Traditional art embodies the cultural heritage and timeless techniques passed down through generations, reflecting the unique stories and values of diverse communities. It often includes mediums such as painting, sculpture, textiles, and pottery, each carrying symbolic meanings and craftsmanship rooted in history. Discover how traditional art continues to influence modern creativity and why it remains vital to preserving cultural identity in the full article.
Table of Comparison
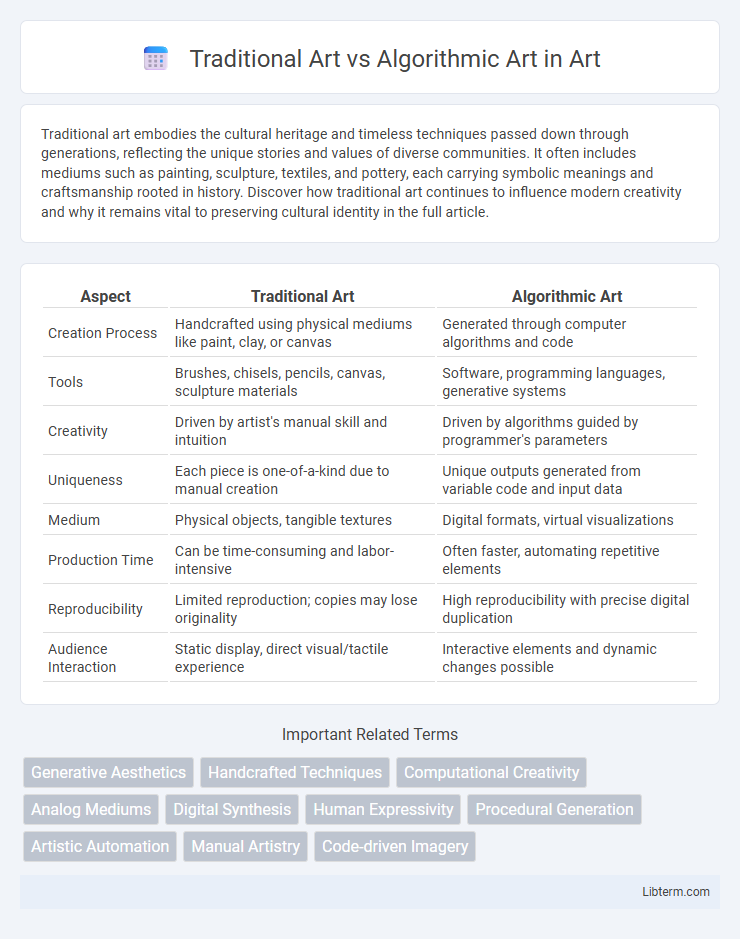
| Aspect | Traditional Art | Algorithmic Art |
|---|---|---|
| Creation Process | Handcrafted using physical mediums like paint, clay, or canvas | Generated through computer algorithms and code |
| Tools | Brushes, chisels, pencils, canvas, sculpture materials | Software, programming languages, generative systems |
| Creativity | Driven by artist's manual skill and intuition | Driven by algorithms guided by programmer's parameters |
| Uniqueness | Each piece is one-of-a-kind due to manual creation | Unique outputs generated from variable code and input data |
| Medium | Physical objects, tangible textures | Digital formats, virtual visualizations |
| Production Time | Can be time-consuming and labor-intensive | Often faster, automating repetitive elements |
| Reproducibility | Limited reproduction; copies may lose originality | High reproducibility with precise digital duplication |
| Audience Interaction | Static display, direct visual/tactile experience | Interactive elements and dynamic changes possible |
Defining Traditional Art and Algorithmic Art
Traditional art encompasses creative expressions through established mediums such as painting, sculpture, and drawing, characterized by manual techniques and tactile materials like canvas, clay, and paper. Algorithmic art, alternatively, is generated through computational processes where algorithms and code direct the creation of visual compositions, often utilizing programming languages such as Python or Processing. Both forms represent distinct paradigms of artistic production, highlighting manual skill in traditional methods and digital innovation in algorithmic approaches.
