Abstract Expressionism revolutionized modern art by emphasizing spontaneous, emotional expression through bold colors and dynamic brushstrokes. This movement broke traditional artistic boundaries, focusing on the subconscious and personal experience to create impactful visual narratives. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Abstract Expressionism continues to influence contemporary art and inspire your creative journey.
Table of Comparison
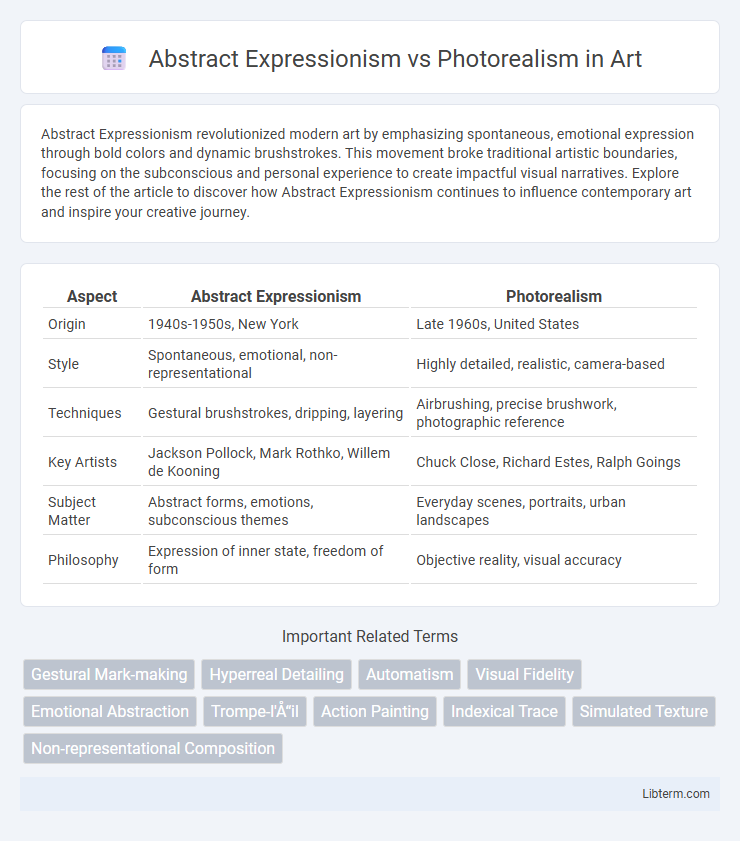
| Aspect | Abstract Expressionism | Photorealism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 1940s-1950s, New York | Late 1960s, United States |
| Style | Spontaneous, emotional, non-representational | Highly detailed, realistic, camera-based |
| Techniques | Gestural brushstrokes, dripping, layering | Airbrushing, precise brushwork, photographic reference |
| Key Artists | Jackson Pollock, Mark Rothko, Willem de Kooning | Chuck Close, Richard Estes, Ralph Goings |
| Subject Matter | Abstract forms, emotions, subconscious themes | Everyday scenes, portraits, urban landscapes |
| Philosophy | Expression of inner state, freedom of form | Objective reality, visual accuracy |
Introduction to Abstract Expressionism and Photorealism
Abstract Expressionism emerged in the 1940s as a movement emphasizing spontaneous, gestural brushstrokes and emotional intensity, pioneered by artists like Jackson Pollock and Mark Rothko. Photorealism developed in the late 1960s, focusing on meticulously detailed and lifelike depictions of photographic scenes, with key figures including Chuck Close and Richard Estes. Both movements radically contrast in technique and intent: Abstract Expressionism seeks to evoke emotion through abstraction, while Photorealism strives for precision and exact visual representation.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Abstract Expressionism emerged in the 1940s in New York City, rooted in post-World War II existential angst and influenced by Surrealism and European modernism. Photorealism developed in the late 1960s as a reaction to Abstract Expressionism, emphasizing meticulous, camera-based realism and often reflecting contemporary American culture. The evolution of Abstract Expressionism involved a shift from gesture-driven spontaneity toward more structured compositions, while Photorealism advanced through technological innovations and critical engagement with mass media imagery.
