Surrealism explores the unconscious mind through dream-like imagery and unexpected juxtapositions, challenging traditional perceptions of reality. This avant-garde movement, prominent in literature and visual arts, seeks to unlock creativity by bypassing rational thought. Discover how surrealism can inspire your imagination and transform your understanding of art in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
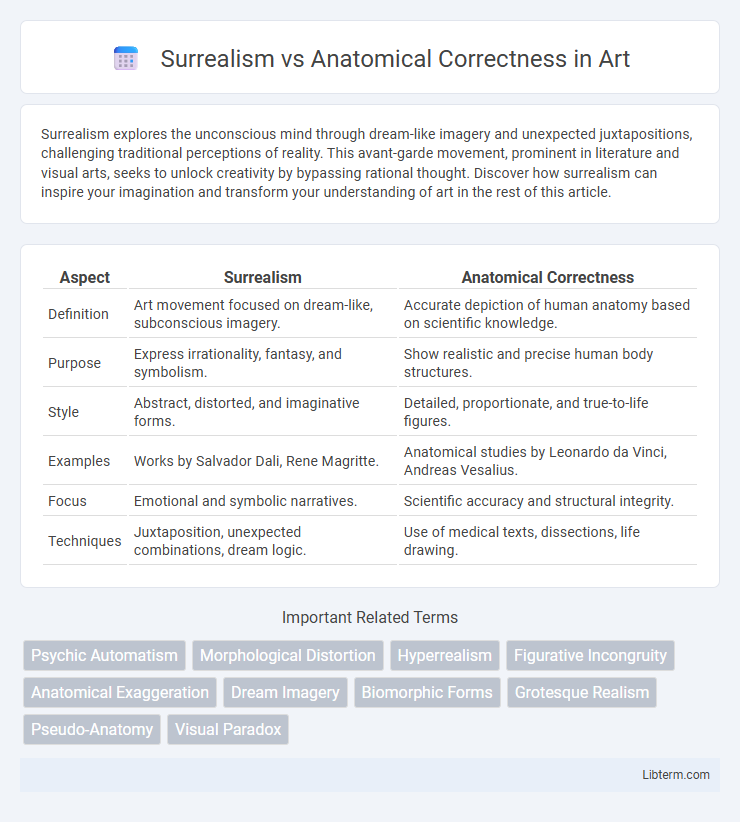
| Aspect | Surrealism | Anatomical Correctness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art movement focused on dream-like, subconscious imagery. | Accurate depiction of human anatomy based on scientific knowledge. |
| Purpose | Express irrationality, fantasy, and symbolism. | Show realistic and precise human body structures. |
| Style | Abstract, distorted, and imaginative forms. | Detailed, proportionate, and true-to-life figures. |
| Examples | Works by Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte. | Anatomical studies by Leonardo da Vinci, Andreas Vesalius. |
| Focus | Emotional and symbolic narratives. | Scientific accuracy and structural integrity. |
| Techniques | Juxtaposition, unexpected combinations, dream logic. | Use of medical texts, dissections, life drawing. |
Introduction to Surrealism and Anatomical Correctness
Surrealism challenges traditional representation by blending dream-like imagery with unexpected juxtapositions, prioritizing subconscious expression over realistic depiction. Anatomical correctness emphasizes precise, scientifically accurate representation of the human body's form and structure, focusing on muscle, bone, and proportion details. These contrasting approaches highlight the tension between imaginative freedom and disciplined accuracy in art.
Historical Roots of Surrealism in Art
Surrealism, emerging in the early 20th century, originated as an avant-garde movement rooted in the exploration of the unconscious mind, dreams, and irrational juxtapositions, contrasting sharply with the precise representation sought in anatomical correctness. Founded by Andre Breton in 1924 with his Surrealist Manifesto, the movement drew inspiration from Dadaism, Freudian psychoanalysis, and symbolism, aiming to transcend the limitations of realistic depiction by embracing imagination and subconscious expression. Historical artists like Salvador Dali and Rene Magritte exemplified surrealism's deliberate departure from anatomical fidelity, favoring distorted, dream-like figures that challenge conventional perceptions of reality and human anatomy.
The Origins and Importance of Anatomical Accuracy
Anatomical accuracy originated from Renaissance artists like Leonardo da Vinci, who emphasized detailed human anatomy to enhance realism and scientific understanding in art. This precision remains essential in various fields such as medical illustration, forensic art, and realistic character design, providing clarity and authenticity. Surrealism, by contrast, intentionally distorts anatomy to evoke subconscious imagery and emotional responses, highlighting the tension between factual representation and creative expression.
Key Differences Between Surrealism and Anatomical Art
Surrealism emphasizes imaginative, dream-like visuals that often distort reality, prioritizing emotional expression over anatomical accuracy. Anatomical correctness focuses on precise, scientifically accurate depictions of the human body, highlighting muscle structure, proportions, and bone placement. Key differences lie in surrealism's abstract, symbolic forms versus anatomical art's detailed, realistic representation rooted in medical study.
Influential Surrealist Artists and Their Techniques
Salvador Dali revolutionized surrealism with his dreamlike imagery and meticulous detail, using techniques like double images and melting forms to challenge anatomical correctness. Rene Magritte employed unexpected juxtapositions and realistic rendering to distort perception while maintaining precise anatomical features. Max Ernst combined frottage and collage methods to create textured, surreal compositions that often abstracted human anatomy beyond conventional correctness.
Celebrated Masters of Anatomical Correctness
Celebrated masters of anatomical correctness, such as Leonardo da Vinci and Andreas Vesalius, achieved unparalleled accuracy through detailed studies of human anatomy. Their work emphasizes precise muscle structures, bone frameworks, and physiological proportions, providing foundational knowledge for realistic art and medical illustrations. Unlike surrealism, which distorts forms for imaginative effect, anatomical correctness remains grounded in scientific observation and exact representation.
The Role of Imagination vs Precision in Artistic Creation
Surrealism harnesses the power of imagination to transcend the boundaries of reality, creating dreamlike, fantastical compositions that challenge conventional perceptions. Anatomical correctness demands precision, emphasizing accurate representation of the human body through detailed study and adherence to biological structures. The interplay between imaginative freedom and rigorous accuracy shapes artistic creation, balancing emotional expression with technical mastery.
Impact on Contemporary Art Practice
Surrealism challenges anatomical correctness by distorting human forms to evoke dreamlike, subconscious experiences, significantly influencing contemporary art's conceptual and visual boundaries. Contemporary artists frequently blend surrealist techniques with anatomical knowledge to create works that explore identity, psychology, and human perception in innovative ways. This fusion allows for expanded expressive potential, pushing artistic practices toward new interpretations of reality and embodiment.
Artistic Movements Influenced by Both Approaches
Surrealism and anatomical correctness have both significantly influenced artistic movements by blending imaginative expression with precise human form studies. Movements such as Abstract Expressionism and Modern Figurative Art incorporate surreal, dream-like elements alongside accurate anatomical details to evoke emotion while maintaining visual realism. This fusion allows artists to explore subconscious themes and psychological depth through both distorted and anatomically accurate representations.
Navigating Personal Style: Finding Balance Between Surrealism and Anatomy
Navigating personal style involves balancing surrealism's imaginative distortions with the precise structure of anatomical correctness to create visually compelling art. Artists blend exaggerated forms and dreamlike elements with accurate muscle and bone details, enhancing both emotional expression and realism. This fusion allows for unique interpretations that maintain viewer engagement through a harmonious interplay of fantasy and biological truth.
Surrealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com