Mixed media art combines various materials and techniques, such as paint, ink, fabric, and found objects, to create textured and layered compositions that push creative boundaries. This approach allows artists to express complex ideas and emotions in a dynamic and tactile way, making each artwork unique and engaging. Discover how incorporating mixed media can transform your creative process by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
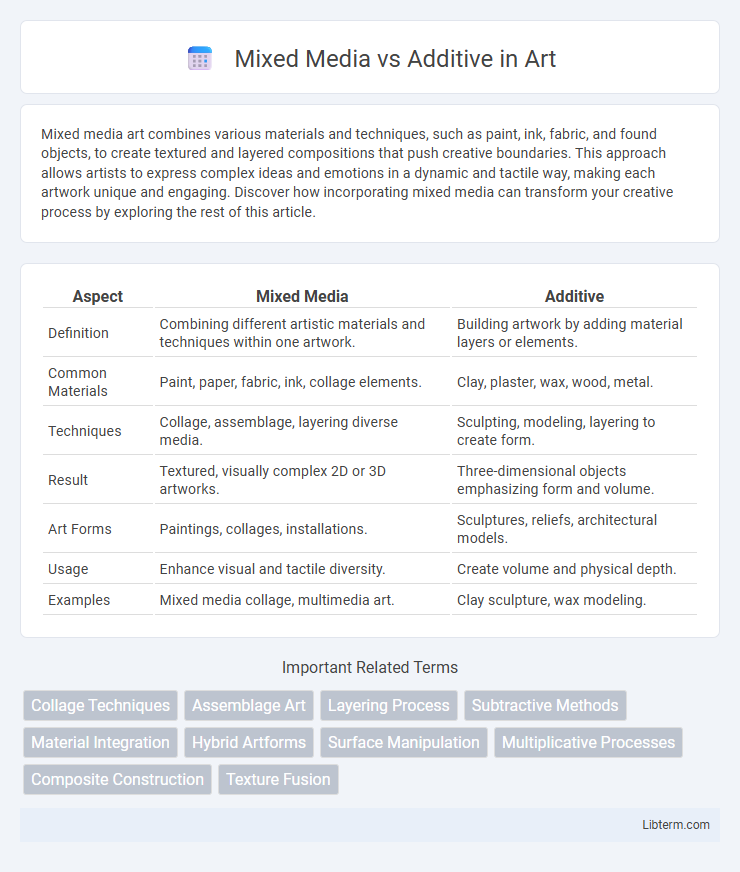
| Aspect | Mixed Media | Additive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining different artistic materials and techniques within one artwork. | Building artwork by adding material layers or elements. |
| Common Materials | Paint, paper, fabric, ink, collage elements. | Clay, plaster, wax, wood, metal. |
| Techniques | Collage, assemblage, layering diverse media. | Sculpting, modeling, layering to create form. |
| Result | Textured, visually complex 2D or 3D artworks. | Three-dimensional objects emphasizing form and volume. |
| Art Forms | Paintings, collages, installations. | Sculptures, reliefs, architectural models. |
| Usage | Enhance visual and tactile diversity. | Create volume and physical depth. |
| Examples | Mixed media collage, multimedia art. | Clay sculpture, wax modeling. |
Introduction to Mixed Media and Additive Techniques
Mixed media art involves combining multiple artistic materials such as paint, ink, paper, and fabric within a single composition, enhancing texture and depth through diverse elements. Additive techniques focus on building up surfaces by layering materials like clay, plaster, or found objects to create sculptural forms and complex textures. Both approaches emphasize layering and textural contrast, but mixed media primarily blends two-dimensional materials, while additive techniques often result in three-dimensional structures.
Defining Mixed Media Art
Mixed media art combines various materials such as paint, ink, fabric, and found objects to create layered and textured compositions that emphasize visual complexity. Unlike additive art, which centers on building three-dimensional forms through the addition of materials like clay or metal, mixed media focuses on integrating diverse two-dimensional and three-dimensional elements within a unified artwork. This approach allows artists to explore a broader range of textures, colors, and conceptual depth by blending different artistic mediums in a single piece.
What is Additive Art?
Additive art is a creative process that involves building up or assembling materials to create a three-dimensional work, often by layering or attaching components such as clay, wire, or found objects. Unlike mixed media, which combines different artistic mediums within a single piece, additive art emphasizes the construction and augmentation of form through positive material addition. This technique allows artists to explore texture, volume, and spatial relationships in their sculptures or installations.
Historical Evolution of Both Methods
Mixed media art, originating in early 20th-century avant-garde movements such as Cubism and Dadaism, blends various materials including paint, fabric, and paper to create textured, multidimensional works. Additive art techniques, deeply rooted in ancient sculptural practices, involve building up materials like clay, plaster, or metal to form three-dimensional shapes, evolving through periods from classical sculpture to contemporary installations. Both methods reflect a historical evolution driven by artistic experimentation and technological advancements, expanding the boundaries of traditional art forms.
Key Materials Used in Mixed Media vs Additive
Mixed media art incorporates diverse materials such as paper, fabric, paint, ink, wood, and found objects combined on a single surface to create layered, textured effects. Additive art primarily uses materials like clay, plaster, metal, and resin, building forms by adding and shaping material cartloads to create three-dimensional sculptures. Mixed media's key characteristic lies in its varied material juxtaposition, while additive art focuses on volumetric expansion through the accumulation of malleable substances.
Creative Process: Layering vs Building
Mixed media emphasizes layering diverse materials such as paint, fabric, and paper to create textured surfaces and depth, fostering spontaneity and experimentation in the creative process. Additive techniques focus on building forms by accumulating materials like clay, plaster, or digital elements, shaping the artwork through structured construction. Layering in mixed media encourages visual complexity and interplay of textures, whereas additive methods prioritize dimensionality and sculptural presence.
Visual Impact and Texture Comparison
Mixed media art combines various materials such as paint, paper, fabric, and found objects, creating rich layers and diverse textures that enhance visual complexity and tactile interest. Additive techniques, primarily involving the application of materials like clay, plaster, or paint in layers to build volume, emphasize three-dimensional form and sculptural depth. The interplay of mixed media's eclectic textures often results in a more dynamic and visually stimulating composition, while additive methods concentrate on structural volume and surface relief to achieve textural impact.
Popular Artists and Notable Works
Mixed media art integrates diverse materials and techniques, exemplified by Pablo Picasso's "Still Life with Chair Caning," combining oil paint and collage elements. Additive art, often seen in sculpture, builds forms by adding materials, highlighted by Auguste Rodin's "The Thinker," crafted through successive layers of clay and bronze. Both approaches showcase innovation, with mixed media thriving in contemporary visual arts and additive methods dominating classical and modern sculpture.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Technique
Mixed media art combines various materials and techniques, often leading to challenges such as material incompatibility, unpredictable drying times, and difficulties in preserving the artwork due to the diverse textures and chemical properties. Additive techniques, which build up layers or elements incrementally, face limitations including structural instability if layers are too thick, longer creation times, and complexity in achieving fine detail without compromising the piece's overall integrity. Both methods require careful planning to balance artistic vision with physical constraints to prevent damage and ensure longevity.
Choosing the Right Approach: Mixed Media or Additive
Choosing between mixed media and additive techniques depends on the desired artistic effect and project requirements. Mixed media combines various materials and methods to create textured, layered compositions, ideal for expressive and experimental works. Additive approaches, involving building up layers or elements sequentially, offer precise control for detailed and structured creations, making them suitable for intricate or architectural designs.
Mixed Media Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com