and a DR site depends on the acceptable recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO), with failover replicas optimized for minimal downtime and performance impact.
Cost Implications in Disaster Recovery Strategies
Disaster Recovery Sites typically incur higher costs due to the need for dedicated physical infrastructure, ongoing maintenance, and potentially underutilized resources reserved for emergencies. Failover Replicas offer a more cost-effective solution by leveraging cloud-based or virtualized environments that replicate data and applications, reducing hardware expenses and enabling pay-as-you-go pricing models. Organizations must balance upfront investment with operational expenditure, considering factors like Recovery Time Objective (RTO), Recovery Point Objective (RPO), and scale of failover requirements when selecting the optimal disaster recovery strategy.
Security Factors for DR Sites and Failover Solutions
Disaster Recovery (DR) sites emphasize robust physical and network security measures such as controlled access, data encryption, and continuous monitoring to protect sensitive data during downtime scenarios. Failover replicas incorporate advanced security protocols including real-time data synchronization with encrypted channels and automated threat detection to ensure minimal risk during failover transitions. Both solutions require stringent compliance with industry standards like ISO 27001 and NIST to safeguard data integrity and availability in disaster recovery processes.
Use Cases: When to Choose DR Site or Failover Replica
Disaster Recovery Site is ideal for organizations requiring comprehensive backup and restoration capabilities after catastrophic failures, such as data center outages or large-scale natural disasters, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss. Failover Replica suits environments demanding real-time data replication and immediate service continuity during localized system failures or maintenance, offering near-instantaneous switchovers with minimal service interruption. Choose a Disaster Recovery Site for long-term recovery with full infrastructure redundancy, while a Failover Replica is best for high availability and quick recovery within the same operational region.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Continuity
Disaster Recovery Site offers a geographically separate location with full infrastructure to restore operations after major outages, ensuring maximum data protection and minimal downtime for critical business functions. Failover Replica provides an instant switch to a secondary system that continuously mirrors the primary environment, allowing rapid recovery with minimal data loss and near-zero downtime. Selecting the right solution depends on your organization's tolerance for downtime, data integrity requirements, budget constraints, and the complexity of your IT infrastructure.
Disaster Recovery Site Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com