Intaglio is a printmaking technique where the design is engraved into a surface, usually a metal plate, creating recessed areas that hold ink. This method produces detailed and high-quality prints, highly valued in art and currency production. Discover how intaglio can enhance your understanding of classic and contemporary printmaking in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
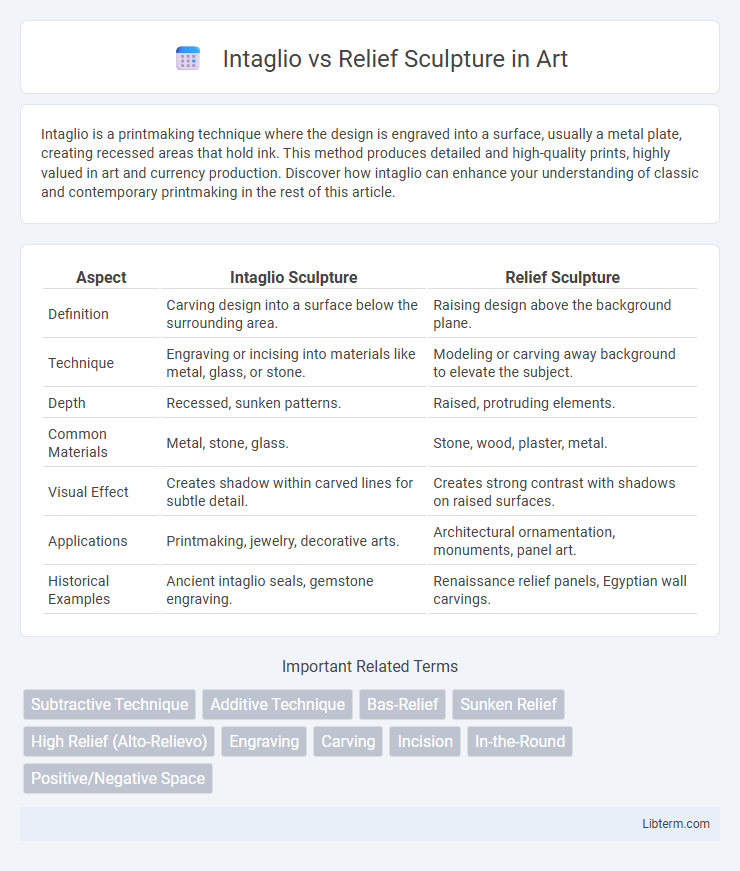
| Aspect | Intaglio Sculpture | Relief Sculpture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Carving design into a surface below the surrounding area. | Raising design above the background plane. |
| Technique | Engraving or incising into materials like metal, glass, or stone. | Modeling or carving away background to elevate the subject. |
| Depth | Recessed, sunken patterns. | Raised, protruding elements. |
| Common Materials | Metal, stone, glass. | Stone, wood, plaster, metal. |
| Visual Effect | Creates shadow within carved lines for subtle detail. | Creates strong contrast with shadows on raised surfaces. |
| Applications | Printmaking, jewelry, decorative arts. | Architectural ornamentation, monuments, panel art. |
| Historical Examples | Ancient intaglio seals, gemstone engraving. | Renaissance relief panels, Egyptian wall carvings. |
Introduction to Intaglio and Relief Sculpture
Intaglio sculpture involves carving or incising into a surface, creating recessed designs often used in printmaking and metalwork. Relief sculpture features raised elements that project from a flat background, allowing the design to stand out prominently in materials like stone, wood, or metal. Both techniques manipulate surface depth to create visual effects but differ fundamentally in the direction of their carving.
Historical Origins of Intaglio and Relief Sculpture
Intaglio sculpture originated in ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, where artisans engraved designs into stone and metal as a form of decorative art and record-keeping. Relief sculpture dates back to prehistoric times, with early examples found in cave paintings and carvings across Europe and the Near East, serving as narrative and religious expressions. Both techniques evolved to reflect cultural and technological advancements, with intaglio emphasizing incised imagery and relief highlighting raised forms.
Defining Intaglio Sculpture
Intaglio sculpture is characterized by designs carved into a surface, creating recessed areas that emphasize depth and shadow. Unlike relief sculpture, where elements project outward from the background, intaglio involves engraving or etching below the original surface level. This technique is commonly used in printmaking and jewelry, allowing for intricate detail and precise lines.
Exploring Relief Sculpture Techniques
Relief sculpture involves carving or molding figures that project from a flat background, with varying depths from low (bas-relief) to high relief, creating dynamic visual effects. Techniques such as subtractive carving, additive modeling, and casting are commonly used to achieve intricate textures and dimensionality in materials like stone, wood, and metal. Mastery of these methods enables artists to manipulate light and shadow effectively, enhancing the sculptural narrative and spatial interaction.
Key Differences Between Intaglio and Relief Sculpture
Intaglio sculpture involves carving into a surface, creating recessed designs that emphasize depth and shadow within the material, commonly used in printmaking and engraving. Relief sculpture raises the design above the background plane, producing a three-dimensional effect visible from the front, with variations such as bas-relief and high relief determining the degree of projection. The key difference lies in the technique: intaglio cuts into the surface, while relief builds outward from it, affecting both the artistic process and visual impact.
Artistic Applications of Intaglio Sculptures
Intaglio sculptures involve carving or engraving designs into a surface, creating recessed areas that hold ink or pigment for printing or visual depth. Commonly used in printmaking techniques such as etching, engraving, and drypoint, intaglio art allows for fine details and intricate textures, making it ideal for creating delicate and precise imagery. The recessed lines and grooves in intaglio sculptures enhance shadows and highlights, contributing to dynamic visual effects in both two-dimensional prints and tactile art pieces.
Notable Examples of Relief Sculpture
Relief sculpture is characterized by figures that project from a flat background, creating a dynamic interplay of light and shadow, with notable examples including the Parthenon frieze in Athens and the intricate bas-reliefs of the Angkor Wat temple complex. These masterpieces exemplify the technique's ability to convey narrative and depth while maintaining a strong connection to the architectural surface. The Bayeux Tapestry and the Assyrian palace reliefs also stand out as significant historical artifacts demonstrating the enduring cultural importance of relief sculpture across different civilizations.
Material Choices in Intaglio vs Relief Sculpture
Intaglio sculpture involves carving into materials like metal, stone, or glass to create recessed designs suitable for printing or detailed artwork. Relief sculpture, often crafted from wood, clay, or plaster, features raised surfaces that stand out from the background, emphasizing form and texture. Material selection in intaglio prioritizes durability and precision for fine lines, while relief sculpture materials favor malleability and surface detail.
Preservation and Restoration of Sculptures
Intaglio sculptures, characterized by their incised or engraved surfaces, require meticulous preservation to prevent erosion of fine details, often involving controlled environments and specialized cleaning techniques to avoid abrasion. Relief sculptures, protruding from their backgrounds, face challenges such as surface wear and structural instability, making restoration efforts focus on reinforcing the raised elements and filling cracks with compatible materials. Both forms benefit from advanced conservation methods like 3D scanning for accurate documentation and minimal intervention restoration to maintain historical integrity.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Intaglio and Relief Approaches
Choosing between intaglio and relief sculpture depends on the desired visual effect and technical complexity; intaglio creates recessed designs ideal for fine detail and printing, while relief stands out from the background, emphasizing dimensionality and texture. Artists seeking precision in line work and reproducibility often prefer intaglio, whereas those prioritizing bold, tactile surfaces lean toward relief techniques. Understanding the distinct characteristics of each method enables informed decisions aligned with artistic vision and project requirements.
Intaglio Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com