Historical Evolution of Art Forms
Traditional art, rooted in prehistoric cave paintings and evolving through Renaissance masterpieces, relies on manual techniques like painting, sculpture, and drawing to express cultural narratives and human experience. Algorithmic art emerges in the late 20th century with the advent of computer programming, using mathematical algorithms and code to generate visuals, marking a shift towards procedural creativity and digital aesthetics. The historical evolution from labor-intensive craftsmanship to algorithm-driven artistry reflects changes in technology, creative processes, and the expanding definition of art in contemporary culture.
Tools and Techniques: Brushes vs. Code
Traditional art relies on physical tools like brushes, canvases, and pigments to create texture and depth through tactile manipulation. Algorithmic art employs code, using programming languages and software algorithms to generate complex, dynamic visuals based on mathematical models. The contrast between the manual precision of brushstrokes and the automated logic of code highlights distinct creative processes and outcomes in each art form.
Human Creativity vs. Machine Logic
Traditional art embodies human creativity through emotional expression, intuition, and cultural storytelling, reflecting the artist's unique perspective and experiential depth. Algorithmic art leverages machine logic, employing mathematical formulas, code, and computational processes to generate patterns and visuals that challenge conventional aesthetics. The interplay between human creativity and machine logic creates a dynamic evolution in art, where organic intuition intersects with systematic precision.
Authenticity and Artistic Value
Traditional art emphasizes authenticity through the artist's direct handcraft, unique brushstrokes, and tactile materials, creating one-of-a-kind physical pieces that convey human emotion and cultural heritage. Algorithmic art relies on code and computational processes to generate visuals, raising debates about originality as the output can be reproduced endlessly and lacks the personal touch of human creators. Artistic value in traditional art is often tied to historical context and artist intention, whereas algorithmic art challenges conventional notions by blending creativity with technology, offering novel aesthetic experiences that redefine authenticity.
Audience Perception and Reception
Traditional art often evokes a tactile and emotional response due to its tangible materials and historical context, fostering a sense of authenticity and cultural heritage among audiences. Algorithmic art engages viewers by showcasing complex patterns generated through computational processes, appealing to those interested in innovation and the intersection of technology and creativity. Audience reception varies with familiarity; traditional art tends to resonate more with conventional art appreciators, while algorithmic art attracts a niche following intrigued by digital aesthetics and conceptual experimentation.
Accessibility and Democratization of Art
Traditional art, rooted in physical mediums like painting and sculpture, often requires access to costly materials and specialized training, limiting its accessibility. Algorithmic art leverages digital tools and coding, enabling a broader range of individuals to create and distribute artwork through widely available technology and online platforms. This shift fosters democratization by reducing barriers, allowing diverse voices to participate in the art world and expanding creative expression beyond conventional boundaries.
Impact on Art Markets and Collectors
Traditional art maintains a strong presence in art markets due to its historical value, unique craftsmanship, and provenance, appealing to collectors who prioritize originality and tangible assets. Algorithmic art introduces new dynamics with its digital origin, scarcity often enforced through blockchain technology, and programmability, attracting a growing segment of tech-savvy collectors seeking innovation and novel investment opportunities. Market valuations increasingly reflect these differences, with traditional art often commanding stable, long-term appreciation while algorithmic art offers rapid growth potential but higher volatility among collectors.
Ethical Considerations in Algorithmic Art
Algorithmic art raises ethical considerations surrounding authorship, originality, and the potential for bias encoded within the algorithms. Concerns about transparency and accountability emerge as creators may rely on opaque AI models, complicating the attribution of creative ownership. Ethical frameworks must address data privacy, consent in training datasets, and the risk of perpetuating stereotypes or cultural misappropriation through automated art generation.
The Future of Artistic Expression
Traditional art, rooted in centuries of human creativity, emphasizes tactile techniques and personal expression, while algorithmic art harnesses computational power and AI to generate dynamic, data-driven visuals. The future of artistic expression lies in the convergence of these methods, where artists use algorithms to expand creative possibilities and push the boundaries of visual storytelling. Emerging technologies like machine learning and generative adversarial networks (GANs) enable the creation of unique, customizable artworks that evolve in real-time, transforming the art world with innovative interactive experiences.
Traditional Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com