Key Philosophies and Artistic Intentions
Abstract Expressionism emphasizes spontaneity, emotional intensity, and the subconscious mind, aiming to capture an artist's inner experience and universal human emotions through bold, gestural brushstrokes. Photorealism centers on meticulous attention to detail and precision, striving to replicate photographs with exacting accuracy to explore themes of reality, perception, and the impact of media images. These contrasting approaches highlight Abstract Expressionism's focus on subjective expression versus Photorealism's pursuit of objective representation.
Notable Artists and Influential Works
Abstract Expressionism, epitomized by artists such as Jackson Pollock with his dynamic drip paintings and Mark Rothko's luminous color fields, emphasized spontaneity and emotional intensity. Photorealism featured figures like Chuck Close, known for his meticulous large-scale portraits, and Richard Estes, whose cityscapes captured reflective surfaces with photographic precision. These movements contrast through Abstract Expressionism's emphasis on abstract emotion and Photorealism's commitment to detailed, lifelike representation, each revolutionizing mid-20th-century art.
Techniques and Materials Used
Abstract Expressionism employs gestural brushstrokes, thick impasto, and spontaneous techniques using oil or acrylic paints on large canvases to emphasize emotional intensity and movement. Photorealism relies on meticulous airbrushing, fine brushes, and photographic projection methods to create highly detailed, lifelike representations using oils or acrylics on smooth surfaces. While Abstract Expressionism prioritizes texture and abstraction through dynamic application, Photorealism focuses on precision, clarity, and exact replication of visual details.
Visual Impact and Audience Perception
Abstract Expressionism evokes emotional intensity and subjective interpretation through bold brushstrokes, dynamic forms, and vibrant color palettes, creating a powerful visual impact that engages viewers' imagination and feelings. Photorealism emphasizes meticulous detail and high-fidelity representation, producing lifelike images that challenge perceptions of reality and invite close scrutiny and appreciation of technical skill. Audience perception of Abstract Expressionism centers on emotional resonance and personal meaning, while Photorealism captivates through visual accuracy and the illusion of reality.
Role of Emotion and Realism in Both Styles
Abstract Expressionism emphasizes raw emotion and spontaneous expression through non-representational forms, prioritizing the artist's inner feelings over objective reality. Photorealism focuses on meticulous detail and replicating visual reality with precision, aiming to evoke emotional responses through lifelike, high-definition imagery. The tension between emotional abstraction in Abstract Expressionism and the exacting realism of Photorealism highlights contrasting approaches to conveying human experience in art.
Influence on Contemporary Art Movements
Abstract Expressionism's emphasis on spontaneous, emotional expression and large-scale canvases profoundly influenced contemporary art movements like Neo-Expressionism and Street Art, fostering a focus on individual creativity and gesture. Photorealism, with its precise, detailed replication of photographic images, impacted hyperrealism and digital art by pushing boundaries in technical skill and visual perception. Both movements redefined artistic approaches, shaping contemporary practices through their distinct philosophies on representation and technique.
Critical Reception and Art Market Value
Abstract Expressionism, celebrated for its emotional intensity and spontaneous technique, gained critical acclaim in the mid-20th century, leading to high demand in prestigious galleries and museums, with iconic artists like Jackson Pollock commanding multi-million-dollar auction prices. Photorealism, emerging in the late 1960s, initially faced skepticism for its technical replication of reality but has since achieved recognition for its meticulous detail and cultural commentary, gradually increasing its market value, exemplified by artists such as Chuck Close. While Abstract Expressionist works consistently achieve higher auction records and institutional endorsement, Photorealist pieces have carved a niche in contemporary collections, reflecting a nuanced but growing appreciation among collectors and critics.
Conclusion: Lasting Legacies and Future Directions
Abstract Expressionism revolutionized the art world with its emphasis on emotional intensity and spontaneous brushwork, inspiring future generations to explore personal expression and conceptual depth. Photorealism, by capturing intricate details and optical accuracy, challenged traditional artistic boundaries and influenced contemporary visual culture, including digital and media art forms. Both movements continue to shape artistic innovation, with Abstract Expressionism fueling experimental abstraction and Photorealism advancing hyperrealistic techniques in modern and digital media.
Abstract Expressionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com