Painting enhances your living space by adding color, texture, and personality to any room, creating a visually appealing environment. Choosing the right paint type and technique ensures durability and a flawless finish that withstands daily wear and tear. Explore the full article to discover expert tips and techniques for transforming your walls effectively.
Table of Comparison
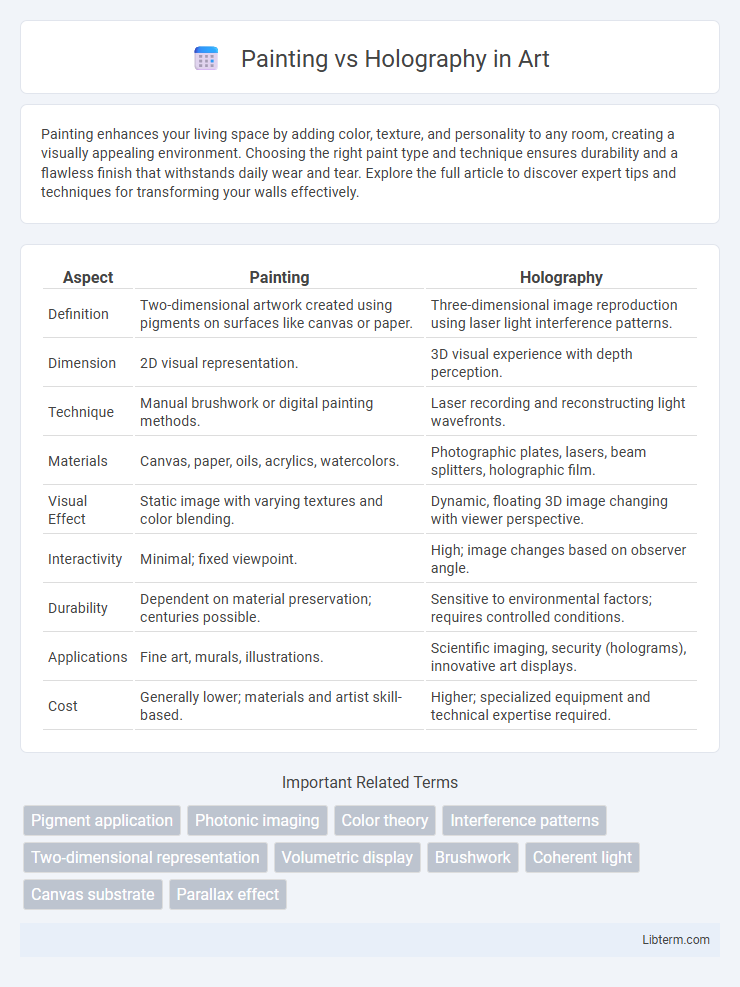
| Aspect | Painting | Holography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two-dimensional artwork created using pigments on surfaces like canvas or paper. | Three-dimensional image reproduction using laser light interference patterns. |
| Dimension | 2D visual representation. | 3D visual experience with depth perception. |
| Technique | Manual brushwork or digital painting methods. | Laser recording and reconstructing light wavefronts. |
| Materials | Canvas, paper, oils, acrylics, watercolors. | Photographic plates, lasers, beam splitters, holographic film. |
| Visual Effect | Static image with varying textures and color blending. | Dynamic, floating 3D image changing with viewer perspective. |
| Interactivity | Minimal; fixed viewpoint. | High; image changes based on observer angle. |
| Durability | Dependent on material preservation; centuries possible. | Sensitive to environmental factors; requires controlled conditions. |
| Applications | Fine art, murals, illustrations. | Scientific imaging, security (holograms), innovative art displays. |
| Cost | Generally lower; materials and artist skill-based. | Higher; specialized equipment and technical expertise required. |
Introduction to Visual Art Forms
Painting, a traditional visual art form, uses pigments applied to surfaces like canvas to create two-dimensional images that convey emotion, perspective, and narrative through color and texture. Holography, an advanced visual art technique, employs laser technology to produce three-dimensional images with depth and realism, allowing viewers to experience art from multiple angles. Both forms explore visual perception but differ fundamentally in medium, technology, and dimensionality, enriching the diversity of artistic expression.
