Abstraction simplifies complex systems by focusing on the essential features while hiding unnecessary details, making problem-solving more efficient. It allows you to manage complexity in software design, enhancing code readability and maintainability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how abstraction can optimize your development process.
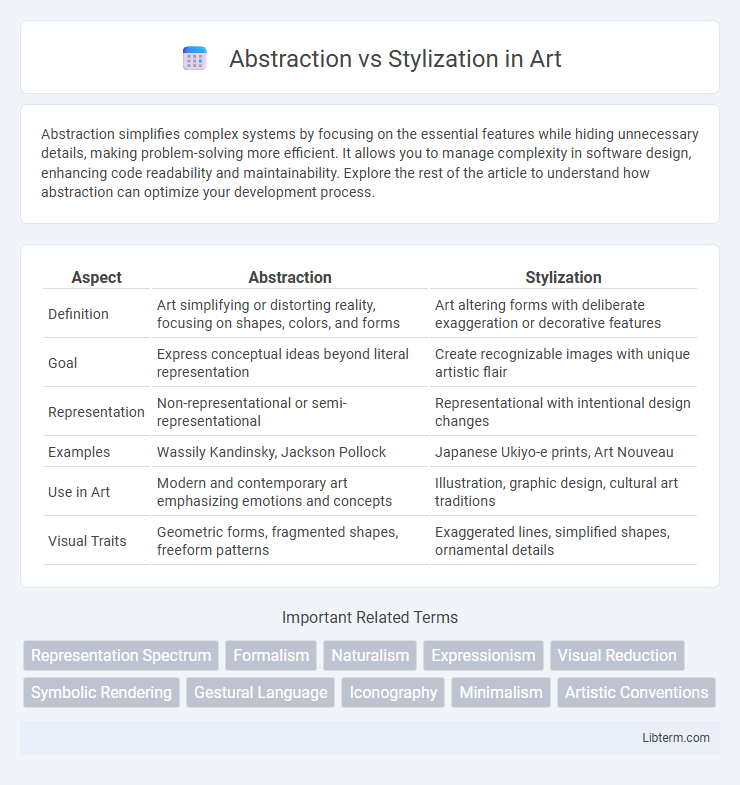
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Abstraction | Stylization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art simplifying or distorting reality, focusing on shapes, colors, and forms | Art altering forms with deliberate exaggeration or decorative features |
| Goal | Express conceptual ideas beyond literal representation | Create recognizable images with unique artistic flair |
| Representation | Non-representational or semi-representational | Representational with intentional design changes |
| Examples | Wassily Kandinsky, Jackson Pollock | Japanese Ukiyo-e prints, Art Nouveau |
| Use in Art | Modern and contemporary art emphasizing emotions and concepts | Illustration, graphic design, cultural art traditions |
| Visual Traits | Geometric forms, fragmented shapes, freeform patterns | Exaggerated lines, simplified shapes, ornamental details |
Understanding Abstraction in Art
Abstraction in art involves distilling complex forms into essential shapes, colors, and lines, enabling artists to express ideas beyond realistic representation. It emphasizes emotional resonance and conceptual depth by simplifying or altering visual elements, encouraging viewers to interpret meaning through personal perception. Understanding abstraction requires recognizing its role in prioritizing symbolic content over literal depiction, which distinguishes it from stylization's focus on decorative patterns or consistent visual motifs.
Defining Stylization in Creative Works
Stylization in creative works refers to the deliberate alteration or simplification of visual elements to emphasize particular features or evoke specific emotions, often deviating from realistic representation. It highlights unique artistic techniques, such as exaggerated shapes, bold colors, and distinctive line work, to convey mood or cultural context effectively. This approach contrasts with abstraction by maintaining recognizable forms while enhancing expressive qualities through consistent design choices.
Key Differences Between Abstraction and Stylization
Abstraction reduces visual elements to their essential forms, focusing on shapes, colors, and lines without representing reality accurately, while stylization emphasizes a recognizable subject but alters details to create a distinct artistic effect. Abstraction often removes context and detail to evoke emotion or concept, whereas stylization maintains identifiable features with deliberate exaggeration or simplification. Key differences include abstraction's aim for conceptual interpretation versus stylization's goal of aesthetic modification within recognizable boundaries.
Historical Evolution of Abstraction and Stylization
Abstraction and stylization have evolved significantly from prehistoric art to contemporary forms, with early examples seen in ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs and Mesopotamian reliefs where symbolic representation replaced realistic depiction. During the modernist movement in the early 20th century, artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Pablo Picasso advanced abstraction by emphasizing emotional expression and geometric forms, while stylization became prominent in Art Nouveau and traditional cultural motifs emphasizing decorative patterns. The historical evolution reflects a shift from naturalistic representation towards expressive simplification, influencing diverse art movements and visual communication methods globally.
Visual Characteristics of Abstract Art
Abstract art emphasizes non-representational forms, using shapes, colors, and textures to convey emotions and ideas rather than depicting real-world objects. Its visual characteristics include geometric patterns, fluid lines, and dynamic compositions that challenge conventional perspectives. Unlike stylization, which simplifies or exaggerates recognizable subjects, abstraction often removes direct references, inviting subjective interpretation.
Techniques and Approaches in Stylization
Stylization techniques emphasize exaggeration, simplification, and selective emphasis to transform realistic elements into more expressive or symbolic forms, using methods such as contour manipulation, color palette alteration, and texture modification. Common approaches include cartooning, where line work and color are bolded for clarity and impact, and minimalism, which reduces detail to focus on essential shapes and forms. These techniques contrast with abstraction by maintaining recognizable imagery while altering features to evoke particular emotions or stylistic themes.
Influential Artists and Iconic Works
Pablo Picasso's Cubist works like "Les Demoiselles d'Avignon" exemplify abstraction by deconstructing forms into geometric shapes, challenging traditional representation. Henri Matisse's use of bold colors and simplified shapes in "The Dance" highlights stylization, emphasizing expressive, decorative elements over realistic detail. Both approaches shaped modern art movements, influencing countless artists in exploring subjective interpretation versus decorative aesthetics.
Role of Abstraction and Stylization in Modern Design
Abstraction in modern design simplifies complex forms to capture essential qualities, enhancing clarity and user engagement by reducing visual noise. Stylization emphasizes distinctive visual elements and artistic expression, creating memorable and unique brand identities. Both abstraction and stylization play crucial roles in balancing functionality with creativity, driving innovation in graphic design, user interfaces, and digital art.
Impact on Viewer Perception and Interpretation
Abstraction reduces visual complexity by emphasizing essential shapes and forms, prompting viewers to engage cognitively and interpret meanings beyond literal representation. Stylization alters realistic features through exaggerated or simplified design, guiding emotional responses and cultural associations tied to specific styles. Both approaches shape viewer perception by influencing how information is processed, with abstraction fostering open-ended interpretation and stylization directing specific narrative or aesthetic reactions.
Choosing Between Abstraction and Stylization: Artistic Intent
Choosing between abstraction and stylization hinges on artistic intent, where abstraction emphasizes conceptual expression by distorting or simplifying forms to evoke emotions or ideas. Stylization, in contrast, maintains recognizable shapes enhanced with decorative or exaggerated elements to convey cultural context or aesthetic appeal. Artists prioritize abstraction for introspective or avant-garde projects, while stylization suits narrative-driven works aiming to communicate identity or tradition.
Abstraction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com