Etching is a precise printmaking technique that uses acid to carve designs into a metal plate, creating detailed and intricate images. This process allows artists to produce multiple reproductions with rich textures and fine lines. Explore the rest of the article to discover how etching can enhance your artistic projects.
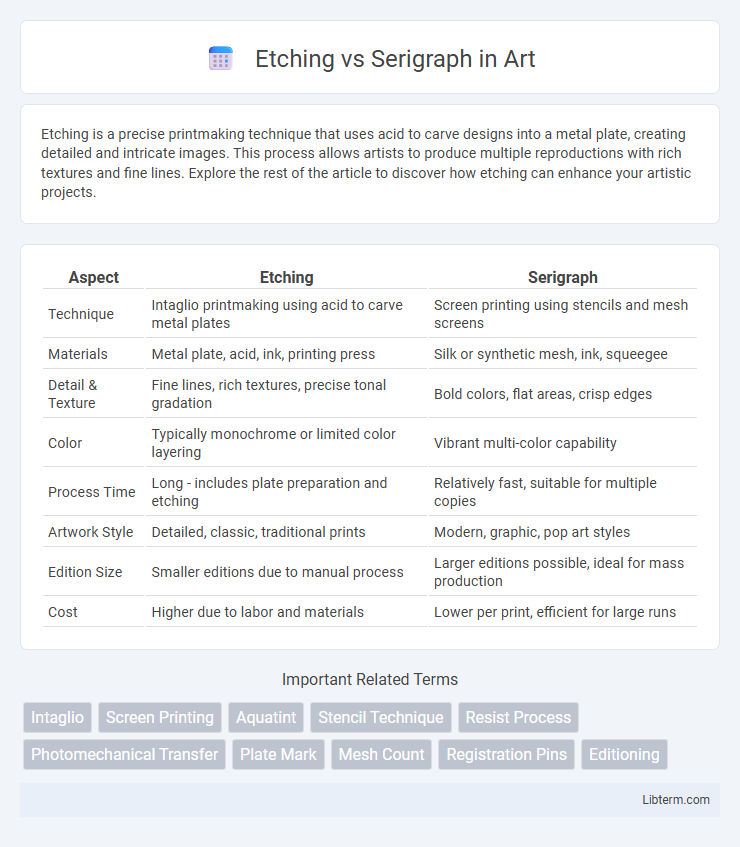
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Etching | Serigraph |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Intaglio printmaking using acid to carve metal plates | Screen printing using stencils and mesh screens |
| Materials | Metal plate, acid, ink, printing press | Silk or synthetic mesh, ink, squeegee |
| Detail & Texture | Fine lines, rich textures, precise tonal gradation | Bold colors, flat areas, crisp edges |
| Color | Typically monochrome or limited color layering | Vibrant multi-color capability |
| Process Time | Long - includes plate preparation and etching | Relatively fast, suitable for multiple copies |
| Artwork Style | Detailed, classic, traditional prints | Modern, graphic, pop art styles |
| Edition Size | Smaller editions due to manual process | Larger editions possible, ideal for mass production |
| Cost | Higher due to labor and materials | Lower per print, efficient for large runs |
Introduction to Etching and Serigraph
Etching is a printmaking technique that involves using acid to carve designs into a metal plate, allowing for detailed and precise imagery. Serigraph, also known as screen printing, uses a stencil and mesh screen to apply ink onto a surface, producing vibrant and bold colors. Both methods have unique artistic qualities and are widely used in fine art and commercial printing.
Historical Background of Etching and Serigraph
Etching, dating back to the 16th century, evolved as a prominent intaglio printmaking technique where artists use acid to carve designs onto metal plates, famously utilized by masters like Rembrandt. Serigraphy, or screen printing, gained prominence in the early 20th century, particularly within the pop art movement, due to its ability to produce vibrant, reproducible images through stenciled ink on fabric or paper. Both methods represent significant historical shifts in artistic reproduction, with etching rooted in traditional craftsmanship and serigraphy embodying modern industrial art.
