Contour lines represent elevation on maps by connecting points of equal height, allowing you to visualize terrain shape and slope easily. These lines help in understanding landforms, guiding hikers, engineers, and geographers in navigation and planning. Explore this article to learn how contour lines can enhance your map reading skills and outdoor adventures.
Table of Comparison
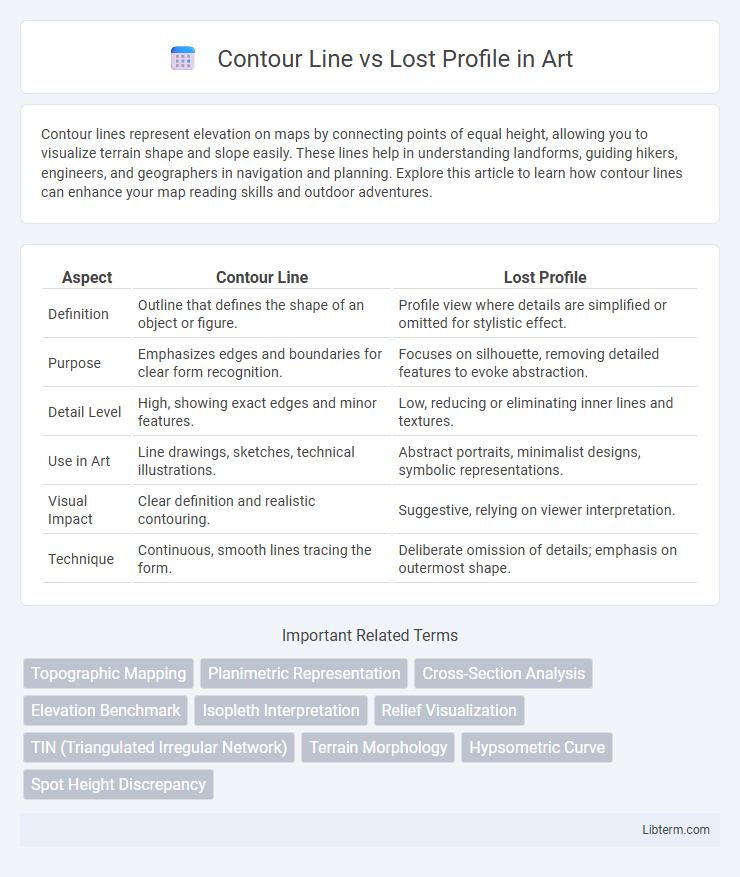
| Aspect | Contour Line | Lost Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outline that defines the shape of an object or figure. | Profile view where details are simplified or omitted for stylistic effect. |
| Purpose | Emphasizes edges and boundaries for clear form recognition. | Focuses on silhouette, removing detailed features to evoke abstraction. |
| Detail Level | High, showing exact edges and minor features. | Low, reducing or eliminating inner lines and textures. |
| Use in Art | Line drawings, sketches, technical illustrations. | Abstract portraits, minimalist designs, symbolic representations. |
| Visual Impact | Clear definition and realistic contouring. | Suggestive, relying on viewer interpretation. |
| Technique | Continuous, smooth lines tracing the form. | Deliberate omission of details; emphasis on outermost shape. |
Introduction to Contour Line and Lost Profile
Contour lines represent continuous lines on a map connecting points of equal elevation, essential for illustrating the shape and slope of the terrain. Lost profiles occur when a contour line is interrupted due to gaps or missing data, causing inaccuracies in terrain representation. Understanding the distinction aids in accurate topographic mapping and effective geographic analysis.
Definition of Contour Line
A contour line represents a continuous line on a map connecting points of equal elevation, used primarily in topographic maps to depict terrain shape and elevation changes. Unlike a lost profile, which refers to a missing or incomplete elevation survey along a specific path, contour lines provide a complete and systematic visual representation of landform elevations. Contour lines help in accurately understanding the gradient, slope, and relief of the terrain for applications in geography, engineering, and environmental planning.
Understanding Lost Profile
Lost profile refers to the absence or distortion of the visible contour line on a surface, making it difficult to perceive the true shape or form of an object. This phenomenon commonly occurs in design, art, and topography when natural or artificial factors obscure edges, creating challenges in visual interpretation and spatial understanding. Recognizing lost profiles is essential for accurate rendering, modeling, and analysis of three-dimensional structures, helping to restore or infer hidden boundaries for better comprehension.
Key Differences Between Contour Line and Lost Profile
Contour lines represent continuous lines on maps connecting points of equal elevation, providing a clear visualization of terrain shape and slope. Lost profiles, often used in engineering, refer to incomplete or missing elevation data along a planned route, complicating accurate terrain analysis. The key difference lies in contour lines offering complete, measurable terrain details, while lost profiles indicate data gaps requiring interpolation or survey to restore.
Applications in Art and Design
Contour lines define the edges and shapes of objects, providing a clear and precise representation essential in classical drawing and graphic design for emphasizing form and structure. Lost profile techniques, which deliberately obscure or omit certain facial features, are widely used in surrealist art and modern portraiture to evoke emotion and create mystery. Both methods complement visual storytelling, with contour lines enhancing clarity and lost profiles adding depth to conceptual and abstract compositions.
Visual Impact: Clarity vs Ambiguity
Contour lines provide clear and precise representation of terrain shapes, enhancing visual clarity by defining edges and elevations with accuracy. Lost profiles introduce ambiguity by omitting detailed outlines, which can create a more abstract or interpretive visual impact. This contrast significantly affects map readability, with contour lines offering distinct, reliable guidance while lost profiles invite subjective interpretation.
Techniques to Draw Contour Lines
Techniques to draw contour lines include using consistent intervals to accurately represent elevation changes on topographic maps, employing tools such as French curves or flexible rulers to maintain smooth, flowing lines, and applying the hill shading method to enhance three-dimensional visualization. Drafting begins by identifying and connecting points of equal elevation, often sourced from survey data or digital elevation models (DEMs), ensuring precise and continuous contour formation. Mastery of these methods allows for detailed terrain analysis, essential in fields like geography, civil engineering, and environmental planning.
Achieving a Lost Profile in Illustration
Achieving a lost profile in illustration involves strategically omitting contour lines to create a sense of depth and subtlety, relying on color, value, and texture instead to define shapes. Unlike strict contour line drawings that emphasize edges and boundaries, lost profiles suggest form through the interplay of light and shadow, enhancing realism and visual interest. This technique demands careful control over tonal transitions to maintain clarity while fostering a more immersive and dynamic composition.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Technique
Contour line techniques offer precise elevation mapping and clear visualization of terrain shapes, making them ideal for topographic analysis and engineering projects, though they require detailed surveying and can be time-consuming. Lost profile methods facilitate faster data collection in complex or inaccessible landscapes, providing practical insight when contour lines are difficult to establish; however, they may lack accuracy and detailed terrain representation. Both approaches serve distinct purposes, with contour lines emphasizing accuracy and lost profiles prioritizing expediency and feasibility in challenging environments.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Artwork
Selecting the appropriate technique between contour line and lost profile depends on the desired artistic expression and detail level. Contour line emphasizes precise outlines and shapes, ideal for clear, defined drawings, while lost profile relies on partial visibility and negative space to create mystery and abstraction. Evaluating your artwork's narrative and style helps determine whether clarity or subtlety best conveys your vision.
Contour Line Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com