Dye ink offers vibrant color saturation and smooth gradations, making it ideal for photo printing and detailed artwork. Its water-based formula absorbs quickly into paper, producing sharp images but may be less resistant to water and fading over time. Explore the article to understand how dye ink can enhance your prints and which applications suit it best.
Table of Comparison
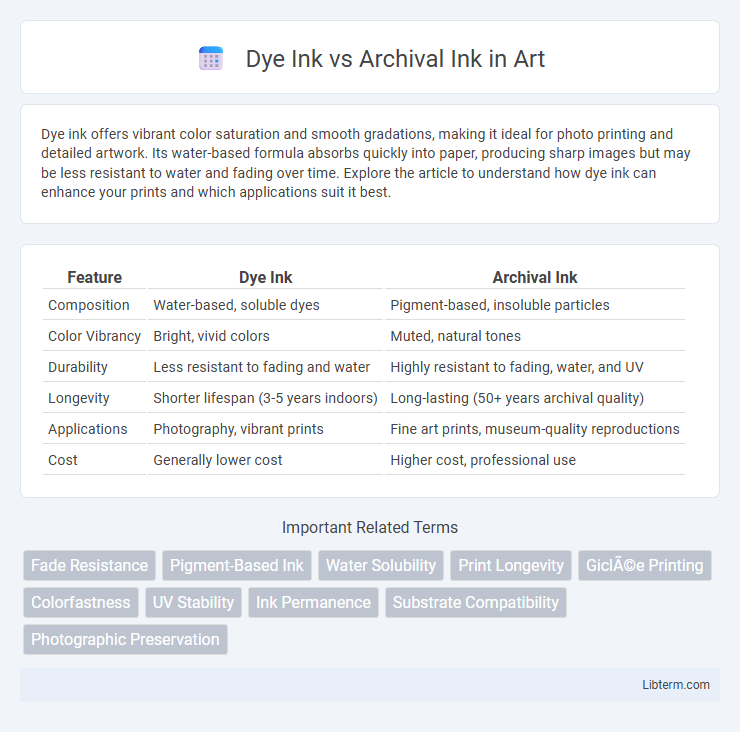
| Feature | Dye Ink | Archival Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Water-based, soluble dyes | Pigment-based, insoluble particles |
| Color Vibrancy | Bright, vivid colors | Muted, natural tones |
| Durability | Less resistant to fading and water | Highly resistant to fading, water, and UV |
| Longevity | Shorter lifespan (3-5 years indoors) | Long-lasting (50+ years archival quality) |
| Applications | Photography, vibrant prints | Fine art prints, museum-quality reproductions |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost, professional use |
Introduction to Dye Ink and Archival Ink
Dye ink consists of colorant dissolved in liquid, offering vibrant colors and quick drying times ideal for everyday printing and photo printing. Archival ink, often pigment-based, contains particles that resist fading, water, and environmental damage, making it suitable for long-lasting documents and professional artwork. Understanding the ink composition helps determine the best choice for either short-term use or preserving prints over decades.
Composition and Formulation Differences
Dye inks are water-based and composed of soluble colorants that penetrate paper fibers, offering vibrant colors but lower resistance to water and fading. Archival inks, often pigment-based, contain microscopic solid particles suspended in a binder, providing superior longevity, UV resistance, and fade-proof qualities. The formulation of archival inks is engineered for durability, maintaining print integrity over decades, whereas dye inks prioritize brightness and ease of use but sacrifice permanence.
Color Vibrancy and Range Comparison
Dye ink offers superior color vibrancy with bright, saturated hues ideal for photo printing and detailed artwork, while archival ink provides a more limited color range with muted tones designed for longevity and fade resistance. Archival inks, typically pigment-based, ensure prints maintain color fidelity over decades by resisting environmental factors such as UV light and humidity. Choosing between dye and archival ink depends on whether color intensity or archival durability is the primary printing requirement.
Fade Resistance and Longevity
Archival ink outperforms dye ink in fade resistance due to its pigment-based composition, which withstands UV exposure and environmental factors more effectively. Dye ink, while vibrant and affordable, tends to fade faster when exposed to light and air, reducing longevity. For archival prints requiring decades-long preservation, pigment-based archival inks are the preferred choice to ensure durability and color stability.
Water Resistance and Smudge Proof Qualities
Dye ink generally offers vibrant colors but lacks strong water resistance, making prints prone to smudging when exposed to moisture. Archival ink, often pigment-based, provides superior water resistance and smudge-proof qualities, ensuring longevity and durability for important documents and artwork. Choosing archival ink enhances print permanence by resisting fading, moisture damage, and smudging over time.
Print Quality and Sharpness
Dye ink produces vibrant colors and smooth gradients, making it ideal for high-quality photo prints with rich detail and sharpness. Archival ink, often pigment-based, offers superior print longevity and resists fading, maintaining sharp edges and text clarity over time. While dye ink excels in color richness, archival ink ensures consistent sharpness and durability for archival-quality prints.
Compatibility with Printers and Paper Types
Dye ink is compatible with a wide range of printers, particularly inkjet models, and performs best on glossy or coated paper types due to its vibrant color output. Archival ink, often pigment-based, is designed for professional printers and works well with various paper types, including matte, fine art, and archival-quality papers, ensuring long-lasting print durability. Printer compatibility varies, as dye inks require less specialized equipment, whereas archival inks may need specific printheads to prevent clogging and maintain print quality over time.
Cost Efficiency and Price Differences
Dye ink typically offers a lower upfront cost and greater affordability for everyday printing needs, making it more cost-efficient for high-volume, short-term projects. Archival ink, while more expensive per cartridge, provides superior longevity and resistance to fading, justifying its higher price for professional or archival-quality prints. Businesses prioritizing long-term durability often find archival ink a worthwhile investment despite the increased initial expense compared to dye ink.
Best Uses and Recommended Applications
Dye ink offers vibrant colors and fast drying times, making it ideal for photo printing, general office use, and everyday documents where brightness and sharpness are priorities. Archival ink, known for its longevity and resistance to fading, is recommended for professional photographs, fine art prints, and important documents that require durability over decades. Choose dye ink for cost-effective, high-quality prints in casual settings, while archival ink suits applications demanding preservation and high archival standards.
Choosing the Right Ink for Your Needs
Dye ink offers vibrant colors and fast drying times ideal for everyday photo printing and short-term displays, while archival ink provides superior fade resistance and longevity suited for professional art prints and documents requiring long-term preservation. Selecting the right ink depends on your need for color intensity versus durability, with archival ink often preferred for valuable or collectible prints. Consider the intended lifespan and exposure conditions of your prints to ensure optimal ink performance and preservation.
Dye Ink Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com