Core Techniques: How Etching Works
Etching is a printmaking technique that involves using acid to carve designs into a metal plate, usually copper or zinc. The plate is first coated with a waxy ground, and the artist scratches the design into the ground, exposing the metal surface beneath. When submerged in acid, the exposed lines are etched into the plate, creating grooves that hold ink for printing, resulting in rich, detailed images.
Core Techniques: The Serigraph Process
The serigraph process, also known as screen printing, involves creating a stencil on a fine mesh screen and using a squeegee to push ink through the open areas onto the printing surface. This technique allows for vibrant, solid color application and is ideal for producing multiple copies with consistent quality. Unlike etching, which relies on incising surfaces, serigraphy emphasizes layering inks and precise stencil preparation to achieve sharp, graphic images.
Materials and Tools Used in Etching vs Serigraph
Etching primarily uses metal plates, typically copper or zinc, and requires tools such as acid-resistant ground, needles for incising, and acid baths to etch designs into the plate. Serigraph, or screen printing, utilizes a fine mesh screen, squeegee, stencil materials, and various inks suitable for fabric or paper surfaces. The fundamental difference in materials lies in etching's reliance on chemical processes and metal substrates, whereas serigraphy depends on physical stencils and mesh screens to transfer ink.
Artistic Styles: Etching vs Serigraph in Visual Expression
Etching showcases intricate line work and rich textures created by incising metal plates, lending a classic, detailed aesthetic to visual expression. Serigraph, or screen printing, emphasizes bold, flat areas of color with sharp edges, often producing vibrant and graphic styles ideal for modern and pop art influences. Both techniques offer distinct artistic styles: etching excels in fine detail and tonal variation, while serigraph provides vivid color saturation and crisp design clarity.
Print Quality and Detail: Etching vs Serigraph
Etching produces prints with fine, intricate lines and subtle tonal variations due to the acid-engraved metal plate, resulting in higher detail and depth. Serigraph, or screen printing, yields vibrant, bold colors with crisp edges but less delicate detail compared to etching. The choice between etching and serigraph hinges on whether the artwork prioritizes precision and texture or vivid color saturation and graphic impact.
Cost, Time, and Accessibility Comparison
Etching involves a detailed process of engraving metal plates, which makes it more time-consuming and costly due to specialized tools and materials, whereas serigraph (screen printing) is generally faster and more affordable, utilizing stencils and mesh screens suitable for mass production. Accessibility for etching is limited by the need for a controlled studio environment and toxic chemicals, while serigraph offers broader accessibility with simpler equipment and safer materials for artists and hobbyists. Cost efficiency and time savings make screen printing a preferred choice for larger print runs, whereas etching is often favored for fine art limited editions despite higher expenses and longer production times.
Collectability and Popularity in the Art Market
Etching remains highly collectible due to its historical significance and the unique tactile quality of intaglio prints, attracting collectors seeking traditional craftsmanship and limited editions. Serigraphs, or screen prints, gain popularity for their vibrant colors and modern appeal, often linked to pop art and mass accessibility, enhancing their appeal in contemporary art markets. Both techniques hold distinct value, with etching favored by connoisseurs and serigraphs appealing to broader audiences and commercial collectors.
Choosing Between Etching and Serigraph for Artists
Choosing between etching and serigraph depends on an artist's desired texture and detail; etching offers rich, fine lines with a classic, intricate appearance, while serigraph excels in bold, vibrant color fields and graphic clarity. Etching involves incising designs on metal plates using acid, ideal for precision and tonal variation, whereas serigraph employs screen printing techniques for layering vivid inks on various surfaces. Artists prioritizing fine detail and timeless craftsmanship may prefer etching, whereas those aiming for striking color and reproducibility often select serigraph.
Etching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com