Defining Painting: Tradition and Techniques
Painting, a traditional art form dating back thousands of years, involves applying pigment to a surface such as canvas, wood, or paper using brushes, knives, or other tools. Techniques vary widely, including oil painting, watercolor, acrylic, and fresco, each offering unique textures, drying times, and effects. These methods emphasize manual skill, color theory, and composition to create two-dimensional representations that evoke emotion and narrative.
Holography Explained: Science Meets Art
Holography combines laser technology and optical physics to record and reconstruct three-dimensional images, offering a dynamic depth perception beyond traditional painting methods. By capturing light wave interference patterns, holography creates images that change perspective with viewer movement, bridging scientific innovation and artistic expression. This fusion of art and science expands visual creativity, enabling immersive and interactive experiences unattainable with conventional flat paintings.
Historical Evolution: Paintings vs. Holograms
Paintings have evolved over millennia from ancient cave art to Renaissance masterpieces, reflecting cultural and technological advancements through traditional pigments and techniques. Holography emerged in the mid-20th century with the invention of laser technology, enabling three-dimensional image recording and playback that revolutionized visual representation. The historical evolution of paintings emphasizes tactile artistry and materiality, whereas holography highlights scientific innovation and optical complexity.
Materials and Technology Comparison
Painting relies on traditional materials like canvas, oil, acrylics, and brushes, emphasizing manual techniques and pigment application for visual effects. Holography uses laser technology, photosensitive materials, and optical components to record and reconstruct light fields, enabling three-dimensional image projection. While painting captures static two-dimensional images through physical media, holography produces dynamic, depth-filled visuals using advanced photonics and digital processing.
Visual Impact and Viewer Experience
Painting offers a tactile, textured visual impact through brushstrokes and color blending, engaging viewers with a unique, static interpretation of light and shadow. Holography creates a dynamic, three-dimensional visual experience by projecting light waves, allowing viewers to perceive depth and change perspectives as they move. The immersive nature of holography can evoke a sense of realism and interactivity that traditional painting cannot replicate.
Artistic Expression and Creativity
Painting offers artists a tactile medium to explore color, texture, and form, allowing for deeply personal and subjective interpretations through brushstrokes and layering techniques. Holography expands artistic expression by incorporating light, space, and dimensionality, enabling dynamic and immersive experiences that challenge traditional flat representations. Both mediums push creative boundaries, with painting emphasizing manual skill and emotional depth, while holography leverages technology to create innovative visual narratives.
Applications in Modern Society
Painting remains a vital medium in contemporary art, used for aesthetic expression, cultural preservation, and interior decoration. Holography finds applications in data storage, security features on credit cards and IDs, and advanced medical imaging techniques. The integration of holography in augmented reality enhances interactive experiences, while painting continues to influence visual storytelling and cultural identity.
Preservation and Longevity Challenges
Painting preservation faces challenges such as vulnerability to environmental factors like humidity, light exposure, and temperature fluctuations, which can cause fading, cracking, or discoloration over time. Holography preservation requires maintaining precise conditions to prevent degradation from laser light exposure, dust contamination, and changes in ambient humidity, which can distort the holographic image. Both mediums demand controlled atmospheric environments and specialized conservation techniques to ensure longevity, but holography often requires more technologically advanced storage solutions to maintain its optical clarity.
Future Trends: Integrating Painting and Holography
Future trends in integrating painting and holography emphasize the fusion of traditional artistic techniques with advanced 3D visualization technologies to create immersive, interactive art experiences. Holographic projections combined with painted surfaces enable dynamic light manipulation and depth perception, pushing the boundaries of visual storytelling and enhancing audience engagement. Emerging applications in virtual galleries and augmented reality showcase the potential for artists to blend tactile brushwork with holographic elements, revolutionizing the presentation and preservation of art.
Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com